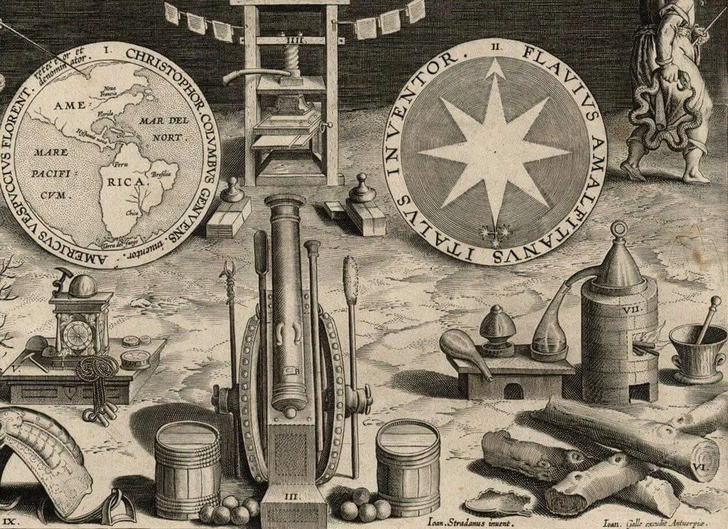
Lorenzo Warby explains why Karl Marx was wrong about the origins of what he called “the three great inventions” and therefore also mistaken about the societal impact of those inventions:
Gunpowder, the compass, and the printing press were the 3 great inventions which ushered in bourgeois society. Gunpowder blew up the knightly class, the compass discovered the world market and founded the colonies, and the printing press was the instrument of Protestantism and the regeneration of science in general; the most powerful lever for creating the intellectual prerequisites.
Karl Marx, “Division of Labour and Mechanical Workshop. Tool and Machinery” in Economic Manuscripts of 1861-63, Part 3) Relative Surplus Value.
With this quote we can see what is wrong both with Marx’s notion of the role of technology in social causation and with a very common notion of the relationship between state and society.
The false — but very common — view of the relationship of state and society is that the state is a product of its society, that the state emanates from its society. This gets the dominant relationship almost entirely the wrong way around. It is far more true to say that the state is a fundamental structuring element of the social dynamics of the territory it rules rather than the reverse.
It is perhaps easiest to see this by noting the glaring flaw in Marx’s reasoning. The gunpowder, the compass and the printing press were all originally Chinese inventions. Indeed, Europe acquired — via intermediaries — gunpowder and the compass from China. (Gutenberg’s printing press appears to have been an independent invention.)
Source: Nova Reperta Frontispiece, 1588.
Yet, as Marx was very well aware, China did not develop a bourgeoisie in his sense. Indeed, Marx’s notion of the Asiatic mode of production grappled with precisely that lack.1
In 1620, Sir Francis Bacon wrote in his Instauratio magna that
… printing, gunpowder, and the nautical compass … have altered the face and state of the world: first, in literary matters; second, in warfare; third, in navigation …
This was true of the effect of these inventions in European, but not Chinese, hands.
Why were these inventions globally transformative in European, but not Chinese hands? Because of the differences in the structure of European state(s) compared to the Chinese state.
Unified China …
The first difference is that the European states were states, plural. Europe had competitive jurisdictions, it had centuries of often intense inter-state conflict. From the Sui (re)unification (581) onwards China was, with brief interruptions, a single polity.2 What the evidence — both Chinese and Roman — shows quite clearly is that civilisational unity in a single polity is bad for institutional, technological and intellectual development.
The second difference is with the internal structure of European states compared to the Chinese state. The Sui dynasty, by introducing the Keju, the imperial examination — refining the use of appointment by exam that went back to the Warring States period — created a structure that directed Chinese human capital to the service of the Emperor.
There were three tiers of examinations (local, provincial, palace). You could sit for them as often as you wished. So a significant proportion of Chinese males devoted decades of their lives to attempting to pass the exams. Over time, the exams became more narrowly Confucian — probably because it required a high level of detailed mastery, so had more of a sorting effect — thereby promoting intellectual conformism.
[…]
… and divided Europe
Conversely, when gunpowder, the compass and the printing press came to Europe, European states already had a military aristocracy; self-governing cities; an armed mercantile elite; organised religious structures; so a rich array of cooperative institutions. Moreover, kin-groups had been suppressed across manorial Europe, forcing — or giving the social space for — alternative mechanisms for social cooperation to evolve.3, 4 In particular, due [to] its self-governing cities with armed militias, medieval Europe had an (effectively) armed mercantile elite before gunpowder, the compass or printing reached Europe.
Alfonso IX of Leon and Galicia (r.1188-1230) first summoned the Cortes of Leon in 1188. This became the start of the first institutionalised use of merchant representatives in deliberative assemblies. Emperor Frederick Barbarossa (r.1155-1190) had tried something similar earlier, but the mercantile elites of North Italy preferred de facto independence, defeating him at the Battle of Legnano in 1176.
The first European reference to the compass is in a text written some time between 1187 and 1202, with its use appearing to expand over the 1200s. The first reference to gunpowder in Europe is not until 1267 and it took centuries before gunpowder played a major role in European warfare.
Both the compass and gunpowder really only have transformative effects from the late C15th onwards, which is also when the printing press is spreading across Latin Europe. By that time, medieval Europe has already become a machine culture and it had been for centuries the civilisation with the most powerful mercantile elite. A reality driven by competitive jurisdictions, a rural-based military aristocracy, law that was not based on revelation (so it could entrench social bargains), suppression of kin-groups, and self-governing cities.
Competition between European states was a powerful driver of the transformative use of technologies. But so was the level of striving within such states: adventurers able to mobilise resources — and seeking wealth, power, prestige — had far more room to operate (and receive official sanction) in Europe than in China.
In other words, the differences in the development and use of technology — and in social dynamics and formations — between China and medieval Europe was fundamentally driven by the differences in state structures, in how the relevant polities worked.
1. Marx was not an honest intellectual reasoner:
As to the Delhi affair, it seems to me that the English ought to begin their retreat as soon as the rainy season has set in in real earnest. Being obliged for the present to hold the fort for you as the Tribune’s military correspondent I have taken it upon myself to put this forward. NB, on the supposition that the reports to date have been true. It’s possible that I shall make an ass of myself. But in that case one can always get out of it with a little dialectic. I have, of course, so worded my proposition as to be right either way.
Marx to Engels, [London,] 15 August 1857, (emphasis in the original).2. The Song (960-1279) failed to fully unify China, but they were the only significant Han polity. That the Song were effectively within a mini-state system does seem to have affected their policies, including the unusually — for a Chinese imperial dynasty — strong focus on trade and technological development.
3. Kin-groups had already been suppressed in the city-states of the Classical world, including Rome. They re-emerged with the incoming Germanic peoples, and then were suppressed again by the Church and the manorial elite, remaining in the agro-pastoralist Celtic fringe and Balkan uplands.
4. Economists Avner Greif and Guido Tabellini define clan (i.e. kin-group) as “a kin-based organization consisting of patrilineal households that trace their origin to a (self-proclaimed) common male ancestor“. They contrast this with a corporation: “a voluntary association between unrelated individuals established to pursue common interests“. They note they perform similar functions: “they sustained cooperation among members, regulated interactions with non-members, provided local public or club goods, and coordinated interactions with the market and with the state“. Triads, tongs and cults can also perform these functions.