![]() This month’s Classic Trains fallen flag feature is the Northern Pacific Railway by George Drury. The NP was a government-authorized transcontinental line planned to run from a Great Lakes port to the Pacific Northwest. Its founding legislation was passed during the American Civil War but construction of the right of way didn’t begin until 1870 and the line was completed in September, 1883. The railway was granted up to 60 million acres in land grants, but eventually only claimed about 40 million acres (much of this land was already occupied or claimed by various First Nations tribal groups who — of course — were given no choice about having a railway built through their lands and many actively fought against the railway eventually requiring formal US Army protection for the surveying and building crews).
This month’s Classic Trains fallen flag feature is the Northern Pacific Railway by George Drury. The NP was a government-authorized transcontinental line planned to run from a Great Lakes port to the Pacific Northwest. Its founding legislation was passed during the American Civil War but construction of the right of way didn’t begin until 1870 and the line was completed in September, 1883. The railway was granted up to 60 million acres in land grants, but eventually only claimed about 40 million acres (much of this land was already occupied or claimed by various First Nations tribal groups who — of course — were given no choice about having a railway built through their lands and many actively fought against the railway eventually requiring formal US Army protection for the surveying and building crews).
Despite the vast land grants, the costs of building the railway eventually drove Jay Cooke, the original financial backer, into bankruptcy which was one of the major triggers of the financial disaster known as the Panic of 1873. The economic impact was widespread and was known — until the 1930s — as the “Great Depression”, and the US economy took several years to resume growth while other industrialized countries suffered the effects for longer.
NP reorganized by converting the bonds to stock, and the Lake Superior & Mississippi was reorganized as the St. Paul & Duluth. In 1881 control of the NP was purchased by Henry Villard, who also controlled the Oregon Railway & Navigation Co. and the Oregon & California Railroad. On Sept. 8, 1883, NP drove a last spike at Gold Creek, Mont., near Garrison, completing a line from Duluth to Wallula Junction, Wash. Northern Pacific trains continued on the rails of the OR&N to Portland, where NP’s own line to Tacoma resumed (it crossed the Columbia River by ferry from Goble, Ore., to Kalama, Wash.).
Even before completing the line at Gold Creek, NP began constructing a direct line from Pasco, Wash., over the Cascade Range to Tacoma. The Puget Sound area was beginning to grow, and NP wanted to reach it with its own line rather than rely on OR&N. Indeed, soon after the last-spike ceremonies, Villard’s empire collapsed and OR&N became part of Union Pacific (Southern Pacific got the Oregon & California). The Pasco–Tacoma line opened in 1887, with temporary switchbacks carrying trains over Stampede Pass until the opening of Stampede Tunnel in May 1888.
To help populate the railway’s claimed lands, colonization offices were established in northern Europe in the mid-1880s to attract immigrants to settle and farm along the right of way. Many Americans of German or Scandinavian ancestry can trace their roots back to these programs, which generally offered very cheap package deals for transportation to the United States along with parcels of land and other inducements.
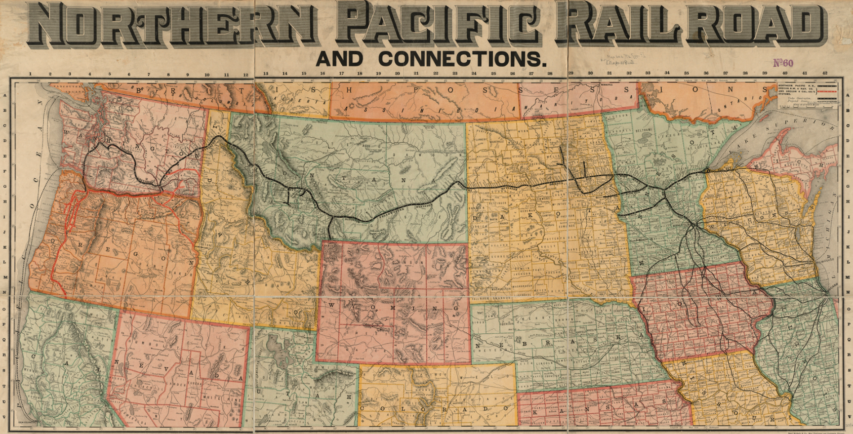
Detail from an 1885 Rand McNally publication showing a “Shipper’s Guide To All Points On And Connections To the Northern Pacific Railroad, Its Branches And Connecting Lines”
Original scan from the Norman B. Leventhal Map Center at the BPL via Wikimedia Commons.
In 1901 Northern Pacific and Great Northern gained control of the Chicago, Burlington & Quincy by jointly purchasing approximately 98 percent of its capital stock. That same year James J. Hill and J. P. Morgan formed the Northern Securities Co. as a holding company for NP and Great Northern. The U.S. Supreme Court dissolved Northern Securities in 1904. In 1905 the two roads organized the Spokane, Portland & Seattle, which was completed from Spokane through Pasco to Portland in 1908. GN and NP attempted consolidation in 1927, but the Interstate Commerce Commission made giving up control of the Burlington a requisite for approval, a condition the roads found unacceptable.
In October 1941 NP purchased the property of the Minnesota & International Railway (Brainerd to International Falls, Minn.), which it had controlled for a number of years.
In image, Northern Pacific was the most conservative of the three northern transcontinentals. (Great Northern was a prosperous, well-thought-out railroad; the Milwaukee Road was a brash newcomer.) Bulking large in NP’s freight traffic were wheat and lumber. In the 1920s and 1930s NP suffered from smaller than usual wheat crops and competition from ships for lumber moving to the East Coast. Ship competition decreased during World War II, and postwar prosperity brought an increase in building activity and population growth to the area NP served. NP was the oldest of the northern transcontinentals and had been instrumental in settling the northern plains. It served the populous areas of North Dakota, Montana, and Washington. Its slogan was “Main Street of the Northwest,” and its secondary passenger train of the 1950s and ’60s was the Mainstreeter. Its flagship was the North Coast Limited, launched in 1900.
In 1956 NP and Great Northern again studied merger of the two roads, the Burlington, and the Spokane, Portland & Seattle. In 1960 the directors of both roads approved the merger terms. On March 2, 1970, NP was merged into Burlington Northern along with Great Northern; Chicago, Burlington & Quincy; and Spokane, Portland & Seattle.