Railways Explained
Published 22 Oct 2023In today’s video we continue uncovering the story of railway development in Great Britain, as part of a special trilogy marking the Railways Explained’s achievement of 100,000 subscribers!
This is actually the second video in series, and it covers a period from the aftermath of World War II to the momentous era of rail privatization, which was quite challenging period for British railways, full of ups and downs, but it is mostly marked by the formidable challenges.
We talked about the pivotal moments, such as the birth of British Railways, the ambitious Modernisation Plan, the influential Beeching Report, structural reforms, and the eventual transition to rail privatization, which all defined the British railways during this transformative period.
This insightful journey through time illuminates the intricacies and milestones of a railway system that has left an indelible mark on the United Kingdom’s transportation history.
(more…)
January 22, 2024
Nationalization of British Railways: What Went Wrong?
QotD: Mao’s theory of “protracted war” as adapted to Vietnamese conditions by Võ Nguyên Giáp
The primary architect of Vietnam’s strategy, initially against French colonial forces and then later against the United States and the US-backed South Vietnamese (Republic of Vietnam or RVN) government was Võ Nguyên Giáp.
Giáp was facing a different set of challenges in Vietnam facing either France or the United States which required the framework of protracted war to be modified. First, it must have been immediately apparent that it would never be possible for a Vietnamese-based army to match the conventional military capability of its enemies, pound-for-pound. Mao could imagine that at some point the Red Army would be able to win an all-out, head-on-head fight with the Nationalists, but the gap between French and American capabilities and Vietnamese Communist capabilities was so much wider.
At the same time, trading space for time wasn’t going to be much of an option either. China, of course, is a very large country, with many regions that are both vast, difficult to move in, and sparsely populated. It was thus possible for Mao to have his bases in places where Nationalist armies literally could not reach. That was never going to be possible in Vietnam, a country in which almost the entire landmass is within 200 miles of the coast (most of it is far, far less than that) and which is about 4% the size of China.
So the theory is going to have to be adjusted, but the basic groundwork – protract the war, focus on will rather than firepower, grind your enemy down slowly and proceed in phases – remains.
I’m going to need to simplify here, but Giáp makes several key alterations to Mao’s model of protracted war. First, even more than Mao, the political element in the struggle was emphasized as part of the strategy, raised to equality as a concern with the military side and fused with the military operation; together they were termed dau tranh, roughly “the struggle”. Those political activities were divided into three main components. Action among one’s own people consisted of propaganda and motivation designed to reinforce the will of the populace that supported the effort and to gain recruits. Then, action among the enemy people – here meaning Vietnamese who were under the control of the French colonial government or South Vietnam and not yet recruited into the struggle – a mix of propaganda and violent action to gain converts and create dissension. Finally, action against the enemy military, which consisted of what we might define as terroristic violence used as message-sending to negatively impact enemy morale and to encourage Vietnamese who supported the opposition to stop doing so for their own safety.
Part of the reason the political element of this strategy was so important was that Giáp knew that casualty ratios, especially among guerrilla forces – on which, as we’ll see, Giáp would have to rely more heavily – would be very unfavorable. Thus effective recruitment and strong support among the populace was essential not merely to conceal guerrilla forces but also to replace the expected severe losses that came with fighting at such a dramatic disadvantage in industrial firepower.
That concern in turn shaped force-structure. Giáp theorized an essentially three-tier system of force structure. At the bottom were the “popular troops”, essentially politically agitated peasants. Lightly armed, minimally trained but with a lot of local knowledge about enemy dispositions, who exactly supports the enemy and the local terrain, these troops could both accomplish a lot of the political objectives and provide information as well as functioning as local guerrillas in their own villages. Casualties among popular troops were expected to be high as they were likely to “absorb” reprisals from the enemy for guerrilla actions. Experienced veterans of these popular troops could then be recruited up into the “regional troops”, trained men who could now be deployed away from their home villages as full-time guerrillas, and in larger groups. While popular troops were expected to take heavy casualties, regional troops were carefully husbanded for important operations or used to organize new units of popular troops. Collectively these two groups are what are often known in the United States as the Viet Cong, though historians tend to prefer their own name for themselves, the National Liberation Front (Mặt trận Dân tộc Giải phóng miền Nam Việt Nam, “National Liberation Front for South Vietnam”) or NLF. Finally, once the French were forced to leave and Giáp had a territorial base he could operate from in North Vietnam, there were conventional forces, the regular army – the People’s Army of Vietnam (PAVN) – which would build up and wait for that third-phase transition to conventional warfare.
