The shift from open concepts demanded by necessity to widespread construction of separate rooms to open concepts demanded by style is relatively recent. Before the 17th century, especially for the poor, “rooms did not have specialized functions”, explains architect Witold Rybczynski in Home: A Short History of an Idea. “Houses were full of people, much more so than today, and privacy was unknown.”
A single room could serve as a study in the morning, a dining room at noon, a living room in the evening, and a bedroom at night. Beds were couches, and couches were beds. Your house was your workspace, and your minimal furniture typically had no fixed arrangement, as it was constantly moved about to accommodate different uses of the only room available. (The French and Italian words for “furniture” still hint at this history: You can see the similarity to “mobile” in meubles and mobilia.)
These open concepts of old were not only motivated by different conceptions of privacy and the expense of building additional walls. They were also required for the lower classes by premodern heating technologies. A single open hearth, or, later, fireplace or stove, could warm one large room but could not do much for other, closed-off spaces. A lord or king could build a heating element into every room, but for the average family, winter warmth required most of life to happen in a single space.
As technology advanced, ideas about privacy changed, and standards of living improved over the last 500 years, ordinary people were increasingly able to move away from an open concept home, and they eagerly did so. “Rooms began to proliferate as wealthy householders discovered the satisfactions of having space to themselves,” notes Bill Bryson in At Home: A Short History of Private Life. Though the transition was slow — toilets long had “multiple seats, for ease of conversation” — rooms were increasingly devoted to particular uses, and those uses were separated from one another as much as resources permitted.
Bonnie Kristian, “Open concept homes are for peasants”, The Week, 2019-05-12.
December 5, 2022
QotD: Open concept house designs
October 21, 2022
What is Gruel?
Tasting History with Max Miller
Published 14 Jun 2022
(more…)
October 17, 2022
QotD: Julius Nyerere
When I worked for three years in the 1980s in the East African country of Tanzania, I was outraged by the quite unnecessary state of impoverishment and pauperism to which the policies of the long-time president, Julius K. Nyerere, had reduced the population. These policies – collectivisation of agriculture, destruction of commercial farming and the elimination of incentives for peasants to produce anything, one-party political control over every detail of daily life – were so obviously counterproductive of Nyerere’s repeatedly stated aim to develop his country economically and lift it from its poverty that I long concluded that he must be some kind of fool or intellectual incompetent. But it was I who was the fool.
One day, the not very difficult thought occurred to me that Nyerere’s stated aim was not the real aim, that the aim of his policies was not the economic development of the country or anything like it, but rather the maintenance of himself and his cronies in power. Once I made this simple assumption, I could see what should have been obvious to me from the first: that far from being a miserable failure, Nyerere was a brilliant and outstanding success. Not only had he maintained himself in power for more than twenty years with very little challenge, apart from an early attempt at a coup by the army, but he had successfully managed to present himself to the world as a man of outstanding principle: indeed, there are even now moves afoot by the Catholic Church, to which he was more attached even than he was to Kim Il Sung, to canonise him, notwithstanding his imprisonment of political opponents and his forced removal of the peasantry from where it was living into collectivised villages. One of his miracles was to have extracted huge sums of aid money from the willing dupes of Scandinavia and elsewhere, which disappeared in Tanzania as water through sand but was so essential to him in the maintenance of his power.
If the aim of politicians is the attainment of power, Nyerere was one of the most successful politicians of the twentieth century, and very far from the fool or incompetent that I had thought him.
Theodore Dalrymple, “Brexit Doesn’t Mean Brexit”, Law & Liberty, 2019-04-15.
October 7, 2022
Pease Pudding – Weird Stuff In A Can #74
Atomic Shrimp
Published 28 May 2018This is Pease Pudding — A sort of spreadable paste made from yellow split peas, and with a very long history as a staple food in England.
Here’s the link to the article on Atomic Shrimp (includes a recipe, of sorts): http://atomicshrimp.com/post/2007/01/…
September 27, 2022
QotD: The Poor Law Reform Act of 1834
The Royal Commission on the Operation of the Poor Laws, set up in 1832, was chaired by Charles Blomfield, Bishop of London. It numbered several other prominent churchmen among its members. The deliberations of this body led to the Poor Law Reform Act of 1834. This charming statute was based on the idea that the provision of poor relief must be made so torturous and degrading that only those suffering from extreme starvation and indigence would accept it. The sole form of assistance was to be within the context of workhouses, which were to be made as miserable and hellish as any prison. Any family unfortunate enough to have no choice but to fall back on the workhouse would be split up, as mixed-sex institutions would “undermine the good administration” of the workhouses, as the authorities euphemistically put it.
