The normal expectation for Greek tyranny is that the system works like the Empire from Star Wars: A New Hope, where the new tyrant abolishes the Senate, appoints his own cronies to formal positions as rulers and generally makes himself Very Obviously and Formally In Charge. But this isn’t how tyranny generally worked: the tyrant was Very Obviously but not formally in charge, because he ruled extra-constitutionally, rather than abolishing the constitution. This is what separates tyranny, a form of extra-constitutional one man rule, from monarchy, a form of traditional and thus constitutional one-man rule.
We see the first major wave of tyrannies emerging in Greek poleis in the sixth century, although this is also about the horizon where we can see political developments generally in the Greek world, still our sources seem to understand this development to have been somewhat novel at the time and it is certainly tempting to see the emergence of tyranny and democracy in this period both as responses to the same sorts of pressures and fragility found in traditional polis oligarchies, but again our evidence is thin. Tyrants tend to come from the elite, oligarchic class and often utilize anti-oligarchic movements (civil strife or stasis, στάσις) to come to power.
Because most poleis are small, the amount of force a tyrant needed to seize power was also often small. Polycrates supposedly seized power in Samos with just fifteen soldiers (Hdt. 3.120), though we may doubt the truth of the report and elsewhere Herodotus notes that he did so in conspiracy with his two brothers of whom he killed one and banished the other (Hdt. 3.39). I’ve discussed Peisistratos’ takeover(s) in Athens before but they were similarly small-ball affairs. In Corinth, Cypselus seized power by using his position as polemarch (war leader) to have the army (which, remember, is going to be a collection of the non-elite but still well-to-do citizenry, although this is early enough that if I call it a hoplite phalanx I’ll have an argument on my hands) expel the Bacchiadae, a closed single-clan oligarchy. A move by any member of the elite to put together their own bodyguard (even one just armed with clubs) was a fairly clear indicator of an attempt to form a tyranny and the continued maintenance of a bodyguard was a staple of how the Greeks understood a tyrant.
Having seized power, those tyrants do not seem to have abolished key civic institutions: they do not disband the ekklesia or the law courts. Instead, the tyrant controls these things by co-opting the remaining elite families, using violence and the threat of violence against those who would resist and installing cronies in positions of power. Tyrants also seem to have bought a degree of public acquiescence from the demos by generally targeting the oligoi, as with Cypselus and his son Periander killing and banishing the elite Bacchiadae from Corinth (Hdt. 5.92). But this is a system of government where in practice the laws appeared to still be in force and the major institutions appeared to still be functioning but that in practice the tyrant, with his co-opted elites, armed bodyguard and well-rewarded cadre of followers among the demos, monopolized power. And it isn’t hard to see how the fiction of a functioning polis government could be a useful tool for a tyrant to maintain power.
That extra-constitutional nature of tyranny, where the tyrant exists outside of the formal political system (even though he may hold a formal office of some sort) also seems to have contributed to tyranny’s fragility. Thales was supposedly asked what the strangest thing he had ever seen was and his answer was, “An aged tyrant” (Diog. Laert. 1.6.36) and indeed tyranny was fragile. Tyrants struggled to hold power and while most seem to have tried to pass that power to an heir, few succeed; no tyrant ever achieves the dream of establishing a stable, monarchical dynasty. Instead, tyrants tend to be overthrown, leading to a return to either democratic or oligarchic polis government, since the institutions of those forms of government remained.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: How to Polis, 101, Part IIa: Politeia in the Polis”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2023-03-17.
March 20, 2024
QotD: Ancient Greek tyranny
February 13, 2024
Greek History and Civilisation, Part 2 – Sparta and Athens: Contrasting Societies
seangabb
Published Feb 11, 2024This second lecture in the course contrasts Athens and Sparta, the two leading societies in Greece — one a commercial society with high levels of personal freedom and citizen participation, the other a militarised oligarchy.