The greater focus on the structure of courses operating in enemy territory reflected Giáp’s adjustment of how the first phase of the protracted war would be fought. Since he had no mountain bases to fall back to, the first phase relied much more on political operations in territory controlled by the enemy and guerrilla operations, once again using the local supportive population as the cover to allow guerrillas and political agitators (generally the same folks, cadres drawn from the regional troops to organize more popular troops) to move undetected. Guerrilla operations would compel the less-casualty-tolerant enemy to concentrate their forces out of a desire for force preservation, creating the second phase strategic stalemate and also clearing territory in which larger mobile forces could be brought together to engage in mobile warfare, eventually culminating in a shift in the third phase to conventional warfare using the regional and regular troops.
Finally, unlike Mao, who could envision (and achieve) a situation where he pushed the Nationalists out of the territories they used to recruit and supply their armies, the Vietnamese Communists had no hope (or desire) to directly attack France or the United States. Indeed, doing so would have been wildly counter-productive as it likely would have fortified French or American will to continue the conflict.
That limitation would, however, demand substantial flexibility in how the Vietnamese Communists moved through the three phases of protracted war. This was not something realized ahead of time, but something learned through painful lessons. Leadership in the Democratic Republic of Vietnam (DRV = North Vietnam) was a lot more split than among Mao’s post-Long-March Chinese Communist Party; another important figure, Lê Duẩn, who became general secretary in 1960, advocated for a strategy of “general offensive” paired with a “general uprising” – essentially jumping straight to the third phase. The effort to implement that strategy in 1964 nearly overran the South, with ARVN (Army of the Republic of Vietnam – the army of South Vietnam) being defeated by PAVN and NLF forces at the Battles of Bình Giã and Đồng Xoài (Dec. 1964 and June 1965, respectively), but this served to bring the United States more fully into the war – a tactical and operational victory that produced a massive strategic setback.
Lê Duẩn did it again in 1968 with the Tet Offensive, attempting a general uprising which, in an operational sense, mostly served to reveal NLF and PAVN formations, exposing them to US and ARVN firepower and thus to severe casualties, though politically and thus strategically the offensive ended up being a success because it undermined American will to continue the fight. American leaders had told the American public that the DRV and the NLF were largely defeated, broken forces – the sudden show of strength exposed those statements as lies, degrading support at home. Nevertheless, in the immediate term, the Tet Offensive’s failure on the ground nearly destroyed the NLF and forced the DRV to back down the phase-ladder to recover. Lê Duẩn actually did it again in 1972 with the Eastern Offensive when American ground troops were effectively gone, exposing his forces to American airpower and getting smashed up for his troubles.
It is difficult to see Lê Duẩn’s strategic impatience as much more than a series of blunders – but crucially Giáp’s framework allowed for recovery from these sorts of defeats. In each case, the NLF and PAVN forces were compelled to do something Mao’s model hadn’t really envisaged, which was to transition back down the phase system, dropping back to phase II or even phase I in response to failed transitions to phase III. By moving more flexibly between the phases (while retaining a focus on the conditions of eventual strategic victory), the DRV could recover from such blunders. I think Wayne Lee actually puts it quite well that whereas Mao’s plan relied on “many small victories” adding up to a large victory (without the quick decision of a single large victory), Giáp’s more flexible framework could survive many small defeats on the road to an eventual strategic victory when the will of the enemy to continue the conflict was exhausted.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: How the Weak Can Win – A Primer on Protracted War”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2022-03-03.