One of the law’s architects, Edwin Chadwick — a man who made Mr Gradgrind [Wiki] look like one of the Cheeryble brothers [Wiki] — infamously commented that it was vital that the inmates of workhouses should be given the coarsest food possible. William Cobbett, a leading opponent of the bill, gleefully seized on this, nicknaming the Whigs, who pushed the legislation hardest, the “Coarser Food Party”. The idea of all this — rooted in the principles of utilitarianism, political economy and Malthusianism — was, as future Archbishop of Canterbury John Bird Sumner put it, to encourage the labouring poor to do everything they could to avoid the “intemperance and want of prudent foresight” that creates poverty, the “punishment which the moral government of God inflicts in this world upon thoughtlessness and guilty extravagance”.
In the 1830s, these ideas were at the very vanguard of progressive thinking. They were promoted by the metropolitan liberal elite of the age, men such as James Mill, Jeremy Bentham and David Ricardo, the forward-thinking “Philosophic Radicals” who spewed out reforming and “improving” ideas through their famous organ The Westminster Review. Other contributors included happy-go-lucky eugenicist pioneer and social Darwinist Herbert Spencer, as well as Harriet Martineau, the sort of woman who would cheerfully have put her “enlightened benevolence” into practice by personally taste-testing workhouse food to ensure it was sufficiently coarse.
These ideas were gleefully leapt upon by a large swathe of the Church leadership, who endorsed the grim dogmas of political economy with an alacrity that would only surprise anyone unfamiliar with the long history of our episcopacy’s lamb-like submission to secular liberal orthodoxies. As E.R. Norman pointed out many decades ago, the Church of England’s leaders have, again and again since at least the eighteenth century, “readily adopted the progressive idealism common to liberal opinion within the intelligentsia, of which they were a part”. They have “always managed to reinterpret their sources in ways which have somehow made their version of Christianity correspond to the values of their class and generation”, a process intimately connected to the fact that bishops are nearly always tied (by personal links, economic interests and a desire to conform) to their secular peers who set the broader cultural and political agenda.
Capel Lofft, “The closing of the Episcopal mind”, The Critic, 2022-06-21.
September 22, 2022
California’s Central Valley of despair
At Astral Codex Ten, Scott Alexander wonders why California’s Central Valley is in such terrible shape — far worse than you’d expect even if the rest of California is looking a bit curdled:
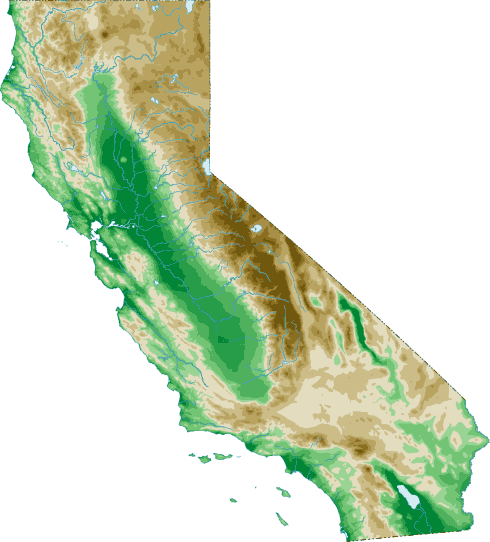
Here’s a topographic map of California (source):
You might notice it has a big valley in the center. This is called “The Central Valley”. Sometimes it also gets called the San Joaquin Valley in the south, or the the Sacramento Valley in the north.
The Central Valley is mostly farms — a little piece of the Midwest in the middle of California. If the Midwest is flyover country, the Central Valley is drive-through country, with most Californians experiencing it only on their way between LA and SF.
Most, myself included, drive through as fast as possible. With a few provisional exceptions — Sacramento, Davis, some areas further north — the Central Valley is terrible. It’s not just the temperatures, which can reach 110°F (43°C) in the summer. Or the air pollution, which by all accounts is at crisis level. Or the smell, which I assume is fertilizer or cattle-related. It’s the cities and people and the whole situation. A short drive through is enough to notice poverty, decay, and homeless camps worse even than the rest of California.
But I didn’t realize how bad it was until reading this piece on the San Joaquin River. It claims that if the Central Valley were its own state, it would be the poorest in America, even worse than Mississippi.
This was kind of shocking. I always think of Mississippi as bad because of a history of racial violence, racial segregation, and getting burned down during the Civil War. But the Central Valley has none of those things, plus it has extremely fertile farmland, plus it’s in one of the richest states of the country and should at least get good subsidies and infrastructure. How did it get so bad?
