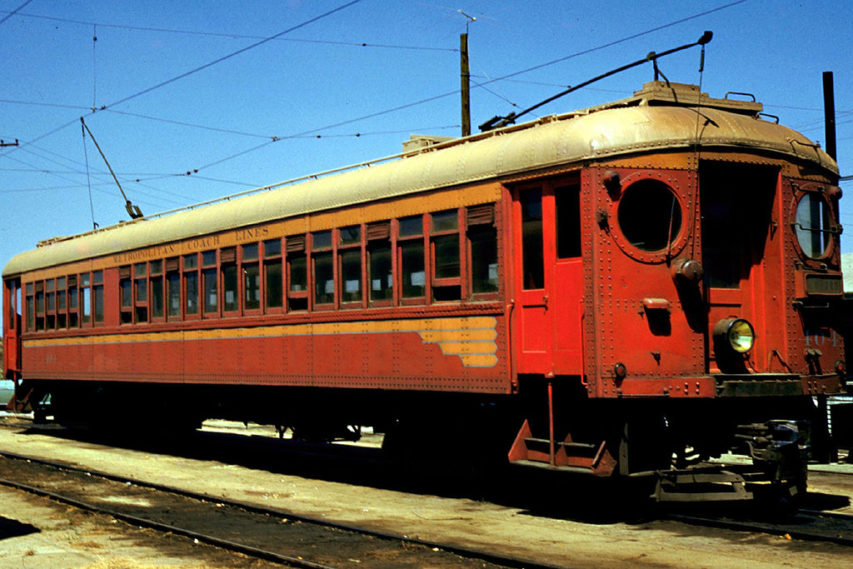
This month’s Classic Trains featured fallen flag is southern California’s iconic Pacific Electric Railway Company, whose streetcars, interurbans, and buses served the vast area in and around Los Angeles and San Bernardino from 1901 until the passenger services were sold off in 1953. The electric service was converted to bus and the last electric rail line was discontinued in 1961. At its peak in the 1920s the “Red Cars” service was said to be the largest electric railway system in the entire world.
This month’s Classic Trains featured fallen flag is southern California’s iconic Pacific Electric Railway Company, whose streetcars, interurbans, and buses served the vast area in and around Los Angeles and San Bernardino from 1901 until the passenger services were sold off in 1953. The electric service was converted to bus and the last electric rail line was discontinued in 1961. At its peak in the 1920s the “Red Cars” service was said to be the largest electric railway system in the entire world.
G. Mac Sebree covers the origins of the line in the late nineteenth century:
The story begins in 1895, when a line was completed from Los Angeles to Pasadena; a mere 10 years later, the system was virtually complete. To a great degree, PE was the brainchild of Henry Huntington, nephew of one of the Central Pacific’s “Big Four,” Collis P. Huntington. An active real-estate promoter, Henry needed the Big Red Cars and the transportation they provided to help sell lots and homes in the hinterlands.
His uncle’s Southern Pacific took control of the PE in 1911 in a deal that left the Los Angeles Railway, the narrow-gauge intracity system, in the nephew’s hands. The PE was built to standard gauge, and SP saw a brilliant future in freight for the interurban.
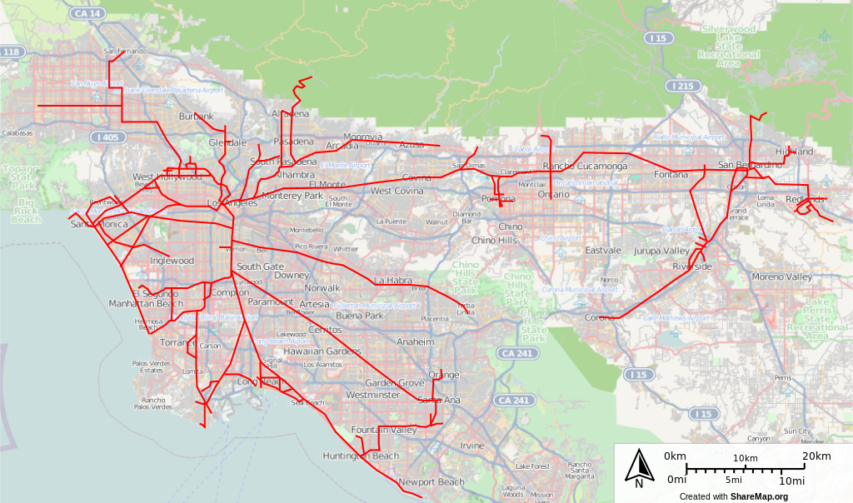
Pacific Electric route map.
Original data from http://sharemap.org/public/Los_Angeles_Pacific_Electric_Railways_(Red_Cars) via Wikimedia Commons.Interurbans were not considered Class I railroads (or any other class — they were not “steam railroads”), but from the very start, PE was big business. The California Railroad Commission said the property was worth $100 million in Depression dollars. Atypically for an interurban, the system served as a gathering network for carload freight shipments from citrus groves, manufacturing plants, oil refineries, warehouses, and the harbor at San Pedro. The three line-haul railroads serving southern California — Santa Fe, Union Pacific, and especially SP — depended on the Pacific Electric to some degree.
Yet in its heyday, PE carried huge numbers of passengers. As late as 1953, 50 percent of its revenue came from riders — but absolutely none of its profit. An all-time list shows that PE operated 143 distinct passenger routes. Despite the so-called “Great Merger of 1911,” in which local and interurban services were supposedly separated, the heaviest PE passenger lines largely served the L.A. urban area. An example was the street-running L.A.–Hollywood–Beverly Hills line, in which two-car trains rumbled down Hollywood Boulevard at 10-minute intervals.
At one time or another, PE single-truck Birney cars plied local lines in Pasadena, Long Beach, Santa Monica, Redlands, Santa Ana, and San Pedro, although the 1920s were not far along before management sought to sell off or abandon these albatrosses.
After World War 2, the writing was on the wall for the Red Cars, as urban expansion and greatly increased car ownership cut at the economic basis for rail passenger service in southern California, especially as the new freeways were built.
After the war, though, things went downhill rapidly. As soon as buses were available, Pacific Electric began wholesale rail passenger-service abandonments. The new freeways were regarded as the rapid transit of the future. PE President Oscar Smith saw one possibility for saving rail service — if the state would pay. Just before the war, a short section of freeway between Hollywood and the San Fernando Valley had been built, with the PE tracks relocated to the center of the new highway.
Why not replicate this all over the basin? The PE would cooperate, but public officials turned a deaf ear, and that was that. Freight service, meanwhile, prospered, but by the mid-1950s, PE began replacing its electric locomotives and box motors with diesels (a few steam locomotives also had been used during the war). Over the years, PE rostered about 100 electric locomotives and at least 75 box motors — big business, indeed.
In 1953, PE sold its passenger service (four rail lines out of the 6th and Main station, two out of Subway Terminal, and many bus lines) to Metropolitan Coach Lines. The Metropolitan Transit Authority, first formed in 1951, bought MCL on March 3, 1958, and the end for electric passenger service came in 1961. SP continued the freight work with diesels, and merged PE away on August 13, 1965. Today under the Union Pacific shield, a good bit of the old PE freight lines remain in service, unique survivors, busier than ever.