January 21, 2024
The Duke of Wellington, perhaps best known as the inventor of the Wellington boot …
Weaver Sheridan expresses some surprise that His Grace’s main source of fame is the credit for the invention of the Wellington, rather than his other, uninteresting achievements:
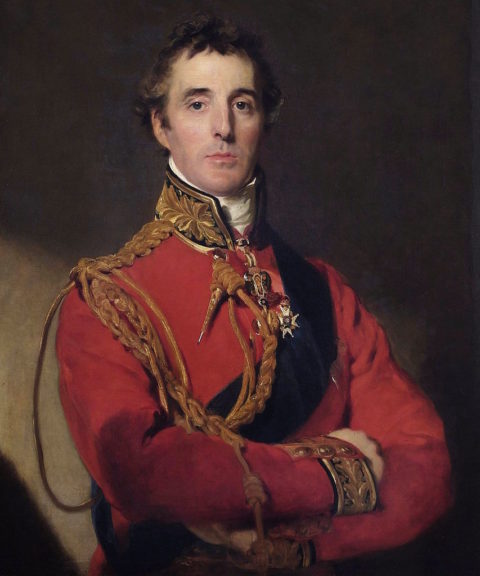

Arthur Wellesley, 1st Duke of Wellington (1769–1852) by Thomas Lawrence, circa 1815-1816.
Wikimedia Commons.
I know nothing should surprise us these days about dumbed-down Britain. But an article on the moronic Mail Online website the other day had me choking on my cornflakes.
It read: “In 2020, Mandy Lieu, 38, bought 935-acre Ewhurst Park in Hampshire, once owned by the inventor of the wellington boot, the Duke of Wellington, and vowed to turn it into a world-class organic farm and nature reserve.”
The inventor of the wellington boot!
Good grief, I know teaching of British history is nowadays outrageously skewed and bowdlerised, but I didn’t realise things had got this bad.
The article’s author obviously thinks the Iron Duke’s main claim to fame was the welly. Does she know nothing about him being a soldier and statesman, victor of the Peninsular War, victor of Waterloo, nemesis of Napoleon, twice Prime Minister? Or is the wellington boot reference made simply to get equally thick readers to relate to the story? Who cares about fusty old battles and boring politics? It is all so yesterday, isn’t it? But everyone knows what wellies are, don’t they?
To anyone with a modicum of interest in this country’s past, such ignorance is deeply depressing, to say the least. But I suppose it could be worse. Think what would happen if some Mail Online know-nothing hack was able to interview other historical figures …
“Sir Winston Churchill, tell us how you came up with the idea of a nodding bulldog to promote your insurance company.”
“Napoleon, having invented a popular type of brandy, was it perhaps rather egotistical to name it after yourself?”
“Pablo Picasso, as a car designer you must be thrilled to see your Citroën Grand C4 Picasso being crowned “Best Used MPV” in the Auto Express Used Car Awards 2023.”
The Red Army Overruns Poland! – WW2 – Week 282 – January 20, 1945
World War Two
Published 20 Jan 2024The huge new Soviet offensives charge ahead this week, taking Warsaw and Krakow; in the west the Battle of the Bulge is officially called over … though there is still fighting there. On Luzon, the Americans push out of their beachhead, though there is heavy fighting to secure their flank.
(more…)
Polycules – “Reading about this shit is like watching paint dry. It’s astoundingly sexless.”
One of the first times I encountered the term “polycule” was in joking reference to the pre-prison lifestyle of SBF and his intimate (?) circle and a photo of the seven diverse individuals from the Disney Snow White cast, but as Chris Bray says, it’s suddenly becoming a popular topic in the legacy media:
Sex is a lagging indicator. As the historians John D’Emilio and Estelle Freedman have written, sexual behaviors reflect everything that happens around them: “Political movements that attempt to change sexual ideas and practices seem to flourish when an older system is in disarray and a new one forming.” Radical changes in sexual practices tell you that significant social change is already well advanced, and sex is trying to catch up.
It appears that an older system is in disarray. Polyamory litters the media landscape, suddenly, like a memo went out.
See if you can spot a trend, because the last week has brought big features on polycules and their enthusiasts from New York magazine, the New York Times, and the New York Post. If you live in Brooklyn, have hand sanitizer and a reliable source of Valtrex.
As the Times notes, television and publishing are similarly rushing to join in:
Along with novels, TV shows and movies that depict throuples, polycules and other permutations of open relationships, there is a growing body of nonfiction literature that explores the ethics and logistical hurdles of polyamory. Recent titles include memoirs like the journalist Rachel Krantz’s 2022 book Open: An Uncensored Memoir of Love, Liberation, and Non-Monogamy, and self-help and inspirational books like The Anxious Person’s Guide to Non-Monogamy, The Polyamory Paradox and A Polyamory Devotional, which has 365 daily reflections for the polyamorous.