First of all, is this claim true?
I can’t find official per capita income statistics for the Central Valley, separate from the rest of California, but you can find all the individual counties here. When you look at the ones in the Central Valley, you get a median per capita income of $21,729 (this is binned by counties, which might confuse things, but by good luck there are as many people in counties above the median-income county as below it, so probably not by very much). This is indeed lower than Mississippi’s per capita income of $25,444, although if you look by household or family income, the Central Valley does better again.
Of large Central Valley cities, Sacramento has a median income of $33,565 (but it’s the state capital, which inflates it with politicians and lobbyists), Fresno of $25,738, and Bakersfield of $30,144. Compare to Mississippi, where the state capital of Jackson has $23,714, and numbers 2 and 3 cities Gulfport and Southhaven have $25,074 and $34,237. Overall Missisippi comes out worse here, and none of these seem horrible compared to eg Phoenix with $31,821. Given these numbers (from Google), urban salaries in the Central Valley don’t seem so bad. But when instead I look directly at this list of 280 US metropolitan areas by per capita income, numbers are much lower. Bakersfield at $15,760 is 260th/280, Fresno is 267th, and only Sacramento does okay at 22nd. Mississippi cities come in at 146, 202, and 251. Maybe the difference is because Google’s data is city proper and the list is metro area?
Still, it seems fair to say that the Central Valley is at least somewhat in the same league as Mississippi, even though exactly who outscores whom is inconsistent.
August 23, 2022
QotD: The fate of suddenly poor Spartiates
What are affairs like for poor spartiates?
First, we need to reiterate that a “poor” spartiate was still quite well off compared to the average citizen in many Greek poleis – we talk about “poor” spartiates the same way we talk about the “poor” gentry in a Jane Austen novel. None of them are actually poor in an absolute sense, they are only poor in the sense that they are the poorest of the rich, clinging to the bottom rung of the upper class.
Nevertheless, we should talk about them, because the consequences of falling off of that bottom rung of the economic ladder in Sparta were extremely severe because of the closed nature of the spartiate system. Here is the rub: membership in a syssition was a requirement of spartiate status, so failure to be a member in a syssition – either because of failure in the agoge or because a spartiate could no longer keep up the required mess contributions – that meant not being a spartiate anymore.
The term we have for ex-spartiates is hypomeiones (literally “the inferiors”), which seems to have been an informal term covering a range of individuals who were (or whose family were) spartiates, but had ceased to be so. The hypomeiones were, by all accounts, mostly despised by the spartiates and the hatred seems to have been mutual (Xen. Hell. 3.3.6). Interestingly in that passage there – Xenophon’s Hellenica 3.3.6 – he lists the Spartan underclasses in what appears to be rising order of status – first the helots (at the bottom), then the neodamodes (freed helots, one step up), then the hypomeiones, and then finally the perioikoi. The implication is that falling off of the bottom of the spartiate class due to cowardice, failure – or just poverty – meant falling below the largest group of free non-citizens, the perioikoi.
Herodotus gives some sense of the treatment of men who failed at being spartiates when he details the two survivors of Thermopylae – Aristodemus and Pantites. Both had been absent from the battle under orders – Pantites had been sent carrying a message and Aristodemus had suffered an infection. When they returned to Sparta, both were ostracized by the spartiates for failing to have died – Pantites hanged himself (Hdt. 7.232) while Aristodemus was held to have “redeemed” himself with a suicidal charge at Plataea which cost his life (Hdt. 7.231). And as a side note: Aristodemus is the model for 300’s narrator, Dilios – so when you see him in the movie, remember: the Spartan system drove these men to pointless suicide because they followed an order.
But my main point here is that falling out of the spartiate system meant social death. Remember that the spartiates are a closed class – failing at being a spartiate because your kleros is too poor to maintain the mess contribution means losing citizen status; it means your children cannot attend the agoge or become spartiates themselves. It means you, your wife, your entire family forever are shamed, their status as full members of society forever revoked and your social orbit collapses on you, since you are cut off from the very ties that bind you to your friends. No wonder Pantites preferred to hang himself.
In essence then, the core of the problem here is not that these poor spartiates were poor in any absolute sense – they weren’t. It was that the difference between being rich and being merely affluent in Sparta was a social abyss completely unlike any other Greek state. And that abyss was completely one way. As we’ll see – there was no way back.
