Christian Monson debunks the common tale taught in western schools of reason for the amazing recovery of West Germany’s economy after World War Two:
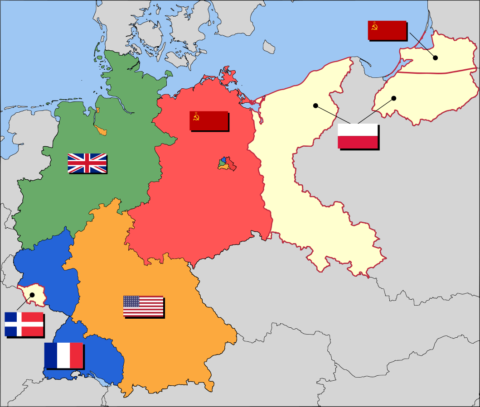
Occupation zone borders in Germany, 1947. The territories east of the Oder-Neisse line, under Polish and Soviet administration/annexation, are shown as cream as is the likewise detached Saar protectorate. Berlin is the multinational area within the Soviet zone.
Image based on map data of the IEG-Maps project (Andreas Kunz, B. Johnen, and Joachim Robert Moeschl of the University of Mainz) — www.ieg-maps.uni-mainz.de, via Wikimedia Commons.
This “economic miracle” is commonly referred to as die Wirtschaftswunder. But how did Germany go from rubble to riches in just a decade while neutral countries like Spain merely treaded economic water? If you ask your average American history student, they will say the Marshall Plan, of course!
Unfortunately, the ubiquity of the myth that the Marshall Plan rebuilt Germany is proof that state-controlled education favors propaganda over economic literacy. Despite the fact that most modern historians don’t give the Marshall Plan much credit at all for rebuilding Germany and attribute to it less than 5 percent of Germany’s national income during its implementation, standard history textbooks still place it at the forefront of the discussion about post-war reconstruction.
Consider this section from McDougal Littell’s World History (p. 968), the textbook I was given in high school:
This assistance program, called the Marshall Plan, would provide food, machinery, and other materials to rebuild Western Europe. As Congress debated the $12.5 billion program in 1948, the Communists seized power in Czechoslovakia. Congress immediately voted approval. The plan was a spectacular success.
Of course, the textbook makes no mention of the actual cause of the Wirtschaftwunder: sound economic policy. That’s because, for the state, the Marshall Plan makes great statist mythology.
Not only is it frequently brought up to justify the United States getting involved in foreign conflicts, but it simply gives support for central planning. Just look at the economic miracle the government was able to create with easy credit, they say.
And of course, admitting that the billions of dollars pumped into Germany after WWII accomplished next to nothing, especially when compared to something as simple as sound money, would be tantamount to admitting that the government spends most of its time making itself needed when it isn’t and thereby doing little besides getting in the way.
Credit for the turnaround should be accorded to Ludwig Erhard, according to Alasdair Macleod at the Cobden Centre:
Anyone who favours regulation needs to explain away Germany’s post-war success. Her economy had been destroyed, firstly by the Nazi war machine, and then by Allied bombing. We easily forget the state of ruin the country was in, with people in the towns and cities actually starving in the post-war aftermath. The joint British and American military solution was to extend and intensify war-time rationing and throw Marshall aid at the problem.
Then a man called Ludwig Erhard was appointed director of economics by the Bizonal Economic Council, in effect he became finance minister. He decided, against British and American misgivings, as well as opposition from the newly-recreated Social Democrats, to do away with price controls and rationing, which he did in 1948. These moves followed his currency reform that June, which contracted the money supply by about 90%. He also slashed income tax from 85% to 18% on annual incomes over Dm2,500 (US$595 equivalent).
Economists of the Austrian school would comprehend and recommend this strategy, but it goes wholly against the bureaucratic grain. General Lucius Clay, who was the military governor of the US Zone, and to whom Erhard reported, is said to have asked him, “Herr Erhard, my advisers tell me what you have done is a terrible mistake. What do you say to that?”
Erhard replied, “Herr General, pay no attention to them! My advisers tell me the same thing.”
About the same time, a US Colonel confronted Erhard: “How dare you relax our rationing system, when there is a widespread food shortage?”
Erhard replied, “I have not relaxed rationing, I have abolished it. Henceforth the only rationing ticket the people will need will be the deutschemarks. And they will work hard to get those deutschemarks, just wait and see.”
The US Colonel did not have to wait long. According to contemporary accounts, within days of Erhard’s currency reform, shops filled with goods as people realised the money they sold them for would retain its value. People no longer needed to forage for the basics in life, so absenteeism from work halved, and industrial output rose more than 50% in the second half of 1948 alone.