I’m begging you: read some of this stuff, because you’re not going to believe what I say about it. At least skim the thing in New York; here’s the link again. Here’s a link to the Amazon preview of A Polyamory Devotional, with daily thoughts about mindfulness and relationship structures. Now, armed with evidence, here’s my Big Conclusion:
Reading about this shit is like watching paint dry. It’s astoundingly sexless.
Polyamory turns out to be a front for therapeutic culture and a neurotic love of mirrors. The sexy thing with Alice and Anna and Nick and Sarah involves a lot of checking in and managing expectations and maintaining supportive dialogue. Actual quote from Nick: “Some people like to run marathons. We like to do polyamory, complex relationship stuff. Sarah’s favorite activity for the two of us to do is couples therapy.” You’re jealous of all that heat and pleasure, right? It’s so sexy that it’s like running a marathon. Of talking. With a therapist.
A Book and a Rifle: The Vercors Resistance in WWII
Forgotten Weapons
Published 20 May 2018One of the single largest actions of the French Resistance during World War Two was Operation Montagnards — the plan to drop about 4,000 Allied paratroops onto the Vercors Massif when the resistance was activated in support of the Allied landings in Normandy and Provence. If you are scratching your head trying to figure out why you don’t remember that operation, it is because it never actually happened. The two Allied landings were originally intended to take place simultaneously, but logistical limitations forced the southern landings to be delayed about two months. In an deliberate decision to prevent the Germans from immediately understanding the nature of the Allied attack, the whole of the French Resistance was activated to support the Normandy landings in June 1944. The internal attacks in the south would force the Germans to keep significant forces in that area in expectation of a second landing, which would increase the chances of the Normandy landings succeeding. Unfortunately, the other result of this decision was that Resistance cells would come into the open in anticipation of imminent military support, which would not be coming. The southern elements of the Resistance were basically sacrificed in this gambit.
The Vercors Massif is a large geographical feature near Lyon and Grenoble which comprises basically a triangular sheer-walled plateau rising well above the surrounding plains. It offers a fantastically defensible redoubt, and that is what it was planned to be. Paratroops dropped onto the top of the massif would reinforce a substantial force of Maquis fighters, and create a serious strong point behind the German lines to aid in the fight inland from the landing beaches. The plan was organized in Algiers by Resistance representatives from the Vercors and Free French officers earlier in the war. Some have argued that the lack of support was simply due to the compromises of the single-landing plan, while others fault de Gaulle for deliberately abandoning the men and women on Vercors as part of a strategy to consolidate post-war political support — but that debate is beyond the scope of today’s discussion.
The fighters and civilians on the massif ultimately held out for about 6 weeks — only just too little to still be there when the Allied armored columns reached Grenoble. The German commander in the area spent several weeks making small probing attacks before the final assault with about 10,000 veteran Wehrmacht soldiers, glider-borne infantry, and tanks. Once that attack came, the fate of the Vercors was sealed. With proper military backing they could have defended their redoubt, but instead they had only a smattering of small arms and no heavy weaponry at all. It was a fight that was gloriously courageous but hopelessly doomed to failure.
I am privileged to have in my own collection a Berthier carbine tied to the Vercors Resistance, as evidenced by the brass embellishments on its stock. While I cannot conclusively prove it came from the Resistance, it was sold to me without any premium attached to them, and I have no reason to believe it is fake. And, of course, since I have no plans to sell it, I am not really concerned about conclusively proving its veracity to others. For me, it is a poignant icon of a tremendously heroic group. I hope I would live up to the bar they set should I ever be in a comparable situation!
(more…)
QotD: The life-cycle of bureaucracies
… a large bureaucracy will, in approximately 100 percent of cases, become extremely wasteful, and essentially corrupt. It will perpetuate the “problem” that it was founded to solve, and at its most creative, invent new and quite imaginative evils. It will become a vested interest — an “economic player” in its own right — and spread, like a cancer, well beyond the flesh it first inhabited. Any attempt to restrain it will then engender new bureaucracies. The idea of a “humane” bureaucracy is a contradiction of terms. There is no such thing.