Our sources are, unfortunately, profoundly uninterested in answering some crucial questions about the hypomeiones: did they keep their kleroi? What happened to the status of their children? What happened to the status of the women in their families? We can say one thing: it is clear that there was no “on-ramp” for hypomeiones to get back into the spartiate system. This is made quite clear, if by nothing else, by the collapsing number of spartiates (we’ll get to it), but also at the inability of extremely successful non-Spartan citizens – men like Gylippus and Lysander – to ever join the homoioi. Once a spartiate was a hypomeiones, they appear to have been so forever – along with any descendants they may have had. Once out, out for good.
All of that loops back to the impact of the great earthquake in 464. It is likely there were always spartiates who – because their kleroi were just a bit poorer, or were hit a bit harder by helot resistance, or for whatever reason – clung to the bottom of the spartiate system financially, struggling to make the contributions to the common mess. When the earthquake hit, the death of so many helots – on whom they relied for their economic basis – combined with the overall disruption seems to have pushed many of these men beyond the point where they could sustain themselves. Unlike in a normal Greek polis, they could not just take up some productive work to survive and continue as citizens, because that was forbidden to the spartiates, so they collapsed out of the class entirely.
(As an aside – the fact that wealthy spartiates, as mentioned, seemed to prefer each other’s company over the rest probably also meant that the social safety-net of the poor spartiates likely consisted of other poor spartiates. Perhaps in normal circumstances they remained stable by relying on each other (you help me in my bad year, I help you in yours – this is very common survival behavior in subsistence agriculture societies), but the earthquake – by hitting them all at once – may well have caused a downward spiral, as each spartiate who fell out of the system made the remainder more vulnerable, culminating in entire social groups falling out.)
As I said, our sources are uninterested in poor spartiates, so we can only imagine what it must have felt like, clinging desperately to the bottom of that social system, knowing how deep the hole was beneath you. One imagines the mounting despair of the spartiate wife whose job it is to manage the household trying to scrounge up the mess contributions out of an ever-shrinking pool of labor and produce, the increasing despair of her husband who because of the laws cannot do anything but watch as his household slides into oblivion. We cannot know for certain, but it certainly doesn’t seem like a particularly happy existence.
As for those who did fall out of the system we do not need to imagine because Xenophon – in a rare moment of candor – leaves us in no doubt what they felt. He puts it this way: “they [the leaders of a conspiracy against the spartiates] knew the secret of all of the others – the helots, the neodamodes, the hypomeiones, the perioikoi – for whenever mention was made of the spartiates among these men, not one of them could hide that he would gladly eat them raw” (Xen. Hell. 3.3.6; emphasis mine).
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: This. Isn’t. Sparta. Part IV: Spartan Wealth”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-08-29.
August 18, 2022
QotD: Nostalgie de la boue
TWS suggests we take a hard look at the concept of nostalgie de la boue:
Nostalgie de la boue (French: “nostalgia for mud”) is the attraction to low-life culture, experience, and degradation, found at times both in individuals and in cultural movements … Tom Wolfe described a party in New York in 1970: “It was at this party that a Black Panther field marshal rose up beside the north piano — there was also a south piano — in Leonard Bernstein’s living room and outlined the Panthers’ ten-point program to a roomful of socialites and celebrities, who, giddy with nostalgie de la boue, entertained a vision of the future in which, after the revolution, there would no longer be any such thing as a two-story, thirteen-room apartment on Park Avenue, with twin grand pianos in the living room, for one family.”
I think TWS is right:
It explains everything from those parties where they pretend to eat people and the Podesta brothers love of pedo-murder art to the Jersey Shore and all rap music. People of Wal-Mart and people who enjoy mocking them. The idea covers everything happening.
Back in the days, they called all that “authenticity”. The Working Man ™ was supposed to have an “authenticity”, a raw experience of life, that the Intelligentsia did not, so the Intelligentsia made it their mission to ape “authentic” proletarian manners and mores. That’s why every self-styled “Intellectual” since Marx has carried on like an unbathed schizophrenic hobo — they think they’re being “authentic”.
It never occurs to them that this is grossly insulting to The Workers they’re supposedly helping, because of course they never ever meet any Workers — they imagine how they think a longshoreman would act, and then go do that.
I have far more respect for “the People of Walmart” than I do for those who make fun of them, because “the People of Walmart” have been beaten down and brutalized by the dominant culture. They’ve had all their self-respect kicked out of them by little college snots with Gender Studies degrees. It’s like the peasantry in pre-Revolution Russia: Everything the intellectuals said about the nobility was true … but everything the nobility said about the serfs was also true. It was a chicken-and-egg problem with no solution save one.
