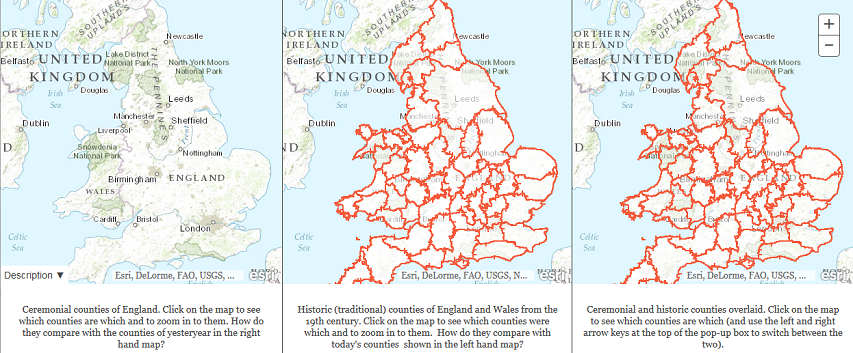
I was born in Yorkshire. If anyone ever asked, that’s what I’d say. But there’s Yorkshire and then there’s “Yorkshire”. At some point shortly after my family emigrated to Canada, they moved my hometown out of Yorkshire and into a new county-like entity. Then they moved the boundaries again. And again. And again. I’ve long since lost track of which county Middlesbrough is officially located in … I think it was now part of Durham (which is nice, because I currently live in a different county-like entity also called Durham). As this BBC News Magazine post illustrates, the counties of England are very confusing and in some cases bear almost no relationship to the historical counties most of us still think of as being “the real counties”:
Middlesex dates back to the 8th Century but Middlesex County Council was abolished in 1965. Middlesex County Cricket Club and Middlesex University live on. So too does the historic county of Middlesex even though most of its inhabitants now live in the ceremonial county of Greater London.
Still following?
England’s counties are the source of much regional pride, not least on cricket pavilions. To identify as a Yorkshirewoman or a Devonian or a Northumbrian is to invite certain expectations about the forthrightness of one’s views or one’s tolerance for cider and clog-dancing.
But successive waves of local government reform have left many people deeply unclear as to which county they live in – the answer to which depends on exactly what you mean by the word “county”.
Now, in an effort to support the “tapestry” of ancient place names, the government has changed its rules allowing councils to put up boundary signs marking traditional English counties – including the likes of Cumberland and Huntingdonshire, names which no longer have any connection to local authorities.
If you’re attempting to keep score at home, here are the different kinds of “county” you need to track for historical purposes:
First there are the historic counties, which date as far back as the mid-Saxon period. Some, like Westmorland, no longer exist in an administrative sense. But especially in places like Yorkshire, Durham and Cornwall, they are important expressions of geographic and cultural identity.
Then there are administrative counties and unitary authority areas created by the 1972 Local Government Act. These include non-metropolitan county councils like Oxfordshire and Surrey (where some services are also provided by districts). Others, like Northumberland, are single-tier unitary councils. Some areas like Berkshire have no county council and the districts are the sole local authorities.
And finally there are the ceremonial counties, established by the 1997 Lieutenancies Act, each of which has a Lord Lieutenant. Bedfordshire and Cheshire, for instance, do not exist as councils but do as ceremonial counties. In metropolitan counties like Merseyside, Tyne and Wear and Greater Manchester, county councils were scrapped in the 1980s, but some services including transport and the police are run jointly by groups of councillors within the old boundaries.
If you’ve followed that, well done. Catherine Staite, director of the Institute of Local Government at Birmingham University, says there was no consistency to the way these overlapping boundaries were drawn. “We’ve ended up with a patchwork of arrangements for which there is no logic.”
There is a new website to attempt to resolve the confusion, but I’m not sure it will do much: