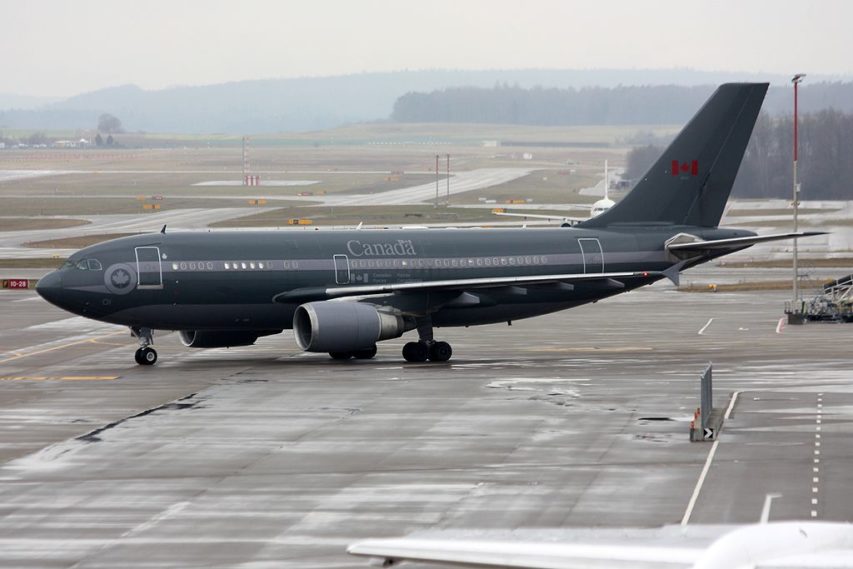
Tristin Hopper rounds up some of the eye-opening details of the security breach at Winnipeg’s National Microbiology Lab which certainly looks like a factor in the Wuhan Coronavirus pandemic story:
Whether or not COVID-19 started as an accidental lab leak, the pandemic just so happens to have originated in the same neighbourhood as the Wuhan Institute of Virology, home to a coronavirus laboratory with a known history of lax security protocols.
For that reason alone it’s a major scandal that Canada’s own high-security biolab was employing two scientists – married couple Xiangguo Qiu and Keding Cheng – who according to CSIS exhibited a reckless disregard of lab security and the protection of confidential information. Now, tack on the fact that both Cheng and Qiu are suspected of prolonged unauthorized contact with the Chinese government.
This week, Health Canada bowed to opposition pressure and published an illuminating package of more than 600 official documents detailing CSIS’s evidence against the couple, as well as internal emails from the Winnipeg-based National Microbiology Laboratory where they worked. The highlights are below.
The lab is surprisingly casual about shipping planet-altering pathogens
One of the main accusations against Qiu is that she sent lab samples to China, the U.S. and the U.K. without proper authorization. Around this same time, she also sent highly virulent Ebola samples to the Wuhan Institute of Virology.
[…]
Cheng was accused of breaking virtually every cyber-security law in the book
If Qiu’s signature offence was sending out lab materials without proper authorization, Cheng’s was that he routinely ignored even the most basic protocols about computer security.
[…]
Throughout, both were in constant (unauthorized) touch with China
The CSIS reports don’t necessarily frame Qiu and Cheng as traitors.
[…]
The pair kept changing their story after being presented with smoking gun evidence, according to CSIS
Some of the documents’ more cinematic passages are when CSIS agents describe lengthy interrogations in which the pair were confronted about their alleged breaches of Canadian national security.