I also have some respect for Walmart as an institution. Yeah, I know, it’s cheap Chinese shit, but trust me: Though I didn’t grow up poor, you could see “poor” from my house for a lot of my childhood. I don’t recall having Walmart back then, but K-Mart’s Blue Light Specials improved our day to day quality of life enormously. And when I first got out on my own, I decorated my entire first apartment in Walmart — it wasn’t fancy, but it worked, and I had a hell of a lot more stuff that I could actually use than I ever could’ve afforded any other way.
You want to make fun of Walmart, and the people who shop there? Ok, fine, motherfucker, but first try living in a trailer where your couch is patched up with duct tape, and go to school wearing your California cousins’ hand me down clothes, so that you’re dressed like a surfer when you’re 500 miles from the nearest ocean.
I will never, ever understand this. You can choose to be ugly, and to surround yourself with ugliness. Or you can choose NOT to do that. Why would anyone pick the former?
Severian, “Friday Mailbag”, Founding Questions, 2022-05-13.
June 5, 2022
Privatize the libraries?
In the latest SHuSH newsletter, Kenneth Whyte discovers — perhaps to his surprise — he’s not actually the most visible crank on public library issues:
I’m no longer the world’s biggest crank on public libraries. My argument, you’ll recall, is that public libraries are a good thing, but that North Americans borrowing rather than buying three out of every four books they read is a bad thing for the incomes of authors, the economics of publishers, and the welfare of just about everyone else involved in the book industry. That’s fainthearted stuff compared to this week’s tweet from Chris Freiman, a philosophy professor at William & Mary:
As you can guess from the 4,152 comments he’d generated by last night, Freiman’s was an unpopular take. Summing up the responses:
No one has been in a mood to ask if Freiman has a point, or where he’s coming from. For what it’s worth, he has a track record of criticism of government welfare spending. His usual schtick is to ask why so many Americans are poor when the poverty line for a family of three is $18,530 (annually) and welfare spending on a family of three from all three levels of government amounts to $61,830 (annually). It’s not the worst question.
His answer appears to be that directly transferring funds to the poor would be a more effective and efficient way of alleviating poverty than allowing governments to keep running expensive programs that are failing to achieve the same end. That’s not the worst answer.
But does he have a point regarding libraries?
I give him half a point. Public libraries are overwhelmingly used by people who can afford to buy books, and those people are reading primarily for pleasure. I’m all for lending books to people who can’t afford them, who have trouble accessing them, or who want to improve their minds by reading important or serious stuff. But to the extent that libraries are giving middle-class patrons free entertainment—sure, privatize them. There are better uses of public money. Apply the funds to reduce tax burdens on low-income families or improve conditions in government-run nursing homes.
Where the privatization argument fails is that libraries do a lot more than provide middle-class patrons with entertainment. They are important community hubs and for a minority of users they continue to fulfill their original purpose, which, says historian Ed D’Angelo, was to “promote and sustain the knowledge and values necessary for a democratic civilization”. Privatization would likely destroy the valuable public service aspects of public libraries.
In fact, the real problem with public libraries today is that they’re already half privatized. Starting in the middle of the last century, they stopped believing in their role as the community’s edifier-in-chief. They adopted the mindset of the marketplace, giving people what they wanted, filling their shelves with multiple copies of the hottest bestsellers, however vacuous, and measuring their success by counting foot traffic at their branches. They now manage those branches like Walmart supercentres, maximizing transactions per square foot of space. Who cares what patrons are reading, or why, so long as the turnstiles are spinning.
I’d prefer they leave private-sector thinking to the private sector, and let public libraries rebuild their lending practices around their original mission of elevating the minds of citizens. Surely we can’t yet afford to abandon the latter objective.
My solutions to the public library problem, in order of preference, are a much more robust public lending right, an exclusive new release window for the retail trade, and user fees for patrons who can afford them. More discussion here.
In any event, thanks to Professor Freiman for revealing me as a moderate.
