I have been using the Internet since 1976. I got involved in its engineering in 1983. Over the years, I’ve influenced the design of the Domain Name System, written a widely-used SMTP transport, helped out with RFCs, and done time on IETF mailing lists. I’ve never been a major name in Internet engineering the way I have been post-1997 in the open-source movement, but I was a respectable minor contributor to the former long before I became famous in the latter. I know the people and the culture that gets the work done; they’re my peers and I am theirs. Which is why I’m going to switch from “them” to “us” and “we” now, and talk about something that really cranks us off.
We’re not thrilled by people who rave endlessly about the wonder of the net. We’re not impressed by brow-furrowing think-pieces about how it ought to written by people who aren’t doing the design and coding to make stuff work. We’d be far happier if pretty much everybody who has ever been described as “digerati” were dropped in a deep hole where they can blabber at each other without inflicting their pompous vacuities on us or the rest of the world.
In our experience, generally the only non-engineers whose net-related speculations are worth listening to are science-fiction writers, and by no means all of those; anybody to whom the label “cyberpunk” has been attached usually deserves to be dropped in that deep hole along with the so-called digerati. We do respect the likes of John Brunner, Vernor Vinge, Neal Stephenson, and Charles Stross, and we’re occasionally inspired by them – but this just emphasizes what an uninspiring lot the non-fiction “serious thinkers” attaching themselves to the Internet usually are.
There are specific recurring kinds of errors in speculative writing about the Internet that we get exceedingly tired of seeing over and over again. One is blindness to problems of scale; another is handwaving about deployment costs; and a third is inability to notice when a proposed cooperative “solution” is ruined by misalignment of incentives. There are others, but these will stand as representative for why we very seldom find any value in the writings of people who talk but don’t build.
We seldom complain about this in public because, really, how would it help? The world seems to be oversupplied with publishers willing to drop money on journalists, communications majors, lawyers, marketers manqué, and other glib riff-raff who have persuaded themselves that they have deep insights about the net. Beneath their verbal razzle-dazzle and coining of pointless neologisms it’s extremely uncommon for such people to think up anything true that hasn’t been old hat to us for decades, but we can’t see how to do anything to dampen the demand for their vaporous musings. So we just sigh and go back to work.
Yes, we have our own shining visions of the Internet future, and if you ask us we might well tell you about them. It’s even fair to say we have a broadly shared vision of that future; design principles like end-to-end, an allergy to systems with single-point failure modes, and a tradition of open source imply that much. But, with a limited exception during crisis periods imposed by external politics, we don’t normally make a lot of public noise about that vision. Because talk is cheap, and we believe we teach the vision best by making it live in what we design and deploy.
Here are some of the principles we live by: An ounce of technical specification beats a pound of manifesto. The superior man underpromises and overperforms. Mechanism outlasts policy. If a picture is worth a thousand words, a pilot deployment is worth a million. The future belongs to those who show up to build it. Shut up and show us the code.
If you can live by these principles too, roll up your sleeves and join us; there’s plenty of work to be done. Otherwise, do everybody a favor and stop with the writing and the speeches. You aren’t special, you aren’t precious, and you aren’t helping.
Eric S. Raymond, “Those who can’t build, talk”, Armed and Dangerous, 2011-07-28.
February 20, 2023
QotD: The early “cyberpunk” writers versus the folks who built the internet
January 15, 2023
QotD: The uncertain “certainties” of war in space
The comments for that post were very active with suggestions for technological or strategic situations which would or would not make orbit-to-land operations (read: planetary invasions) unnecessary or obsolete, which were all quite interesting.
What I found most striking though was a relative confidence in how space battles would be waged in general, which I’ve seen both a little bit here in the comments and frequently more broadly in the hard-sci-fi community. The assumptions run very roughly that, without some form of magic-tech (like shields), space battles would be fought at extreme range, with devastating hyper-accurate weapons against which there could be no real defense, leading to relatively “thin-skinned” spacecraft. Evasion is typically dismissed as a possibility and with it smaller craft (like fighters) with potentially more favorable thrust-to-mass ratios. It’s actually handy for encapsulating this view of space combat that The Expanse essentially reproduces this model.
