Politicians in particular have a problem – in good times, people vote for them, and in tough times … not so much.
The temptation is to delay the tough times until your successor can carry the can.
Poor old Keynes inadvertently gave politicians the answer they were looking for – the idea that during the downturn, the government should spend money into the economy to keep it going along nicely. Making sure that those lifeguards sacked from the Skegness lido can swiftly get jobs working at a government Skegness lido prevents them claiming the dole, and keeps them in the economy earning and spending until the economy washes out all the malinvestment and starts growing again. At which point the government Skegness lido closes and the lifeguards go to work at a lido somewhere where the biting Easterly wind doesn’t sandblast your skin off. The government has bridged the gap.
There’s one problem.
The government has no money of its own, so where will it get the money for their lido?
Well, Keynes said it should run a surplus during the good times and stash that surplus money away so it can be used during the downturn – a national rainy-day fund, if you will.
But guess what? Politicians don’t run surpluses.
Why would they? Every penny spent making lives better for voters today makes it more likely they will vote for you. And every penny saved against a rainy day makes it possible for your rivals to win votes tomorrow, by doing the same once they are in power.
So politicians don’t ever HAVE a rainy day fund. But that doesn’t stop them wanting to bridge the gap.
So they borrow the money.
And now what they are doing is not Keynesian, or even neo-Keynesian, but pseudo-Keynesian
By bridging the current gap with borrowed money, they simply make sure that the next gap will be costlier to bridge. Because the interest on the borrowing means that the gap will be wider.
But that’s not even the biggest problem – the biggest problem is that the gap is intrinsically important. We NEED it, to give us pause.
Whereas bridging it enables us to carry on being silly and prevents the misallocations from being flushed out – a lido remains operating in Skegness despite having no customers, and the lifeguards continue to work. Their lifesaving skills (which should be fruitfully employed elsewhere) stagnate at a lido with no punters. Their customer service skills deteriorate as the customers disappear, and what they learn instead is how to sit in a chair and stare into space. Their skills are degrading. Hysteresis, technically.
And so by delaying the collapse of the Skegness lido in pursuit of benign conditions for the voters, the government destroys the skills of our workforce.
Sowell was right – the problems we battle today were caused by the government’s interventions yesterday.
Surely using government to solve our problems is like a man quenching his thirst with seawater?
Alex Noble, “Drinking Brine”, Continental Telegraph, 2019-06-14.
February 28, 2023
QotD: Politicians respond to different economic incentives than the rest of us
September 17, 2022
In the wake of the Russo-Ukrainian war, Europe’s cold winter looms ahead
Andrew Sullivan allows his views on the fighting in Ukraine to be a bit more optimistic after Ukrainian gains in the most recent counter-attacks on Russian-held territory around Kharkiv:
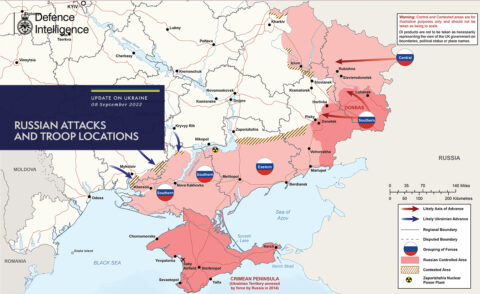
Approximate front-line positions just before the Ukrainian counter-attack east of Kharkiv in early September 2022. The MOD appears to have stopped posting these daily map updates sometime in the last month or so (this is the most recent as of Friday afternoon).
As we were going to press last week — I still don’t know a better web-era phrase for that process — Ukraine mounted its long-awaited initiative to break the military stalemate that had set in after Russia’s initial defeat in attempting a full-scale invasion. The Kharkiv advance was far more successful than anyone seems to have expected, including the Ukrainians. You’ve seen the maps of regained territory, but the psychological impact is surely more profound. Russian morale is in the toilet — and if it seems a bit premature to say that Ukraine will soon “win” the war, it’s harder and harder to see how Russia doesn’t lose it. By any measure, this is a wonderful development — made possible by Ukrainian courage and Western arms.