Gentle reader must understand that I am not speaking only of “guvmint”, but of bureaucracy, at large. The thing is not necessarily a government department. Any big corporation will quickly show symptoms. The only difference between “public” and “private” is in longevity. A private bureaucracy will kill its host, but thanks to the power of taxation, a public bureaucracy can be long sustained. It is also backed by law and police action, which even today is more effective than mere pointless rules and regulations. The latter, however, are more nimble in expansion, and prepare the ground for law — the full spiritual stasis.
David Warren, “Austrian schoolboy”, Essays in Idleness, 2019-09-17.
January 20, 2024
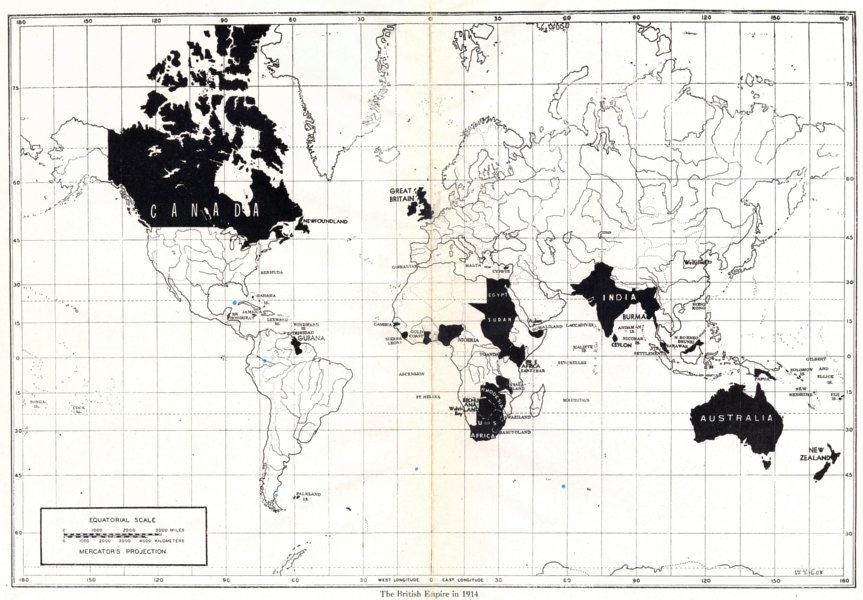
The British Empire would have failed a proper cost-benefit analysis
At the Institute of Economic Affairs, Kristian Niemietz is working on a paper on the economics of empire that, as he shows in this article, indicates that the empire was never a winning economic proposition for Britain as a whole, no matter how well certain well-connected individuals and companies benefitted:
But is it actually true that imperialism makes countries richer? Does imperialism make economic sense?
This question was already hotly debated at the heyday of imperialism. Adam Smith believed that the British Empire would not pass a cost-benefit test:
The pretended purpose of it was to encourage the manufactures, and to increase the commerce of Great Britain. But its real effect has been to raise the rate of mercantile profit, and to enable our merchants to turn into a branch of trade, of which the returns are more slow and distant than those of the greater part of other trades, a greater proportion of their capital than they otherwise would have done […]
Great Britain derives nothing but loss from the dominion which she assumes over her colonies.
He believed that Britain would be better off if it dissolved its Empire:
Great Britain would not only be immediately freed from the whole annual expense of the peace establishment of the colonies, but might settle with them such a treaty of commerce as would effectually secure to her a free trade, more advantageous to the great body of the people, though less so to the merchants, than the monopoly which she at present enjoys.
The liberal free-trade campaigner Richard Cobden agreed:
[O]ur naval force, on the West India station […], amounted to 29 vessels, carrying 474 guns, to protect a commerce just exceeding two millions per annum. This is not all. A considerable military force is kept up in those islands […]
Add to which, our civil expenditure, and the charges at the Colonial Office […]; and we find […] that our whole expenditure, in governing and protecting the trade of those islands, exceeds, considerably, the total amount of their imports of our produce and manufactures.
If imperialism was a loss-making activity – why did Britain and other European colonial empires engage in it for so long?
Smith and Cobden explained it in terms of clientele politics (or Public Choice Economics, as we would say today). Somebody obviously benefited, even if the nation as a whole did not. And the beneficiaries were politically better organised than those who footed the bill.