May 27, 2022
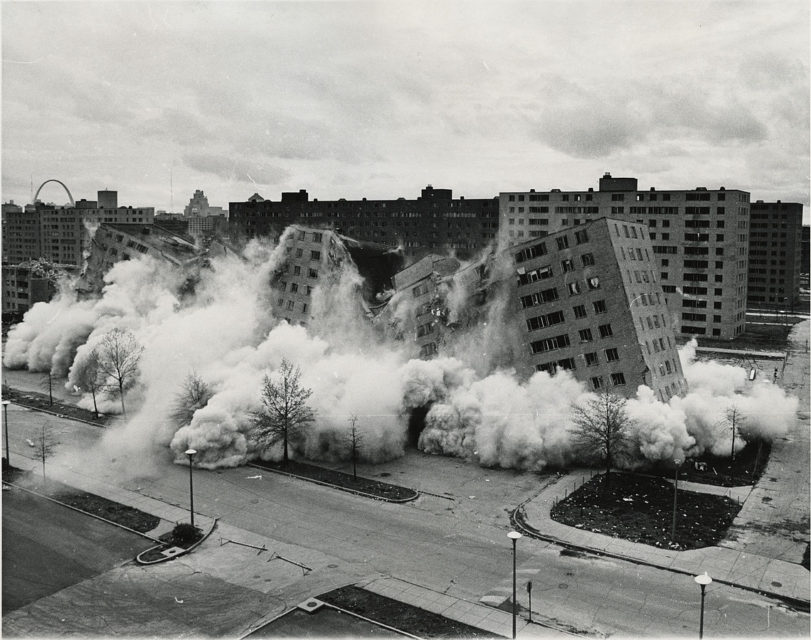
Minoru Yamasaki and the Pruitt–Igoe urban housing project
Joseph Kast recounts the story of a post-war government scheme to demolish slums, re-house the slum-dwellers in a massive public housing project and the architect whose career was forever blighted by the failure of the design:

An undated overview of some of the 33 buildings of the Pruitt-Igoe complex in St. Louis, Missouri. Designed by Japanese-American architect Minoru Yamasaki and built in the early 1950s. All had been demolished by 1976.
Uncredited photo from Wikimedia Commons.
Can society be designed? Can an expert engineer alleviate people’s pains and struggles with a good-enough central plan and blueprint?
Minoru Yamasaki thought so.
Yamasaki was one of America’s most well-respected architects in the 20th century and was a member of the school of thought that people’s human nature could be improved (whether those people needed or wanted improving) by a properly planned building surrounding them.
Yamasaki got to test his theory by designing the public housing complex that promised to be a template for all public housing going forward. The complex, St. Louis’ Pruitt-Igoe, was made possible by post-war New Deal housing and urban development programs. And like many New Deal initiatives, Pruitt-Igoe was guided by the idea that good intentions, centralized planning, and strong government power would progress society more than protecting people’s rights or personal choices.
Pruitt-Igoe and Yamasaki’s designs were sold as the solution to poverty, crime, and housing in America’s major cities, but within just a few years, the complex would show the dangerous consequences when government planners take away people’s liberties and homes.
As with so many vast schemes to use the government’s power to reshape people’s lives, the hopes of the central planners quickly fell afoul of economic and social realities that the plan never took into account.
St. Louis quickly realized that Pruitt-Igoe was a problem. But it was unclear who, if anyone, could fix it. The federal government, the St. Louis Housing Authority, the state, and the City of St. Louis itself all shared responsibility for the complex. When a problem belongs to everyone, it belongs to no one.
Within five years of its launch, Yamasaki was regularly apologizing for his role in the project. Though the final design of the complex differed from his original vision, he came to question the core assumption behind the project: that people’s lives could be effectively engineered through urban design. He expressed regret for his “deplorable mistakes” with Pruitt-Igoe. By the late 1950s, he was giving eloquent speeches about the “tragedy of housing thousands in exactly look alike cells,” which “certainly does not foster our ideals of human dignity and individualism.”
To the Detroit Free Press, he put it more simply: “Social ills can’t be cured by nice buildings.”
By the early 1970s, the 33 concrete tombstones lining St. Louis’ skyline were a cautionary tale for utopian housing schemes. It was a den of crime and misery, rather than anything anyone could call home. When the decision came to demolish the complex, occupancy was only 10 percent.
The day the demolitions began at Pruitt-Igoe, architectural historian Charles Jencks declared the death of high modernist architecture and its grand assumptions: “It was finally put out of its misery. Boom, boom, boom.”
Three towers were demolished in 1972. The last tower finally came down in 1976, leaving nothing of Pruitt-Igoe behind.
May 26, 2022
Alex Tabarrok reviews The Parent Trap
At Marginal Revolution, Alex Tabarrok looks at Nate G. Hilger’s new book, The Parent Trap:
Hilger argues that the problems of poverty, pathology and inequality that bedevil the United States are not primarily due to poor schools, discrimination, or low incomes per se. The primary cause is parents: parents who are unable to teach their children the skills that are necessary to succeed in the modern world. Since parents can’t teach the necessary skills, Hilger calls for the state to take their place with a dramatic expansion of not just child care but collective parenting.
Let’s unpack some details. Begin with schooling. It’s very common to bemoan the state of schools in the “inner city” or to complain about “local financing” which supposedly guarantees that poor counties will have underfunded schools. All of this, however, is decades out-of-date.