Does this change my gloomy assessment of Putin’s economic war on Europe, which will gain momentum as the winter drags on? Yes and no. Yes, it will help shore up nervous European governments who can now point to Ukraine’s success to justify the coming energy-driven recession. No, it will not make that recession any less intense or destabilizing. It may make it worse, as Putin lashes out.
More to the point, the Kharkiv euphoria will not last forever. September is not next February. Russia still has plenty of ammunition to throw Ukraine’s way (even if it has to scrounge some from North Korea); it is still occupying close to a fifth of the country; still enjoying record oil revenues; has yet to fully mobilize for a war; and still has China and much of the developing world in (very tepid) acquiescence. Putin is very much at bay. But he is not finished.
Europe’s scramble to prevent mass suffering this winter is made up of beefing up reserves (now 84 percent full, ahead of schedule), energy rationing, government pledges to cut gas and electricity use, nationalization of gas companies, and billions in aid to consumers and industry, with some of the money recouped by windfall taxes on energy suppliers. The record recently is cause for optimism:
The Swedish energy company Vattenfall AB said industrial demand for gas in France, the U.K., the Netherlands, Belgium and Italy is down about 15% annually.
But the use of gas by households is trivial in the summer in Europe compared with the winter — and subsidizing the cost doesn’t help conservation. Russia will now cut off all gas — which could send an economy like Italy’s to contract more than 5 percent in one year. There really is no way out of imminent, deep economic distress across the continent. Even countries with minimal dependence on Russia, like Britain, are locked into an energy market with soaring costs.
That will, in turn, strengthen some of the populist-right parties — see Italy and Sweden. The good news is that the new right in Sweden backs NATO, and Italy’s post-liberal darling, Georgia Meloni, who once stanned Putin, “now calls [him] an anti-Western aggressor and said she would ‘totally’ continue to send offensive arms to Ukraine”. The growing evidence of the Russian army’s war crimes — another mass grave was just discovered in Izyum — makes appeasement ever more morally repellent.
So what will Putin do now? That is the question. His military is incapable of recapturing lost territory anytime soon; he is desperate for allies; and mobilizing the entire country carries huge political risks. It’s striking to me that in a new piece, Aleksandr Dugin, the Russian right’s guru, is both apoplectic about the war’s direction and yet still rules out mass conscription:
Mobilization is inevitable. War affects everyone and everything, but mobilization does not mean forcibly sending conscripts to the front, this can be avoided, for example, by forming a fully-fledged volunteer movement, with the necessary benefits and state support. We must focus on veterans and special support for the Novorossian warriors.
This is weak sauce — especially given Dugin’s view that the West is bent on “a war of annihilation against us — the third world war”. It’s that scenario that could lead to a real and potentially catastrophic escalation — which may be why the German Chancellor remains leery of sending more tanks to Ukraine. The danger is a desperate Putin doing something, well, desperate.
I have no particular insight into intra-Russian arguments over mobilization, but there seems to be zero point (other than for propaganda … and that cuts both ways) to instituting a “Great Patriotic War”-style mass conscription drive at this point. The Russian army could absolutely be boosted to vast numbers through conscription. Vast numbers of untrained, unwilling young people with little military training and no particular passion to save the Rodina this time, despite constant regime callbacks to desperate struggle against Hitler in 1941-45. Pushing under- or untrained troops into battle against a Ukrainian army equipped with relatively modern western weaponry would be little more than deliberate slaughter and I can’t believe even Putin would be that reckless.
September 8, 2022
July 27, 2022
Baghdad Biden speaks
Chris Bray recounts the story of a local government attempting and — for a while — succeeding with the Baghdad Bob blanket denial strategy:
In the Deep Blue suburban town where I live, our city government has been stumbling through a series of crises. For a couple of years, employees fled from City Hall like the building was on fire, and nowhere was the crisis more acute than in the finance department — where we had five directors in a little over two years, and lost most of the other staff, including one who sued the city over her departure. There was a year when we couldn’t pass a budget, because the budget proposal was such a shambles, and a discussion at a meeting of an advisory commission in which a commissioner asked one of the many finance directors if the numbers in the city’s bank accounts matched the numbers in the city ledger. (Try to guess the answer.)