And, to be clear, I am not suggesting that this vision of future combat is wrong in any particular way. It may be right! But I find the relative confidence with which this model is often offered as more than a little bit misleading. The problem isn’t the model; it’s the false certainty with which it gets presented.
[…]
Coming back around to spaceships: if multiple national navies stocked with dozens of experts with decades of experience and training aren’t fully confident they know what a naval war in 2035 will look like, I find myself with sincere doubts that science fiction writers who are at best amateur engineers and military theorists have a good sense of what warfare in 2350 (much less the Grim Darkness of the Future Where There is Only War) will look like. This isn’t to trash on any given science fiction property mind you. At best, what someone right now can do is essentially game out, flow-chart style, probable fighting systems based on plausible technological systems, understanding that even small changes can radically change the picture. For just one example, consider the question “at what range can one space warship resolve an accurate target solution against another with the stealth systems and electronics warfare available?” Different answers to that question, predicated on different sensor, weapons and electronics warfare capabilities produce wildly different combat systems.
(As an aside: I am sure someone is already dashing down in the comments preparing to write “there is no stealth in space“. To a degree, that is true – the kind of Star Trek-esque cloaking device of complete invisibility is impossible in space, because a ship’s waste heat has to go somewhere and that is going to make the craft detectable. But detectable and detected are not the same: the sky is big, there are lots of sources of electromagnetic radiation in it. There are as yet undiscovered large asteroids in the solar-system; the idea of a ship designed to radiate waste heat away from enemies and pretend to be one more undocumented large rock (or escape notice entirely, since an enemy may not be able to track everything in the sky) long enough to escape detection or close to ideal range doesn’t seem outlandish to me. Likewise, once detected, the idea of a ship using something like chaff to introduce just enough noise into an opponent’s targeting system so that they can’t determine velocity and heading with enough precision to put a hit on target at 100,000 miles away doesn’t seem insane either. Or none of that might work, leading to extreme-range exchanges. Again, the question is all about the interaction of detection, targeting and counter-measure technology, which we can’t really predict at all.)
And that uncertainty attaches to almost every sort of technological interaction. Sensors and targeting against electronics warfare and stealth, but also missiles and projectiles against point-defense and CIWS, or any kind of weapon against armor (there is often an assumption, for instance, that armor is entirely useless against nuclear strikes, which is not the case) and on and on. Layered on top of that is what future technologies will even prove practical – if heat dissipation problems for lasers or capacitor limitations on railguns be solved problems, for instance. If we can’t quite be sure how known technologies will interact in an environment (our own planet’s seas) that we are intimately familiar with, we should be careful expressing confidence about how future technology will work in space. Consequently, while a science fiction setting can certainly generate a plausible model of future space combat, I think the certainty with which those models and their assumptions are sometimes presented is misplaced.
Bret Devereaux, “Fireside Friday: August 14th, 2020”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2020-08-14.
