The Psmiths, John and Jane, decided to jointly review a book by David Reich called Who We Are and How We Got Here: Ancient DNA and the New Science of the Human Past. This is Jane’s first contribution to an extended email thread between the Psmiths:
The problem with history is that there just isn’t enough of it. We’ve been around for, what, fifty thousand years? Conservatively.1 And we’ve barely written things down for a tenth of that. Archaeological excavation can take you a little farther back, but as the archaeologists always like to remind us, pots are not people. If you get lucky with a society that made things out of durable materials in a cold and/or dry environment (or you get very lucky with anaerobic preservation of organic materials, like in ice or bogs), maybe you can trace a material culture’s expansion and contraction across time and space. But that won’t tell you whether it’s a function of people moving and taking their stuff with them, or people’s neighbors going “ooh, using string to make patterns on your pots, that’s cool” and copying it. It certainly doesn’t tell you what their descendants were doing several thousand years later, potentially in an entirely different place and probably using an entirely different suite of technologies. Trying to understand what happened in the human past based on the historical and archaeological records is like walking into a room where a bomb has gone off and trying to reconstruct the locations of all the objects before the explosion. You can get some idea, but it’s all very broad strokes. And actually it’s worse than that, because it wasn’t just one explosion, it was lots, and we wouldn’t even know how many if we didn’t have a way of winding the clock back. But these days we do, and it’s ancient DNA.
Sometime between when my grandfather gave me a copy of Luca Cavalli-Sforza’s Genes, Peoples, and Languages for my birthday and when you and I decided to read Reich’s book together, two big things happened: humans got really, really good at sequencing and reading genomes, and Svante Pääbo’s lab in Leipzig got really, really good at extracting DNA from ancient bones. (How they developed their procedures is actually a really interesting story, which Pääbo retells in his book, but Reich — whose lab uses the same techniques on an industrial scale — gives a good, brief summary of how it works.) Together, these two advances unlocked … well, not quite everything about the deep past, but an absolutely enormous amount. Suddenly we can track the people, not just the pots, and the story is more complicated and fascinating than anything we might have expected. I’ve written elsewhere about some of the aDNA discoveries about human evolution (Neanderthal admixture, the Denisovans, etc.), but I’m even more excited about what ancient DNA reveals about our more recent past. Luckily, that’s what Reich spends most of the book on, with discussion of ancient ghost populations who now exist only in admixture and then chapters on the specific population genetic histories of Europe, India, North America, East Asia, and Africa, each of which contains some discoveries that would make (at least the more sensible) archaeologists and historical linguists go “well, duh” and others that are real surprises.
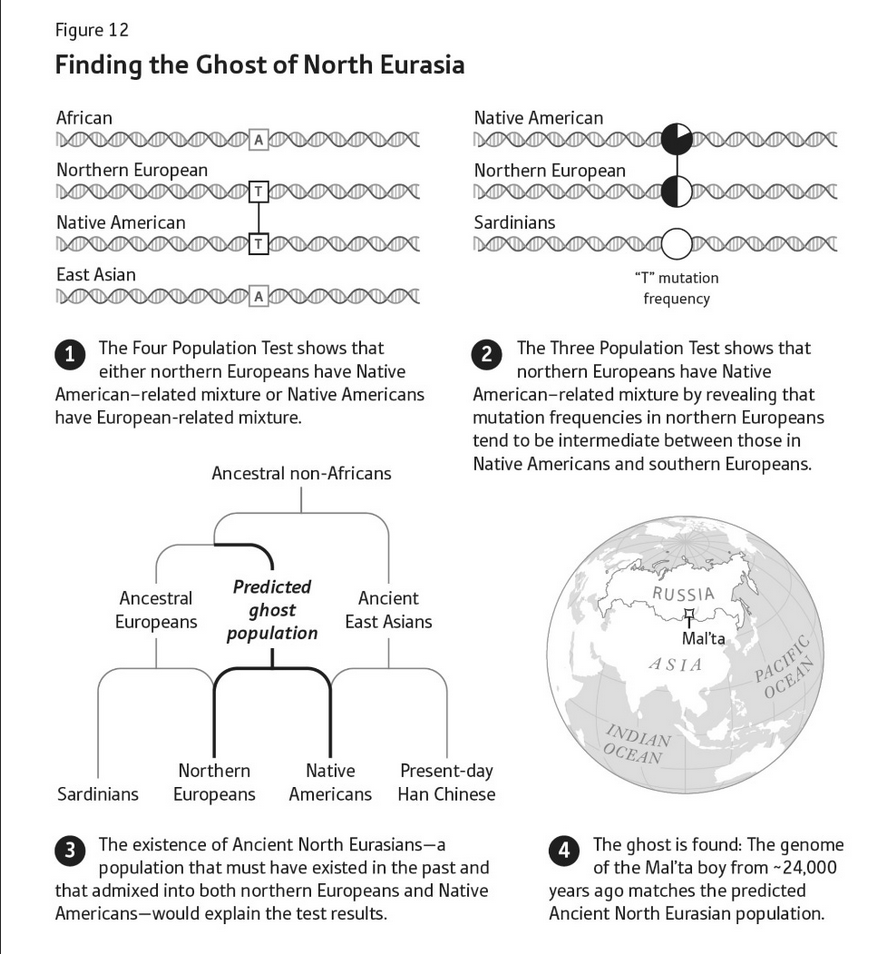
One of the “duh” stories is the final, conclusive identification of the people who brought horses, wagons, and Indo-European languages to Europe with the Yamnaya culture of the Pontic Steppe and their descendants. (David Anthony gives a very good overview of the archaeological case for this in The Wheel, the Horse, and Language, including some very cool experimental archaeology about horse teeth; you have my permission to skim the sections on pots.) My favorite surprising result, though, comes from a little farther north. People usually assume that Native Americans and East Asians share a common ancestor who split from the ancestors of Europeans and Africans before dividing into those two populations, but when Reich’s lab was trying to test the idea they found, to their surprise, that in places where Northern European genomes differ from Africans’, they are closer to Native Americans than to East Asians. Then, using a different set of statistical techniques, they found that Northern European populations were the product of mixture between two groups, one very similar to Sardinians (who are themselves almost-unmixed descendants of the first European farmers) and one that is most similar to Native Americans. They theorized a “ghost” population, which they called the “Ancient North Eurasians”, who had contributed DNA both to the population that would eventually cross the Bering land bridge and to the non-Early European Farmer ancestors of modern Northern Europeans. Several years later, another team sequenced the genome of a boy who died in Siberia 24kya and who was a perfect match for that theorized ghost ANE population.
But we’ve already established that I’m the prehistory nerd in this family; were you as jazzed as I was to read about the discovery of the Ancient North Eurasians?
1. That’s the latest plausible date for the arrival of full “behavioral modernity” in Africa, though our genus goes back about two million years, tool use probably three million, and I think there’s a good case that Homo was meaningfully “us” by 500kya. (That’s “thousand years ago” in “I talk about deep history so much I need an acronym”, fyi.)