Recently, an ad hoc committee of local citizens — all finance professionals — wrote a report on the period of crisis, and presented our city council with a recommendation that they hire someone to do a forensic audit of the city’s accounting during those years. The council scheduled the report as a “receive and file” item, placing it on a 28-item agenda as, you’ll never guess, item #28. Then, in a brief discussion that began after midnight, they said that the report was nonsense and hearsay. The end.
So, yes, there was no financial crisis in our city during the years when we had five finance directors, when “permanent” finance directors left after a few months, when we lost most of the finance department staff, when we couldn’t pass a budget, and when we had no idea how much money we were actually supposed to have in the bank. Our city council says so. “These are not the ‘droids you are looking for.”
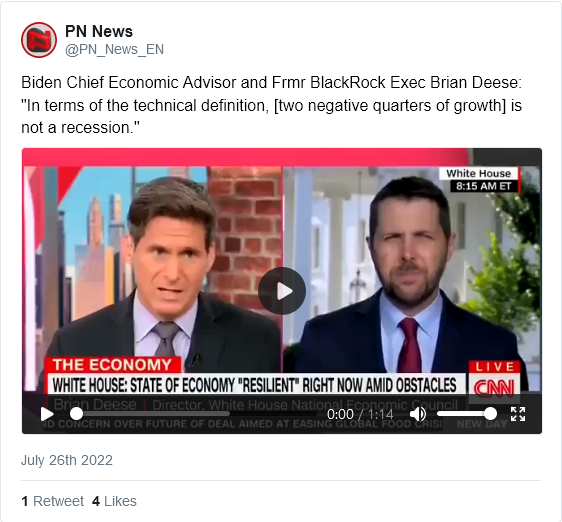
Meanwhile, we’re not in a recession, or even facing the risk of a recession, because that’s not Joe Biden’s view, and because the technical definition of a recession is very complicated.
Also, the inflation of 2021 was transitory. Zipped right by! Also, Joe Biden has a plan to shut down the virus.
The war in Ukraine is SHUT UP SHUT UP SHUT UP, the economy is SHUT UP SHUT UP SHUT UP, the continuing Covid-19 “emergency” is SHUT UP SHUT UP SHUT UP, and the mRNA injections are REALLY REALLY SHUT UP. Actually, the way experts measure this is really complicated, and technically …
March 31, 2022
QotD: Nixon’s 1971 gamble to win re-election also tanked the economy for a full decade
[In 1971, economist Herb] Stein was saying aloud what they all knew. Prettifying a political grab by dressing it as an economic rescue was precisely the kind of action against which eminences like Burns warned foreign governments when they made grand speeches abroad. Nixon was indeed now preparing to do what Harold Wilson had done in 1967: disingenuously pretend that devaluing a currency would not affect the consumer. Stimulating the economy in this way might win Nixon the election, but inflation would eventually explode, as Friedman sometimes said, like a closed pot over high heat. Wage and price controls and taxes on imports could make the kind of growth America was accustomed to, the old bonanza, disappear for years, even a decade. True scarcity of key goods might suddenly become the rule. And that was true no matter how many times that cowboy Connally went around bragging about tariffs and telling others that America was “the strongest economy on earth”.
[…]
The 1971 run on American gold also, however, reflected foreigners’ insight. Outsiders knew a tipping point when they saw one. America had moved closer to Michael Harrington’s socialism than even Harrington understood. The United States had locked itself into social spending promises that might never be outgrown. Today, interest in Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies serves as a measure of markets’ and individuals’ distrust of the U.S. dollar. In those days there was no Bitcoin, but gold played a similar role. The dollar was the common stock of America, and foreigners used gold to short it.