This proto-Public Choice case against imperialism was not limited to political liberals. Otto von Bismarck, the Minister President of Prussia and future Chancellor of the German Empire, hated liberals in the Smith-Cobden tradition, but he rejected colonialism in terms that almost make him sound like one of them:
The supposed benefits of colonies for the trade and industry of the mother country are, for the most part, illusory. The costs involved in founding, supporting and especially maintaining colonies […] very often exceed the benefits that the mother country derives from them, quite apart from the fact that it is difficult to justify imposing a considerable tax burden on the whole nation for the benefit of individual branches of trade and industry [translation mine].
In his writing about the economics of imperialism, even Michael Parenti, a Marxist-Leninist political scientist (who is, for obvious reasons, popular among Twitter hipsters), sounds almost like a Public Choice economist:
[E]mpires are not losing propositions for everyone. […] [T]he people who reap the benefits are not the same ones who foot the bill. […]
The transnationals monopolize the private returns of empire while carrying little, if any, of the public cost. The expenditures needed […] are paid […] by the taxpayers.
So it was with the British empire in India, the costs of which […] far exceeded what came back into the British treasury. […]
[T]here is nothing irrational about spending three dollars of public money to protect one dollar of private investment – at least not from the perspective of the investors.”
This leads us to a curious situation. Today’s woke progressives disagree with their comrade Parenti on the economics of empire, but they do agree with Britain’s old imperialists, who argued that the Empire was vital for Britain’s prosperity.
Why Tyrian Purple Dye Is So Expensive | So Expensive | Insider Business
Insider Business
Published 21 Jan 2023Making authentic Tyrian purple dye starts with extracting a murex snail gland. After a series of painstaking steps, Tunisian dye maker Mohamed Ghassen Nouira turns as much as 45 kilograms of snails into a single gram of pure Tyrian purple extract. When he’s done, he can sell it for $2,700. Some retailers sell a gram of the pigment for over $3,000. In comparison, 5 grams of synthetic Tyrian purple costs under $4.
So, why is real Tyrian purple so hard to make? And is that why it’s so expensive?
(more…)
QotD: 19th Century techno-optimism
In The Politics of Cultural Despair (a book I recommend, with reservations), Fritz Stern called the writers of the 19th century “conservative revolution” in Germany “intellectual Luddites”. Just as the original Luddites wanted to stop “progress” by breaking machines, so the intellectual Luddites wanted to un-enlighten the Enlightenment, wiping out “Manchesterism” to return to a largely imaginary communitarian, agrarian past. The “machine” the intellectual Luddites sought to break, Stern argues, was reason … or, at least, rationalism, which by the later 19th century was basically the same thing in most people’s minds.
They had a point, those intellectual Luddites. If you haven’t read up on the later 19th century in a while, it’s almost impossible to convey their boundless optimism, their total faith that “science” could, would, and should solve every conceivable problem. The best I can do is this: Back when they were still allowed to be funny, The Onion published a book called Our Dumb Century, which purported to be a collection of their front pages from every year of the 20th century. The headline for 1903 was something like: “Wright Brothers’ Flyer Goes Airborne for 30 Seconds! Conquest of Heaven Planned for 1910.”
That’s the late 19th century, y’all.
Severian, “Digital Infants”, Rotten Chestnuts, 2021-04-16.
January 19, 2024
Music journalism, RIP
Ted Gioia explains why music journalism is collapsing and who committed the murder:
Just a few weeks ago, Bandcamp laid off 58 (out of 120) employees — including about “half of its core editorial staff“.
And Bandcamp was considered a more profitable, stable employer than most media outlets. The parent company before the recent sale (to Songtradr) and subsequent layoffs, Epic Games, will generate almost a billion dollars in income this year — but they clearly don’t want to waste that cash on music journalism.
Why is everybody hating on music writers?
Many people assume it’s just the same story as elsewhere in legacy media. And I’ve written about that myself — predicting that 2024 will see more implosions of this sort.
Sure, that’s part of the story.
But there’s a larger problem with the music economy that nobody wants to talk about. The layoffs aren’t just happening among lowly record reviewers — but everywhere in the music business.
- Universal Music announced layoffs two days ago.
- YouTube announced layoffs yesterday.
