Stewart Brand wants us to stop presenting so many conservation concerns in the headline-grabbing “Fluffy Bunnies At Risk!” format:
The way the public hears about conservation issues is nearly always in the mode of ‘[Beloved Animal] Threatened With Extinction’. That makes for electrifying headlines, but it misdirects concern. The loss of whole species is not the leading problem in conservation. The leading problem is the decline in wild animal populations, sometimes to a radical degree, often diminishing the health of whole ecosystems.
Viewing every conservation issue through the lens of extinction threat is simplistic and usually irrelevant. Worse, it introduces an emotional charge that makes the problem seem cosmic and overwhelming rather than local and solvable. It’s as if the entire field of human medicine were treated solely as a matter of death prevention. Every session with a doctor would begin: ‘Well, you’re dying. Let’s see if we can do anything to slow that down a little.’
Medicine is about health. So is conservation. And as with medicine, the trends for conservation in this century are looking bright. We are re-enriching some ecosystems we once depleted and slowing the depletion of others. Before I explain how we are doing that, let me spell out how exaggerated the focus on extinction has become and how it distorts the public perception of conservation.
Many now assume that we are in the midst of a human-caused ‘Sixth Mass Extinction’ to rival the one that killed off the dinosaurs 66 million years ago. But we’re not. The five historic mass extinctions eliminated 70 per cent or more of all species in a relatively short time. That is not going on now. ‘If all currently threatened species were to go extinct in a few centuries and that rate continued,’ began a recent Nature magazine introduction to a survey of wildlife losses, ‘the sixth mass extinction could come in a couple of centuries or a few millennia.’
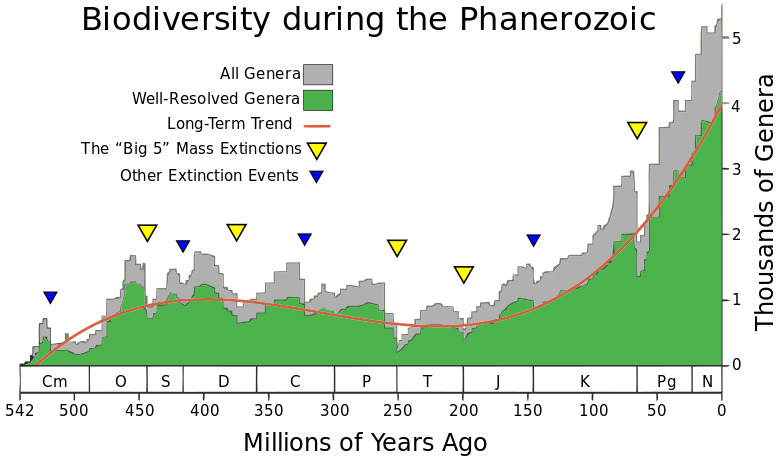
The fossil record shows that biodiversity in the world has been increasing dramatically for 200 million years and is likely to continue. The two mass extinctions in that period (at 201 million and 66 million years ago) slowed the trend only temporarily. Genera are the next taxonomic level up from species and are easier to detect in fossils. The Phanerozoic is the 540-million-year period in which animal life has proliferated. Chart created by and courtesy of University of Chicago paleontologists J. John Sepkoski, Jr. and David M. Raup.
The range of dates in that statement reflects profound uncertainty about the current rate of extinction. Estimates vary a hundred-fold – from 0.01 per cent to 1 per cent of species being lost per decade. The phrase ‘all currently threatened species’ comes from the indispensable IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature), which maintains the Red List of endangered species. Its most recent report shows that of the 1.5 million identified species, and 76,199 studied by IUCN scientists, some 23,214 are deemed threatened with extinction. So, if all of those went extinct in the next few centuries, and the rate of extinction that killed them kept right on for hundreds or thousands of years more, then we might be at the beginning of a human-caused Sixth Mass Extinction.