November 16, 2022
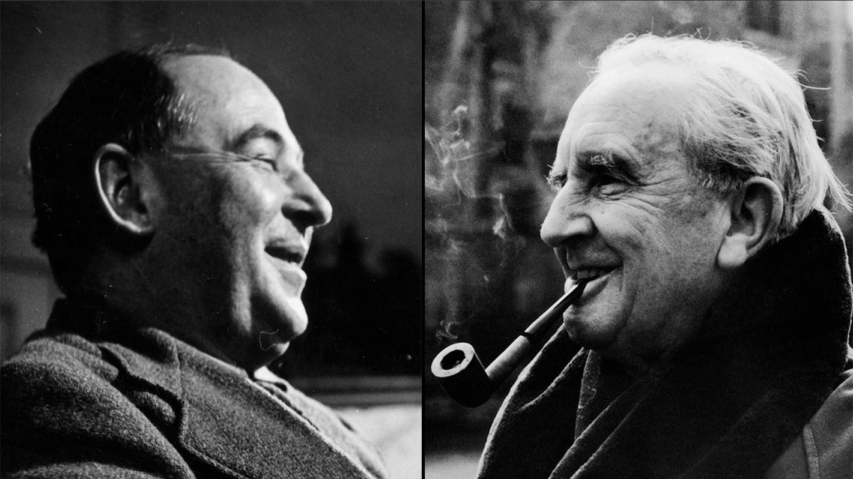
C.S. Lewis and J.R.R. Tolkien … arch-dystopians?
In The Upheaval, N.S. Lyons considers the literary warnings of well-known dystopian writers like Aldous Huxley and George Orwell, but makes the strong case that C.S. Lewis and J.R.R. Tolkien were even more prescient in the warnings their works contain:
Which dystopian writer saw it all coming? Of all the famous authors of the 20th century who crafted worlds meant as warnings, who has proved most prophetic about the afflictions of the 21st? George Orwell? Aldous Huxley? Kurt Vonnegut? Ray Bradbury? Each of these, among others, have proved far too disturbingly prescient about many aspects of our present, as far as I’m concerned. But it could be that none of them were quite as far-sighted as the fairytale spinners.
C.S. Lewis and J.R.R. Tolkien, fast friends and fellow members of the Inklings – the famous club of pioneering fantasy writers at Oxford in the 1930s and 40s – are not typically thought of as “dystopian” authors. They certainly never claimed the title. After all, they wrote tales of fantastical adventure, heroism, and mythology that have delighted children and adults ever since, not prophecies of boots stamping on human faces forever. And yet, their stories and non-fiction essays contain warnings that might have struck more surely to the heart of our emerging 21st century dystopia than any other.
The disenchantment and demoralization of a world produced by the foolishly blinkered “debunkers” of the intelligentsia; the catastrophic corruption of genuine education; the inevitable collapse of dominating ideologies of pure materialist rationalism and progress into pure subjectivity and nihilism; the inherent connection between the loss of any objective value and the emergence of a perverse techno-state obsessively seeking first total control over humanity and then in the end the final abolition of humanity itself … Tolkien and Lewis foresaw all of the darkest winds that now gather in growing intensity today.
But ultimately the shared strength of both authors may have also been something even more straightforward: a willingness to speak plainly and openly about the existence and nature of evil. Mankind, they saw, could not resist opening the door to the dark, even with the best of intentions. And so they offered up a way to resist it.
Subjectivism’s Insidious Seeds
The practical result of education in the spirit of The Green Book must be the destruction of the society which accepts it.
When Lewis delivered this line in a series of February 1943 lectures that would later be published as his short book The Abolition of Man, it must have sounded rather ridiculous. Britain was literally in a war for its survival, its cities being bombed and its soldiers killed in a great struggle with Hitler’s Germany, and Lewis was trying to sound the air-raid siren over an education textbook.
But Lewis was urgent about the danger coming down the road, a menace he saw as just as threatening as Nazism, and in fact deeply intertwined with it, give that:
The process which, if not checked, will abolish Man goes on apace among Communists and Democrats no less than among Fascists. The methods may (at first) differ in brutality. But many a mild-eyed scientists in pince-nez, many a popular dramatist, many an amateur philosopher in our midst, means in the long run just the same as the Nazi rulers of Germany. Traditional values are to be “debunked” and mankind to be cut into some fresh shape at will (which must, by hypothesis, be an arbitrary will) of some few lucky people …
Unfortunately, as Lewis would later lament, Abolition was “almost totally ignored by the public” at the time. But now that our society seems to be truly well along in the process of self-destruction kicked off by “education in the spirit of The Green Book“, it might be about time we all grasped what he was trying to warn us about.