A hundred years ago there really were massive public-school resource gaps by class and race. These days, however, state and federal spending play a larger role than local property tax revenue and distribute educational resources more progressively … In fact, when we include federal aid, 42 states spent more on poor school districts than on rich school districts in 2012. The same pattern holds between schools within districts
… The highest spending districts are large urban centers such as New York City, Boston and Baltimore. These cities spend large sums to educate rich and poor children alike. p. 10-11
Hilger is correct. No matter what you saw on The Wire, Baltimore spends more than sixteen thousand dollars per student, among the highest in the nation in large school districts and above average for the nation as a whole. Public schools are quite egalitarian in funding with any bias running towards more funding for poorer districts.
Schools, Hilger writes are “actually the smallest and most equalizing part of a much larger skill-building system.” The real problem, says Hilger, are parents.
But what about discrimination? When it comes to wage discrimination, Hilger is brutally honest:
If we compare individuals with similar cognitive test scores, Black college graduates earn higher wages than white college graduates. Studies that don’t control for test score differences but examine earnings gaps within specific professions — lawyers, physicians, nurses, engineers, scientists — tend to find Black workers earn zero to 10 percent less than white workers. These gaps could reflect discrimination, unmeasured skill differences, or other factors such as geography. In any case, such gaps are small compared to the 50 percent overall Black-white earnings gap and reinforce the idea that closing skills gaps would go a long way toward closing income gaps.
Hilger argues that racism does play an important role in explaining Black-white wage differentials but it’s the historical racism that made black parents less skilled and less able to pass on skills to their children. In the twentieth century, Asians, Hilger argues, were discriminated against in the United States at least much as Black Americans. But the Asians that came to the United States had high skills while the legacy of slavery meant that Black Americans began with low skills. Asians, therefore, were better able to overcome discrimination. The success of Nigerians and Jamaican immigrants in the United States also speaks to this point. (Long time readers may recall that in 2016 I dubbed Hilger’s paper on Asian Americans and Black Americans the Politically Incorrect Paper of the Year.)
May 7, 2022
November 21, 2021
QotD: Britain’s middle class after WW1
One of the most important developments in England during the past twenty years has been the upward and downward extension of the middle class. It has happened on such a scale as to make the old classification of society into capitalists, proletarians and petit bourgeois (small property-owners) almost obsolete.
England is a country in which property and financial power are concentrated in very few hands. Few people in modern England own anything at all, except clothes, furniture and possibly a house. The peasantry have long since disappeared, the independent shopkeeper is being destroyed, the small business-man is diminishing in numbers. But at the same time modern industry is so complicated that it cannot get along without great numbers of managers, salesmen, engineers, chemists and technicians of all kinds, drawing fairly large salaries. And these in turn call into being a professional class of doctors, lawyers, teachers, artists, etc., etc. The tendency of advanced capitalism has therefore been to enlarge the middle class and not to wipe it out as it once seemed likely to do.
But much more important than this is the spread of middle-class ideas and habits among the working class. The British working class are now better off in almost all ways than they were thirty years ago. This is partly due to the efforts of the Trade Unions, but partly to the mere advance of physical science. It is not always realized that within rather narrow limits the standard of life of a country can rise without a corresponding rise in real-wages. Up to a point, civilization can lift itself up by its boot-tags. However unjustly society is organized, certain technical advances are bound to benefit the whole community, because certain kinds of goods are necessarily held in common. A millionaire cannot, for example, light the streets for himself while darkening them for other people. Nearly all citizens of civilized countries now enjoy the use of good roads, germ-free water, police protection, free libraries and probably free education of a kind. Public education in England has been meanly starved of money, but it has nevertheless improved, largely owing to the devoted efforts of the teachers, and the habit of reading has become enormously more widespread. To an increasing extent the rich and the poor read the same books, and they also see the same films and listen to the same radio programmes. And the differences in their way of life have been diminished by the mass-production of cheap clothes and improvements in housing. So far as outward appearance goes, the clothes of rich and poor, especially in the case of women, differ far less than they did thirty or even fifteen years ago. As to housing, England still has slums which are a blot on civilization, but much building has been done during the past ten years, largely by the local authorities. The modern council house, with its bathroom and electric light, is smaller than the stockbroker’s villa, but it is recognizably the same kind of house, which the farm labourer’s cottage is not. A person who has grown up in a council housing estate is likely to be – indeed, visibly is – more middle class in outlook than a person who has grown up in a slum.
George Orwell, “The Lion And The Unicorn: Socialism and the English Genius”, 1941-02-19.