The disastrous performance of the U.S. economy in the following years proved the foreigners’ 1971 wager correct. To pay for its Great Society commitments, the U.S. government in the next decade found itself forced to set taxes so high that it further suppressed the commercialization of innovation. Products that could have been developed from patents awarded in the 1960s remained on the researchers’ shelves. Today we assume all markets will rebound given a decade. But there was to be no 1970s rebound for the Dow Jones Average. The Dow flirted with the 1,000 level throughout the decade, but did not cross the line definitively until 1982, an astonishingly long period to stagnate, nearly a generation. While markets languished, unemployment for all Americans rose. High prices, high interest rates, and federal budget deficits plagued the nation. “Guns and butter” had proved too expensive, but so indeed had butter alone. The 1960s commitments required spending that, then and down the decades, would be far greater than for Vietnam or most other wars. Those on the far left who had originally pushed for aggressive public-sector expansion had achieved what they sought, to subordinate the private sector. In 1977, Harrington actually titled a new book The Twilight of Capitalism.
Those who had counted on the private sector to sustain prosperity saw they had expected too much. The nation’s confidence evaporated. Indeed, by the late 1970s, President Jimmy Carter felt the need to undertake a national campaign to restore confidence, the kind of campaign Franklin Roosevelt had launched in response to the Great Depression. From being a nation that could afford everything, America morphed into a country that could afford nothing, a place where the president warned citizens to set their living room thermostats to sixty-five in January, or face catastrophe.
In a supreme irony, many of the people who caused the economic damage found themselves mired in the dirty work of reversing what they had wrought. The task of reducing inflation through punishing interest rates fell to Paul Volcker, who as a junior official aided leaders in the 1971 decisions that triggered the 1970s inflation in the first place. Mortgage rates rose to today incredible-sounding levels, over 15 percent. In the 1980s, the same John Connally who as treasury secretary in 1971 pounded on Nixon’s desk for populist measures that ensured an economic quagmire, went bankrupt, a casualty of the mess he had helped to create.
Amity Schlaes, Great Society: A New History, 2019.
August 18, 2020
Don’t worry your pretty little heads, normies, the enlightened ones are planning “The Great Reset” for 2021
Mark Steyn on how the great and the good of the world are figuring out the road ahead of us:
… most of the chaps who matter in this world are people you’ve never heard of — by which I mean they are other than the omnipresent pygmies of the political scene: In a settled democratic society such as Canada, for example, if you wind up with an electoral contest between a woke mammy singer with a banana in his pants and a hollow husk less lifelike than his CBC election-night hologram whose only core belief is that he has no core beliefs other than that party donations should pay for his kids’ schooling, you can take it as read that the real action must be elsewhere.
A lot of those chaps you’ve never heard of turn up in this video from the “World Economic Forum” — ie, the Davos set. After five months of Covid lockdown, you’ll be happy to hear that all the experts have decided that 2021 will be the year of “The Great Reset”:
I see my chums at the Heartland Institute headline this the “World Leaders’ ‘Great Reset’ Plan“. But, if by “leader” you mean an elected head of government accountable to the people, there is a total dearth. Indeed, it’s a melancholy reflection on the state of “world leadership” that the nearest to anyone accountable to the people in this video is HRH The Prince of Wales, in whom one day in the hopefully extremely far distant future the executive authority of the United Kingdom, Canada, Australia, etc will be nominally vested but which cannot be exercised without the consent of the people’s representatives. Yet even that token accountability is, as noted, in the future. So right now he’s just another guy who’s a “world leader” because he gets invited to Davos and you don’t — and, even if you were minded to show up anyway, you’d need a private jet because all the scheduled flights have been Covid-canceled and the world’s airports are ghost towns.
As is the custom among our big thinkers, the blather is very generalized. “Now is the time to think about what history would say about this crisis,” says the head of the IMF. If you say so. Personally, I was thinking that now is the time to eat a meal in a restaurant, if they weren’t closed.
But, why is it history’s job to say something about this crisis? Why, don’t you “world leaders” of the here and now say anything about it? “It is imperative that we reimagine, rebuild, redesign, re-invigorate and re-balance our world,” declares the UN Secretary-General.