This “Green Book” that Lewis viewed as such a symbol of menace was his polite pseudonym for a fashionable contemporary English textbook actually titled The Control of Language. This textbook was itself a popularization for children of the trendy new post-modern philosophy of Logical Positivism, as advanced in another book, I.A. Richards’ Principles of Literary Criticism. Logical Positivism saw itself as championing purely objective scientific knowledge, and was determined to prove that all metaphysical priors were not only false but wholly meaningless. In truth, however, it was as Lewis quickly realized actually a philosophy of pure subjectivism – and thus, as we shall see, a sure path straight out into “the complete void”.
In Abolition, Lewis zeros in on one seemingly innocuous passage in The Control of Language to begin illustrating this point. It relates a story told by the English poet Samuel Taylor Coleridge, in which two tourists visit a majestic waterfall. Gazing upon it, one calls it “sublime”. The other says, “Yes, it is pretty.” Coleridge is disgusted by the latter. But, as Lewis recounts, of this story the authors of the textbook merely conclude:
When the man said This is sublime, he appeared to be making a remark about the waterfall … Actually … he was not making a remark about the waterfall, but a remark about his own feelings. What he was saying was really I have feelings associated in my mind with the word “sublime”, or shortly, I have sublime feelings … This confusion is continually present in language as we use it. We appear to be saying something very important about something: and actually we are only saying something about our own feelings.
For Lewis, this “momentous little paragraph” contains all the seeds necessary for the destruction of humanity.
May 8, 2022
April 12, 2022
QotD: Writers are like otters
Tor editor Teresa Nielsen Hayden had a wonderful rant some years back. She had been talking to an animal trainer, who explained to her why otters were untrainable. Other animals, it seemed, when given their food reward or whatever by their human handler, would seem to think, “Great, he liked it! I’ll do that again!” Otters, by contrast, would seem to think, “Great, he liked it! Now I’ll do something else that’s even cooler!” Writers, Teresa concluded in a moment of Zen enlightenment, were otters. At least from an editor’s point of view.
When I boot up a new book in my brain, I am not greatly interested in what has and hasn’t won awards. I want to write something else that’s even cooler.
Lois McMaster Bujold, interview at Blogcritics, 2005-05-24.
April 6, 2022
Where To Start With Terry Pratchett (And The Debt That I Owe Him)
Mark Stay
Published 6 Nov 2020New to Terry Pratchett? Which book should you read first? I’ve been reading Terry’s books for over 30 years and will give you a quick guided tour of the best places to start with Terry and the Discworld. I also acknowledge the influence of Terry’s writing on my own work and my new book The Crow Folk.
Discover my Witches of Woodville series here: https://witchesofwoodville.com/#bookshop
My blog is here: https://markstaywrites.com
I’m co-presenter of the Bestseller Experiment podcast: https://bestsellerexperiment.com/podc…
March 23, 2022
QotD: Fansplaining that feudalism is bad
One that continues to baffle me is the indefatigable enthusiasm of some fans for explaining to others that Barrayaran neo-feudalism is a terrible system of government, as if their fellow readers couldn’t figure that out for themselves. It seems to rest on an a-historical understanding, or simply a lack of understanding, of feudalism, a system that died out in our world five hundred years ago, to be replaced by geographically based national states. (Well, four hundred years ago, in Japan.) From the passion these readers bring to the table, one would gather they imagine insidious card-carrying Feudalists are dire threat to the lifeblood of our nation. I’m not sure I should tell them about the SCA.
Portrayal is not promulgation, people.
That said, I’ve spent thirty years learning that no writer, be they ever so clear and plain, can control how readers read, or misread, their texts. Reading is a dance, not a march. If some readers step on one’s feet, well, it’s still better than sitting by the wall … Usually.