November 17, 2021
Environmental pessimism despite the facts
Alexander Hammond refutes one of the many, many articles preaching global environmental doom and disaster:
Last week, The Scotsman published an article by the journalist Anastasiia Zagoruichyk. In the piece, Zagoruichyk claims that thanks to climate change, fires, and deforestation in her native Ukraine, her children won’t get to experience childhood joys like “walking in the autumn forest, picking mushrooms and breathing fresh air.”
Forest coverage in Ukraine is, admittedly, a niche topic, but alarmism about the future of our forests and our children is unfortunately widespread. Indeed, it was not long ago that Extinction Rebellion founder Roger Hallam confidently declared that due to deforestation and other environmental damage, “our children are going to die in the next 10-20 years.” Thankfully for humanity, these far-fetched claims are not based in reality.
Contrary to what Zagoruichyk would have you believe, forest coverage in Ukraine has increased drastically in recent years. Between 1992 (the oldest data available) and 2020, the share of land in Ukraine covered by forest increased from 16.1 percent to 16.7 percent. While a 0.6 percentage point increase might seem like a small amount, this equates to an additional 3,622 square kilometers of forest – a land area roughly 1.5 times larger than the country of Georgia.
Globally, the world does continue to lose forest area. However, according to the United Nation’s Food and Agriculture Organisation (FAO), the rate of deforestation between 2010-2020 was 40 percent lower than in 1990-2000. At this rate, even without additional promises from world leaders at COP, the global deforestation rate will likely hit zero. Indeed, over the last 30 years, net afforestation has occurred in Europe (including Russia), North America, Oceania, and Asia.
The world’s two poorest regions, South America and Africa, are also the only ones that continue to experience net deforestation. This is no coincidence; many environmental scientists and commentators suggest that economic and ecological well-being are intimately related. According to one hypothesis, called the Environmental Kuznets Curve, a region’s environment worsens in tandem with economic growth but only until a certain income per capita is reached. At that point, people can afford to protect the environment, and ecosystems flourish. This environmental recovery has occurred across Europe and North America and is currently happening in China, Russia, India, and Vietnam.
Therefore, as South America and Africa continue to become richer, we can expect their rate of forest loss to slow and eventually reverse. Given this good news, why is there so much pessimism about the future of our forests? Zagoruichyk’s article offers some answers.
Earlier this month, Michael Shellenberger also had good-but-ignored environmental news to report in UnHerd:
No global problem has ever been more exaggerated than climate change. As it has gone from being an obscure scientific question to a theme in popular culture, we’ve lost all sense of perspective.
Here are the facts: in Europe, emissions in 2020 were 26% below 1990 levels. In the United States, emissions in 2020 were 22% below 2005 levels. Emissions are likely to start declining, too, in developing nations, including China and India, within the next decade. Most nations’ emissions will be bigger this year than last, due to post-Covid economic growth. But global emissions are still likely to peak within the next decade.
And the result will be a much smaller increase in global average temperatures than almost anyone predicted just five years ago. The best science now predicts that temperatures are likely to rise just 2.5-3°C above pre-industrial levels. It’s not ideal, but it’s a far cry from the hysterical and apocalyptic predictions of 6°C, made just a decade ago. A 3°C increase is hardly an existential threat to humanity.
Not that you’d know it, if you had half an eye on the headlines this summer. The floods, fires and heatwaves that plagued the world were, for many observers, proof that the impacts of climate change have already become catastrophic. In Europe, more than 150 people died in flooding. In the United States, wildfire season started earlier and lasted longer, razing hundreds of thousands of acres. Around the world, hundreds died from heatwaves.
But again, it’s worth reminding ourselves of the facts: there has been a 92% decline in the per decade death toll from natural disasters since its peak in the 1920s. In that decade, 5.4 million people died from natural disasters. In the 2010s, just 0.4 million did. Globally, the five-year period ending in 2020 had the fewest natural disaster deaths of any five-year period since 1900. And this decline occurred during a period when the global population nearly quadrupled — and temperatures rose more than 1°C degree centigrade above pre-industrial levels.
November 8, 2021
QotD: The Nanny State
By treating the poor as if they are not choosing their diets in any meaningful sense, people license themselves to start making choices for the poor. John doesn’t realise that his hamburger is killing him, so I’ll just take it away and give him a nice sliced turkey sandwich and an apple and if Johnny is very, very good Mommy will take him to the zoo later. I’ve never understood how the belief that a large swathe of our society is in need of a nanny is reconciled, ideologically speaking, with the belief that we should do everything we can to encourage those people to vote.
Jane Galt, “Suddenly, and for no apparent reason …”, Asymmetrical Information, 2005-05-16.