That’s almost a full set, but he forgot “redefined”. “Possibilities are being redefined each and every day,” says the chief exec of British Petroleum, who as is his wont sounds like he’s in any business other than petroleum.
There is, of course, an inscrutable Oriental, who is chairman of something called the “China Green Finance Committee”. He’s there as a not so subtle reminder not even to bring up the subject of China, whose lies amplified by their sock puppet at the WHO are the sole cause of the present crisis – and whose death-grip on our future is the thing that most urgently needs to be reimagined, rebuilt, re-balanced and redefined. As I’ve mentioned many times over the spring and summer, twenty years ago we were told to forget about manufacturing — from widgets to “These Colors Don’t Run” T-shirts, that’s never coming back; from now on, we’re going to be “the knowledge economy”. Yet mysteriously, with the 5G and the Huawei and all the rest, China seems to have snaffled all that, too.
April 27, 2020
The Economy of Ancient Rome
Economics Explained
Published 26 Apr 2020Ancient Rome was perhaps the most significant ancient civilisation to have existed throughout history, the empire lived for over 1000 years and in that time, it gave us the foundations for our modern society. Democracy, a court based legal system, Latin languages and alphabet, three course meals, and perhaps it was one of the first modern economies to move beyond a simple agrarian empire and develop things like modern banking, lending, taxation and yes even financial crisis as we know them today.
In the same way that scholars study a dead language like Latin to discerned the foundation of meaning in our modern dialects economists can study the histories of ancient civilisations like Rome to determine basic economic functions in a time before modern financial systems could skew results and Rome was perhaps the most developed case study we could look at.
#rome #economics #recession
Patreon – https://www.patreon.com/EconomicsExpl…
Discord – https://discord.gg/7kM7Tw9
Enquiries – loungejita@gmail.com
References –
Morley, N., 2002. Metropolis and hinterland: the city of Rome and the Italian economy, 200 BC-AD 200. Cambridge University Press.
Temin, P., 2006. “The economy of the early Roman Empire”. Journal of Economic Perspectives
Temin, P., 2017. The Roman market economy. Princeton University Press.
Garnsey, P., Hopkins, K. and Whittaker, C.R. eds., 1983. Trade in the ancient economy
Brown, P., 2012. Through the Eye of a Needle: Wealth, the Fall of Rome, and the Making of Christianity in the West, 350-550 AD. Princeton University Press.
Braund, D.C., 1983. Gabinius, Caesar, and the publicani of Judaea. Klio
Articles
http://penelope.uchicago.edu/Thayer/E…
April 15, 2020
When the Fed Does Too Much
Marginal Revolution University
Published 22 Aug 2017In the 2000s, the Fed kept interest rates low to stimulate aggregate demand. But the cheap credit also helped fuel the housing market bubbles. We’ll look at the case of the Great Recession as an example of where the Fed did too much in one area, and perhaps not enough in others.
April 4, 2020
Monetary Policy: The Negative Real Shock Dilemma
Marginal Revolution University
Published 15 Aug 2017Imagine a negative real shock, like an oil crisis, just hit the economy. How should the Fed respond?
Decreasing the money supply will help with inflation, but make growth worse. Increasing the money supply will improve growth, but inflation will climb higher. What’s the Fed to do?!
September 28, 2019
How the Federal Reserve Works: After the Great Recession
Marginal Revolution University
Published on 3 Apr 2018In response to the Great Recession, the Federal Reserve has implemented some new instruments and policies – including quantitative easing, paying interest on reserves, and conducting repurchase (and reverse repurchase) agreements. In this video we cover how these tools work, and why they matter.
August 18, 2019
The Austrian School on the causes and cures of economic recessions
Tim Worstall responds to a Guardian article on recessions (we’re apparently due for another one, according to the writer) and suggests that the Austrian theories may be helpful to understand what’s going on:

A Mises Institute graphic of some of the key economists in the Austrian tradition (Carl Menger, Ludwig von Mises, Friedrich Hayek, Murray Rothbard, and Hans-Hermann Hoppe.
Mises Institute via Wikimedia Commons.
