Colby Cosh on the latest refugee to flee from Canada:
On Dec. 10, the World Magnetic Model used to calibrate compasses was officially updated. The “model” can be thought of as a map that you would use, given your location on or near the Earth’s surface, to find out how many degrees your magnetic compass is off from true geographic north (or south). This ordinarily happens every five years, but the wizards in charge of the system decided to update a year early because the north magnetic pole is moving particularly fast right now.
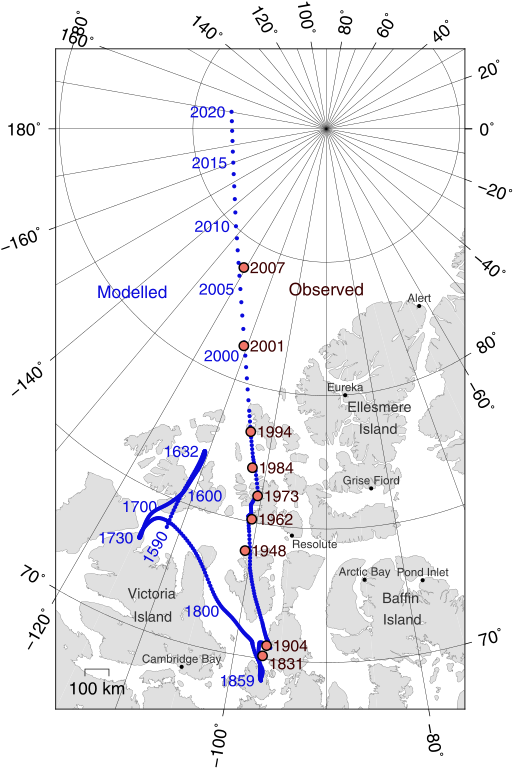
Positions of North Magnetic Pole of the Earth. Poles shown are dip poles, defined as positions where the direction of the magnetic field is vertical. Red circles mark magnetic north pole positions as determined by direct observation, blue circles mark positions modelled using the GUFM model (1590–1890) and the IGRF-12 model (1900–2020) in 1 year increments. For the years 1890–1900, a smooth interpolation between the two models was performed. The modelled locations after 2015 are projections.
Map by Cavit via Wikimedia Commons.As most Canadians will have heard, magnetic north is, at the moment, fleeing Canadian territory and heading toward Russia. The rate of change is still very high by historic standards, first established in the early 19th century, but it has slowed just a little. In the year 1900 the pole was firmly in the Canadian Arctic, off Somerset Island. It wandered north, broke out of our high Arctic archipelago in about 2000, and has been streaking Siberia-ward across the open sea at more than 50 km a year since. The time component in the new WMM forecasts a slight slowing over the next five-year period, to about 40 km/yr.
This, like everything else involving Earth’s magnetic field, is a bit of a guess. The WMM has to be updated often because it does incorporate guesswork about the magnitude and direction of changes in the short-term future. The model will be most accurate now, and increasingly less so over the five-year term as the magnetic poles do their little dance — independently, by the way; the magnetic poles are not exactly opposite the Earth from one another, and the “south” one is scooting along much more slowly than the “north.” (Also, the magnetic north pole, the one to which the “north” needle of your compass is attracted, is actually a “south” pole to physicists.)
The truth is that the naive inquirer should not research Earth’s magnetism in the expectation that it is as well understood by scientists as, say, oceanic tides. (You can probably detect that I am talking about myself here.) The question “Why is the magnetic pole leaving Canada?” does not really admit of a solid answer. Maybe it’s the investment climate?
Probably most everybody is dimly aware that the magnetic poles flip outright from time to time — every half-million years on average. But the assumptions embedded in your handheld compass run much deeper than that. The Earth itself is only a big dipole magnet generally, rather than locally, and there is no guarantee of only one “north magnetic pole” as the field is measured near the surface. Competing “north poles” can form. (Which would, at least, let Russia and Canada each have their own …)