Lois McMaster Bujold, “Lois McMaster Bujold on Fanzines, Cover Art, and the Best Vorkosigan Planet”, Tor.com, 2017-11-02.
January 1, 2022
QotD: Heinlein’s “Crazy Years”, Alfred Korzybski’s General Semantics, and modern times
While Heinlein (as far as I know) supplied no rationale for the advent and the recession of the craziness in the Crazy Years, A.E. van Vogt was freer with his speculations: insanity, either of individuals or of peoples, in van Vogt’s stories (and perhaps in the theories of Alfred Korzybski, who discovered or invented General Semantics) is caused by a fracture or disjunction between symbol and object. When your thoughts, and the thing about which you think, do not match up on a cognitive level, that is a falsehood, a false belief. When the emotions associated with the thought do not match to the thing about which you think, that is a false-to-facts association, which can range from merely a mistake to neurosis to psychosis, depending on the severity of the disjunction. You are crazy. If you hate your sister because she reminds you of your mother who beat you, that association is false-to-facts, neurotic. If you hate your sister because you have hallucinated that you are Cinderella, that association is falser-to-facts, more removed from reality, possibly psychotic.
The great and dire events of the early Twentieth Century no doubt confirmed Korzybski in the rightness of this theory. Nothing prevents a race of people from contracting and fomenting a false-to-facts belief: the fantasies of the Nazi Germans, pseudo-biology and pseudo-economics combined with the romance of neo-paganism, stirred the psyche of the German people for quite understandable reasons. From the point of view of General Semantics, the Germans had divorced their symbols from reality, they mistook metaphors for truth, and their emotions adapted to and reinforced the prevailing narrative. They told themselves stories about Wotan and the Blood, about being betrayed during the Great War, about needing room to live, about the wickedness of Jewish bankers and shopkeepers, about the origin of the wealth of nations — and they went crazy.
The Russians, earlier, and for equally psychological and psychopathic reasons told themselves a more coherent but more unreal story about history and destiny, taken from a Millenarian cultist named Marx, and they were, on an emotional level even if not on a cognitive level, convinced that shedding the blood of millions would bring about wealth as if from nowhere. And, because they used the word “scientific” to describe their brand of socialism, they actually thought their play-pretend neurotic story was a scientific theory that had been discovered by rigorous ratiocination — and they went crazy.
Berlin was bombed into submission during the Second World War, and the Berlin Wall collapsed along with the Soviet Empire at the end of the Cold War. But the modern methods of erecting false-to-facts dramas appealing to mass psychology, once discovered, did not fall when their practitioners fell: scientific socialism, naziism, fascism, communism, all have in common the subordination of word-association to political will. All these doctrines have a common ancestor, which is the social engineering theory of language: if you change the connotation of word, so the theory runs, you change the connotations of thoughts. General Semantics says that if an individual, or whole people en mass, adopt deliberately false beliefs, supported by deliberately manipulative word-uses, he or they will have increasingly unrealistic and maladaptive behaviors. Introduce Political Correctness, ignore factual correctness, and the people will go crazy.
The main sign of when madness has possessed a crowd, or a civilization, is when the people are fearful of imaginary or trivial dangers but nonchalant about real and deep dangers. When that happens, there is gradual deterioration of mores, orientation, and social institutions — the Crazy Years have arrived.
John C. Wright, “The Crazy Years and their Empty Moral Vocabulary”, John C. Wright, 2019-02-18.
November 30, 2021
QotD: Getting to dystopia
I’d like to pick up on that first thought of mine: When I was a kid and watched sci-fi movies set in a futuristic dystopia where dehumanized individuals are mere chattels of an unseen all-powerful machine policed by commissars in identikit variety-show tinfoil suits in a land where technology has advanced but liberty has retreated, I always found the caper less interesting than the unseen backstory: How did they get there from here? And […] we’re now in the getting-there-from-here phase.