As a pencil sketch – all you can do in a single article – that’s rather good. So, fine, let’s run with that. We’ve not had a normal recession for ages, one will come along soon enough and we’ve forgotten how to deal with it.
However, we can take this idea a little further too. Off into the wild spaces of Austrian theory. There a recession happens because of the built up malinvestment across the economy. Essentially, when it’s too easy to finance stuff then too much bad stuff gets financed. We need the regular recession to flick off the froth and get back to a more sensible allocation of capital.
My own view is that there is no one correct macroeconomic theory but that all of them contain elements of the truth. The trick is to work out which theory to apply to which happenstance. Reorganising the Soviet economy wasn’t going to be done by a bit of Keynesian demand management, there was a century of misallocation to chew through. Getting out of 2008 was different because it was the financial system that had fallen over, we didn’t just have that cyclical decline in business investment. Etc. Austrians can – perish the thought, eh? – be a little too fervent in the insistence that all recessions are about misallocation that must be purged.
But note the underlying thing we can pick up from Davies here. We’ve been staving off that normal recession for decades through that management. Perhaps it’s not all that good an idea to continually do that? He really does say that the Crash stemmed from those attempts to stave off after all. Thus, in a sense, we could argue that we’re going to get the recessionary horrors come what may. Even Keynesian demand management might not be the correct solution if it just gives us once in a generation collapses rather than more regular downturns?
That is, perhaps the Austrians are at least in part right? We need the regular purges for fear of something worse?
May 27, 2019
Game of Theories: The Great Recession
Marginal Revolution University
Published on 5 Dec 2017Tyler Cowen puts Keynesian, monetarist, real business cycle, and Austrian theories to work to explain a downturn from recent economic history: the Great Recession of 2008.
May 23, 2019
Game of Theories: The Keynesians
Marginal Revolution University
Published on 7 Nov 2017When the economy is going through a recession, what should be done to ease the pain? And why do recessions happen in the first place? We’ll take a look at one of four major economic theories to find possible answers – and show why no theory provides a silver bullet.
March 5, 2019
Changes in Velocity
Marginal Revolution University
Published on 16 May 2017What happens when aggregate demand shifts because of a change in the velocity of money? You’ll recall from earlier videos that an increase or decrease in velocity means that money is changing hands at a faster or slower rate.
Changes in velocity are temporary, but they can still cause business fluctuations. For instance, say that consumption growth slows as consumers become pessimistic about the economy.
In fact, we saw this play out in 2008, when workers and consumers became afraid that they might lose their jobs during the Great Recession. This fear drove them to cut back on their spending in the short run. But, since changes in velocity are temporary, this fear receded as time passed and the economy began to recover.
Dive into this video to learn more about what causes shifts in the aggregate demand curve.
January 9, 2019
Sticky Wages
Marginal Revolution University
Published on 2 May 2017Imagine you’re an employer during a recession, and you desperately need to cut labor costs to keep your firm afloat. Are you more likely to cut wages across the board for all employees, or institute layoffs for only some?
While it may seem that wage cuts are the “better” choice, they aren’t as common as you might think. Why is that?
To answer that question, this video explores a phenomenon known as “sticky wages.”
In other words, wages have a tendency to get “stuck” and not adjust downwards. This occurs even during a recession, when falling wages would help end the recession more quickly.
However, that’s not to say that wages cannot adjust downward for an individual during a recession. This can happen, but likely only after an employee has been fired from their initial job, and eventually rehired by a different firm at a lower wage rate.
Back to our original question — why are employers unlikely to cut wages? A big reason has to do with the effect on morale. Employees may become disgruntled and angry when they experience a nominal wage cut, and become less productive.
An important note here — notice that we said nominal wage cut, meaning, not adjusted for inflation. If an employee receives a 3% raise in nominal wages, they may remain happy in their current position. But what if inflation is 5%? What does this mean for their real wage? (Hint: For an in depth answer to this question check out our earlier Macroeconomics video on “money illusion.”)
Next week we’ll return to our discussion on the AD/AS model for a look at how factors such as “sticky wages” affect the economy in the short run.