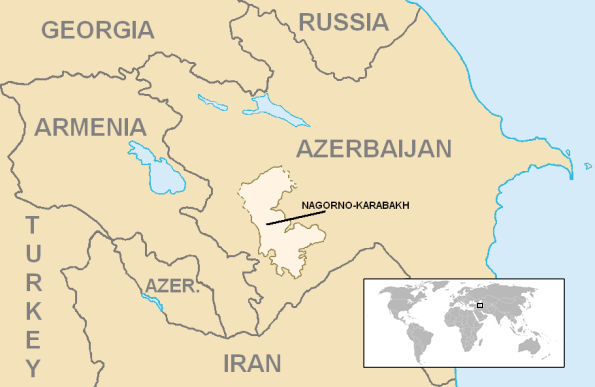
Fighting broke out between Azerbaijan and Armenia last week over the status of the Nagorno-Karabakh region, a quasi-independent Armenian-majority territory still technically part of Azerbaijan (Nagorno-Karabakh’s declaration was not followed by formal recognition by other states). Mark Movsesian provides some historical background to the conflict in First Things:
Thirty years ago, in response to discriminatory treatment and outright pogroms against Armenians, the region declared independence. Armenia (population 3 million) supported Karabakh — though it has never formally recognized its independence — and a bloody war followed, in which 30,000 people died and hundreds of thousands on both sides became refugees. Against all odds, Armenia and Karabakh prevailed and established a buffer zone comprising perhaps 20 percent of Azeri territory.
An unstable ceasefire has held since 1994. But last week, Azerbaijan launched a military offensive against Karabakh and Armenia itself. This is more serious than past Azeri efforts to break the stalemate. Flush with petrodollars, Azerbaijan has purchased a large stockpile of heavy weapons, which it now employs against Armenia. Moreover, Turkey (population 80 million), which borders Armenia on the other side, is supporting Azerbaijan. Azeris are a Turkic people, though they are Shia, not Sunni, Muslims, and the Erdogan government sees the conflict as a way to pursue its goal of pan-Turanism. Turkey has supplied Azerbaijan with military advisers and equipment, including drones and fighter jets and thousands of Islamist soldiers from Syria, who fight for Azerbaijan on the front lines.
[…]
One needs to go back at least a century, to the collapse of the Ottoman and Czarist Empires. The two empires had long contested the border between them, which ran to the southwest of the Caucasus. Armenians, an ancient Christian people who lived on both sides of the border, found themselves in the crosshairs. During World War I, fearful that Armenians on the border would rise up and side with Russia — some Armenians did fight with the Russians, but many others fought with the Ottomans, and the Armenian threat was always exaggerated — the Ottoman government undertook an ethnic cleansing campaign, killing millions of Armenians and other Christians in the Armenian Genocide.
The Genocide eliminated Turkey’s once sizable Christian population. It likely would have eliminated the Armenian population on the other side of the border, too, except that a hastily-organized Armenian militia stopped a Turkish army in 1918 at the Battle of Sardarabad, which took place just outside the city of Yerevan, today Armenia’s capital. Sardarabad is unknown in the West, but the image of a small group of Christian Armenians fighting, alone, to stop a Muslim Turkish army bent on their annihilation is a powerful part of Armenian consciousness today.
When the war ended, the Soviet Union quickly settled the border dispute with Turkey, giving up some historic Armenian lands around the city of Kars, and took over the Caucasus and divided it among the region’s ethnic groups. The Soviets initially promised to place Karabakh, whose Armenian identity dated back many centuries and whose population was more than 90 percent Armenian, in the new Soviet Republic of Armenia. But Stalin, as commissar for nationalities, decided to place the region in Azerbaijan instead, as part of a divide-and-conquer strategy. Armenians never accepted the decision and, when the Soviet Union collapsed and the nations of the Caucasus gained independence, the conflict over the region resumed.