Things are changing very fast. And, if we don’t fully understand why they’re changing and where they’re heading, we’re going to end up in one of those dehumanized dystopias — and very soon.
Mark Steyn, “Live Around the Planet: Tuesday January 22nd”, Steyn Online, 2019-01-22.
November 16, 2021
QotD: Writing SF and fantasy
Science fiction and fantasy are the only genres in which a series can be defined by the universe in which it is set, which, when you think about it, gives a vast lot of creative elbow-room, potentially.
Lois McMaster Bujold, interview at Blogcritics, 2005-05-24.
November 5, 2021
The New York Times identifies the next big threat to humanity – “Muskism”
In Thursday’s NP Platformed newsletter, Colby Cosh outlines the “evidence” amassed in a recent New York Times essay blaming Elon Musk for, well, everything:
Lepore commences by describing Bill Gates’s 66th birthday party, for which a bunch of rich people — including Amazon’s Jeff Bezos — were helicoptered to a private beach from a nearby yacht. Neither Elon Musk, thought to be the world’s richest person, or Mark Zuckerberg, founder of newly rebranded Facebook, were present at the party. Zuckerberg was busy illuminating plans for his “metaverse”, which Lepore describes as “a virtual reality,” wherein you wear “a headset and gear that closes out the actual world.”
Here’s where Lepore goes from this: “The metaverse is at once an illustration of and a distraction from a broader and more troubling turn in the history of capitalism. The world’s techno-billionaires are forging a new kind of capitalism: Muskism.”
In literally the next sentence, Lepore admits that the subject of her essay, Elon Musk, immediately and publicly made fun of the Facebook “metaverse” plans. We are on the third paragraph of the essay, and Lepore has already: a) blamed Elon Musk for an A-hole billionaire party he didn’t attend, because he was busy with his engineering and manufacturing projects; and b) applied the new coinage “Muskism” to a virtual reality project that actual Musk loudly criticized. Somehow this essay has severed its own hydrocephalic head twice over, within 500 words.
It gets worse from there as Lepore attempts to complete her mission of denouncing Muskism, which she describes as an “extreme extraterrestrial capitalism.” She quickly has to admit that Bill Gates, who is mostly spending a computing fortune on global philanthropy these days when he’s not lifting off from yachts in choppers, doesn’t have one single freaking thing to do with absolutely any of this. NP Platformed was an editor back in the day, so we notice that the intro of Lepore’s essay is at this point not only detached from its body, but has been left to rot several miles away. Gates-Musk-Bezos-Zuckerberg: they’re all tentacles of the same menacing Muskist octopus here, as in so much newspaper and magazine commentary, and abuse flung in their general direction will suffice to condemn all.
Lepore’s accusation against Musk turns out to be … that he likes some classic science fiction but doesn’t always concur with the politics of its authors. Musk has called himself a “utopian anarchist of the kind best described by Iain Banks,” but Banks was “an avowed socialist.” Gasp! Banks (1954-2013), the Scottish science fiction author best known for the Culture series, was a particular kind of U.K. “libertarian socialist” who believed strongly in spacefaring as a step toward post-scarcity life for sentient beings. His politics are easily misunderstood by Americans, who don’t have this particular kind of weirdo, and the interstellar “Culture” he envisioned was never intended to be admired unironically. In other words, that part of Lepore’s essay is as mangled and obtuse as the rest.