- Soundcloud announced last week that the company is up for sale — after two rounds of layoffs during the last 18 months.
- Spotify announced layoffs five weeks ago.
- That same week, Tidal announced layoffs.
- A few weeks earlier, Amazon Music laid off employees on three continents.
Meanwhile, almost every music streaming platform is trying to force through price increases (as predicted here). This is an admission that they don’t expect much growth from new users — so they need to squeeze old ones as hard as possible.
As you can see, the problem is more than just music writers — something is rotten at a deeper level.
What’s the real cause of the crisis? Let’s examine it, step by step:
- The dominant music companies decided that they could live comfortably off old music and passive listeners. Launching new artists was too hard — much better to keep playing the old songs over and over.
- So major labels (and investment groups) started investing huge sums into acquiring old song publishing catalogs.
- Meanwhile streaming platforms encouraged passive listening — so people don’t even know the names of songs or artists.
- The ideal situation was switching listeners to AI-generated tracks, which could be owned by the streaming platform — so no royalties are ever paid to musicians.
- These strategies have worked. Streaming fans don’t pay much attention to new music anymore.
I’ve warned about each of these — but we are now seeing the long-term results.
This is why Pitchfork is in deep trouble. If people don’t listen to new music, they don’t need music reviews.
And they don’t need interviews with rising stars. Or best of year lists. Or any of the other things music writers do for their readers.
But this problem will get much, much worse. Even the people who made these decisions will suffer — because living in the past is never a smart business strategy.
If these execs were albums, they’d deserve a zero score on the Pitchfork scale.
Those passionate Houthi and the Blowfish fans
Chris Selley wonders why the rest of the Canadian legacy media are being so careful to proactively curate and “contextualize” the violent and hateful message of the pro-Hamas and pro-Houthi protesters in our cities:

The Houthi Ansarullah “Al-Sarkha” banner. Arabic text:
الله أكبر (Allah is the greatest)
الموت لأمريكا (death to America)
الموت لإسرائيل (death to Israel)
اللعنة على اليهود (a curse upon the Jews)
النصر للإسلام (victory to Islam)
Image and explanatory text from Wikimedia Commons.
The record will show I had little sympathy for the Ottawa convoy crowd, especially once they had made their point and refused to go away. You can’t occupy the downtown of a G7 capital for a month. Sorry, you just can’t.
At the same time, I cringed at the media’s fevered attempts to cast the entire crowd as neo-Nazi oafs, based on what seems to have been two observed flags — one Confederate, one Nazi.
I recalled this while watching video footage of protesters in Toronto over the weekend chanting “Yemen, Yemen, make us proud! Turn another boat around!” Because the Houthis, who control Yemen’s Red Sea coast and have been waging war on commercial shipping, are about as neo-Nazi as it gets in the world nowadays.
The movement’s official slogan: “Allahu Akbar! Death to America! Death to Israel! Curse the Jews! Victory for Islam!” As if to drive home the point, there is ample video evidence of Houthi fighters chanting that slogan with their hands raised skywards in a Nazi salute.
The Houthis use child soldiers (as video evidence also makes horrifyingly plain). They are literally slavers. I have seen it suggested, by way of context, that they really don’t have that many slaves. Just a few slaves. It’s so hard to get good help.
But I haven’t seen anyone try to “contextualize” the Houthi slogan, the way Palestinian supporters will tell you “from the river to the sea” isn’t a call for Israel’s destruction and cheering for “intifada” doesn’t mean further terrorist attacks against Jews. Perhaps it’s just too big a job for even the most dedicated and creative of apologists.
Outside of the Postmedia empire, so far as I can see, not a single Canadian media outlet has seen fit to mention the chanting in Toronto streets in support of a rabidly antisemitic death cult. You can read several articles, however, about how Canadian media are terribly biased against the Palestinian cause. It’s ludicrous.
A nice little illustration, as the National Post‘s Tristin Hopper noted in November: When the convoy crowd appropriated Terry Fox’s statue, just opposite Parliament Hill, for their “mandate freedom” message, the Laurentian bubble nearly burst with righteous fury. When pro-Palestinian protesters draped a keffiyeh over Fox’s shoulders and had their kids pose with him, there was all but total silence.
Of course, flamboyant media double-standards aren’t the worst of our problems.