Matt Ridley is somewhat uncharacteristically concerned about the major Ebola outbreak in west Africa:
As you may know by now, I am a serial debunker of alarm and it usually serves me in good stead. On the threat posed by diseases, I’ve been resolutely sceptical of exaggerated scares about bird flu and I once won a bet that mad cow disease would never claim more than 100 human lives a year when some “experts” were forecasting tens of thousands (it peaked at 28 in 2000). I’ve drawn attention to the steadily falling mortality from malaria and Aids.
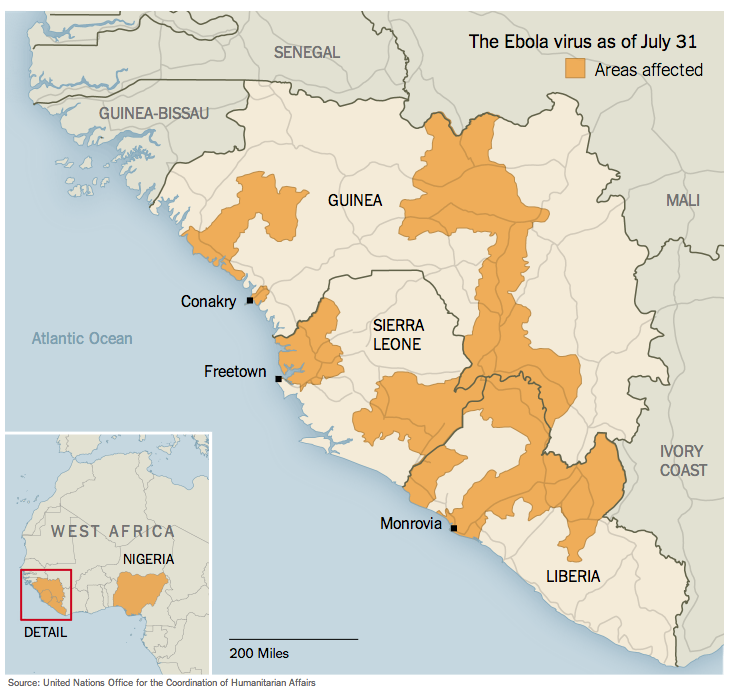
Well, this time, about ebola, I am worried. Not for Britain, Europe or America or any other developed country and not for the human race as a whole. This is not about us in rich countries, and there remains little doubt that this country can achieve the necessary isolation and hygiene to control any cases that get here by air before they infect more than a handful of other people — at the very worst. No, it is the situation in Liberia, Sierra Leone and Guinea that is scary. There it could get much worse before it gets better.
This is the first time ebola has got going in cities. It is the first time it is happening in areas with “fluid population movements over porous borders” in the words of Margaret Chan, the World Health Organisation’s director-general, speaking last Friday. It is the first time it has spread by air travel. It is the first time it has reached the sort of critical mass that makes tracing its victims’ contacts difficult.
One of ebola’s most dangerous features is that kills so many health workers. Because it requires direct contact with the bodily fluids of patients, and because patients are violently ill, nurses and doctors are especially at risk. The current epidemic has already claimed the lives of 60 healthcare workers, including those of two prominent doctors, Samuel Brisbane in Liberia and Sheik Umar Khan in Sierra Leone. The courage of medics in these circumstances, working in stifling protective gear, is humbling.