October 31, 2021
QotD: We’re still trapped in Heinlein’s “Crazy Years”
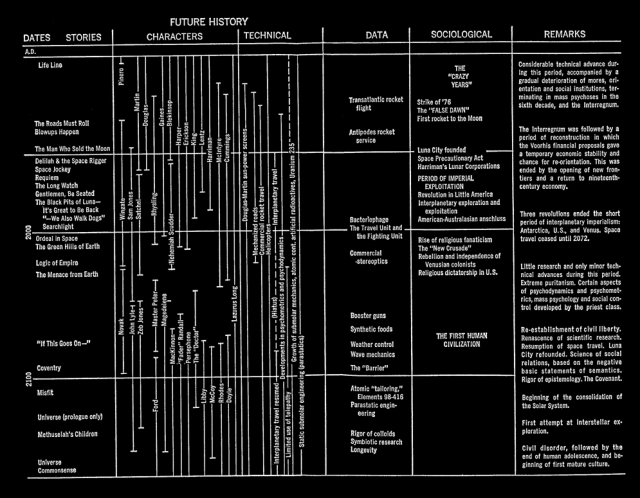
In Robert Heinlein’s famed “Future History” he constructed an elaborate timeline of thing to come, to provide a structure for his short stories.
Looking forward from the year 1940, when the timeline was first formed, it was reasonable, even conservative, guesswork to predict the moon landing by the 1980’s, forty years later, since the first powered flight by the Wright Brothers had been forty years earlier. Heinlein’s Luna City founded in 1990 a decade or so later, with colonies on Mars and Venus by 2000. Compare: a submersible ironclad was written up as a science romance by Jules Verne in 1869, based on the steam-powered “diving boat” of Robert Fulton, developed in 1801. In 1954 the first atomic-powered submarines — all three boats were named Nautilus — put to sea. The gap between Verne’s dream and Rickover’s reality was eight decades, about the time separating Heinlein’s writing of “Menace from Earth” and its projected date.
Looking back from the year 2010, however the dates seem remarkably optimistic and compressed. We have not even mounted a manned expedition to Mars as yet, and no return manned trips to the Moon are on the drawing boards.
One prediction that was remarkably prescient, however, was the advent of “The Crazy Years” described as “Considerable technical advance during this period, accompanied by a gradual deterioration of mores, orientation, and social institutions, terminating in mass psychoses in the sixth decade, and the interregnum.”
He optimistically predicts a recovery from the Crazy Years, the opening of a new frontier in space, and a return to nineteenth-century economy. Full maturity of the human race is achieved by a science of social relations “based on the negative basic statements of semantics.” Those of you who are A.E. van Vogt fans will recognize our old friends, general semantics and Null-A logic cropping up here. Van Vogt, like Heinlein, told tales of a future time when the Non-Aristotlean logic or “Null-A” training would give rise to a race of supermen, fully integrated and fully mature human beings, free of barbarism and neuroses.
Here is the chart [full size version here]. Note the REMARKS column to the right.
What Heinlein failed to predict was that the Crazy Years would simply continue up through 2010, with no sign of slackening. Ladies and gentlemen, we live in the Crazy Years.
John C. Wright, “The Crazy Years and their Empty Moral Vocabulary”, John C. Wright, 2019-02-18.
September 29, 2021
QotD: Lizard people
Many years ago I read a penetrating analysis of UFOlogy arguing that the reports of people who believed themselves UFO contactees or witnesses were expressing the same sorts of psychological drama that in past centuries would gave been coded as religious experiences – eruptions of nigh-incomprehensible powers into the mundane world.
In this telling, to understand UFO reports and the weird little subculture that has grown up around their believers, you need to understand that for those people the imagery of the cheesiest sort of B-movie science fiction has taken up the same receptors in their minds that religious mythology does for the conventionally devout. What they are really grappling with is mystical experience – altered states of consciousness, mindstorms that are very real phenomena in themselves but one which they lack any context to understand in a rational and generative way.
When I remembered this, I found a fruitful question to ask. That is, what is it about their experience of reality that believers in lizard people are coding in this cheesy SFnal imagery? What are they actually trying to talk about?
The answer came to me almost immediately once I managed to formulate the question. That was the moment at which I realized that, barring one unimportant detail, lizard-people theory is actually true.
The unimportant detail is the part about the lizard people being actual extraterrestrials. But let’s look at the rest of it. The believer says: Our elites behave as though they are heavily infiltrated by beings hostile to the interests of ordinary humans. They hide behind a mask of humanity but they have alien minds. They are predators and exploiters, cunning at hiding their nature – but sometimes the mask slips.
Nothing about this is in any way wrong, once you realize that “lizard” is code for “sociopath”. Sociopaths do, differentially, seek power over others, and are rather good at getting it. The few studies that have dared to look have found they are concentrated in political and business elites where drive and ruthlessness are rewarded.
“Lizard” is actually a rather clever code, if you happen to know your evolutionary neuroanatomy. Oversimplifying a little, humans have an exceptionally elaborate neocortex wrapped around a monkey brain wrapped around a lizard brain. The neocortex does what we are pleased to consider higher cognitive functions, the monkey brain does emotions and social behavior, and the lizard brain does territoriality/aggression/dominance.
What is wrong with sociopaths (and psychopaths – these categories are not clearly distinguished) is not entirely clear, but it is certain that their ability to experience emotions is damaged. The monkey brain is compromised; sociopaths live more in their lizard brain and display a lizard-like ability to go from flat affect to aggressive violence and back again in two blinks of an eye.
So, yeah, aliens. We have a live conspiracy theory because a lot of people can sense the alienness in their sociopathic/psychopathic bosses and politicians – and sometimes the mask slips. Not having any grasp of the language of abnormal psychology, they reach for the nearest metaphor handy. There’s a close relative of lizard-people theory in which which many of our elites are held to be members of an ancient Satanic conspiracy and have become demon-ridden; this is different language carrying the same freight.
Eric S. Raymond, “The reality of the lizard people”, Armed and Dangerous, 2020-02-15.
September 12, 2021
Terry Pratchett: Discworld And Beyond
September 7, 2021
L. Neil Smith, 12 May 1946 – 27 August 2021
From what might be the penultimate issue of the Libertarian Enterprise, Neil’s daughter Rylla Smith says farewell to her father:
Lester Neil Smith III, novelist and political commentator, gunsmith and musician, visionary and futurist, passed away on Friday, August 27th at Poudre Valley Hospital after a lengthy battle with heart and kidney disease. He was 75 years old.
A long-time resident of Fort Collins, Colorado, Neil was born on May 12th, 1946 at Mercy Hospital in Denver, Colorado to Maj. Lester N. Smith II and Marie L. Coveleskie Smith.
Neil, known in the world of science fiction as L. Neil Smith or, affectionately, “El Neil”, is survived by his beloved wife, Cathy L.Z. Smith, his daughter, Rylla C. Smith, his brother Roger L. Smith, his nephews Nolan and Travis, and his aunt, Barbara Ohlwiler, as well as countless friends and brothers-in-arms. He was preceded in death by his mother and father.
Neil’s life was one spent perpetually looking forward — toward the future of freedom, of technology, of the continuation of the evolution of the human body, mind, and spirit, and toward the endless sea of stars. As a child, he wanted to be a marine biologist, to discover the unknown in the depths of the seas; this translated naturally in his young adulthood to a thirst for knowledge of the far greater unknown beyond the shores of this world.
Neil had an avid interest in the politics of personal liberty and always stood for what he believed to be right. He had a passion for friendly debate and never shied away from speaking his mind.
In the late 1970s, he wrote the first of his many novels, The Probability Broach, which began a long and prolific career in the burgeoning world of liberty-oriented science fiction, and was the creator of the Prometheus Award, as well as the recipient of the 2016 Special Prometheus Award for Lifetime Achievement.
Memorial services will be held in Fort Collins, Colorado on a date yet to be determined; for more information, please follow Neil’s memorial page on EverLoved.com or contact Rylla Smith at ryllacat@gmail.com.
“And yet, what is bravery but the capacity to reject our fears, ignore and supress them, then go on to do whatever it is we are afraid to do.” — L. Neil Smith