[NR: Some additional information to supplement Dr. Gabb’s lecture:
– “Citizenship” in the ancient and clasical world
– Sparta had Lycurgus, while Athens had Solon … who at least actually existed
– The Constitution of Athens
– The Constitution of the Spartans
– The Myth of Spartan Equality
– Relative wealth among the Spartiates
– Sparta’s military reputation as “the best warriors in all of Greece”
– Sparta – the North Korea of the Classical era
– Spartan glossary]
(more…)
December 22, 2022
QotD: Sparta as the pre-eminent foe of tyranny
One of the ways that Sparta positioned itself was as the state which championed the freedom of the Greeks. Sparta had fought the Persian tyrant, had helped to oust tyrants in Athens and had later framed Athens itself as a “tyrant city”. Sparta itself had never had a tyrant (until Cleomenes III seized sole power in the 220s). On the flip side, Spartan hegemony was, apparently, little better than Athenian hegemony, given how Sparta’s own allies consistently reacted to it and Sparta would, in the end, do absolutely nothing to stop Philip II of Macedon from consolidating sole rule over Greece. When the call went out to once again resist a foreign invader in 338, Sparta was conspicuous in its absence.
It also matters exactly how tyranny is understood here. For the ancient Greeks, tyranny was a technical term, meaning a specific kind of one-man rule – a lot like how we use the word dictatorship to mean monarchies that are not kingdoms (though in Greece this word didn’t have quite so strong a negative connotation). Sparta was pretty reliable in opposing one-man rule, but that doesn’t mean it supported “free” governments. For instance, after the Peloponnesian War, Sparta foisted a brutal oligarchy – what the Athenians came to call “The Thirty Tyrants” – on Athens; their rule was so bad and harsh that it only lasted eight months (another feat of awful Spartan statecraft). Such a government was tyrannical, but not a tyranny in the technical sense.
But the Spartan reputation for fighting against tyrannies – both in the minds of the Greeks and in the popular consciousness – is predicted on fighting one very specific monarchy: the Achaemenids of Persia. […] This is the thing for which Sparta is given the most credit in popular culture, but Sparta’s record in this regard is awful. Sparta (along with Athens) leads the Greek coalition in the second Persian war and – as discussed – much of the Spartan reputation was built out of that. But Sparta had largely been a no-show during the first Persian war, and in the subsequent decades, Sparta’s commitment to opposing Persia was opportunistic at best.
During the late stages of the Peloponnesian War, Sparta essentially allied with Persia, taking funding and ships first from the Persian satrap Tissaphernes and later from Cyrus the Younger (a Persian prince and satrap). Sparta, after all, lacked the economic foundation to finance their own navy and the Spartans had – belatedly – realized that they needed a navy to defeat Athens. And of course the Persians – and any Spartan paying attention – knew that the Athenian navy was the one thing keeping Persia out of Greek affairs. So Sparta accepted Persian money to build up the fleets necessary to bring down the Athenian navy, with the consequence that the Ionian Greeks once again became subjects to the Persian Empire.
Subsequent Spartan diplomatic incompetence would lead to the Corinthian War (395-387), which turned into a nasty stalemate – due in part to the limitations of Spartan siege and naval capabilities. Unable to end the conflict on their own, the Spartans turned to Persia – again – to help them out, and the Persians brokered a pro-Spartan peace by threatening the Corinthians with Persian intervention in favor of Sparta. The subequent treaty – the “King’s Peace” (since it was imposed by the Persian Great King, Artaxerxes II) was highly favorable to Persia. All of Ionian, Cyprus, Aeolia and Carnia fell under Persian control and the treaty barred the Greeks from forming defensive leagues – meaning that it prevented the formation of any Greek coalition large enough to resist Persian influence. The treaty essentially made Sparta into Persia’s local enforcer in Greece, a role it would hold until its defeat in 371.
If Sparta held the objective of excluding Persian influence or tyranny from Greece, it failed completely and abjectly. Sparta opened not only the windows but also the doors to Persian influence in Greece – between 410 and 370, Sparta probably did more than any Greek state had ever or would ever do to push Greece into the Persian sphere of influence. Sparta would also refuse to participate in Alexander’s invasion of Persia – a point Alexander mocked them for by dedicating the spoils of his victories “from all of the Greeks, except the Spartans” (Arr. Anab. 1.16.7); for their part, the Spartans instead tried to use it as an opportunity to seize Crete and petitioned the Persians for aid in their war against Alexander, before being crushed by Alexander’s local commander, Antipater, in what Alexander termed “a clash of mice”.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: This. Isn’t. Sparta. Part VII: Spartan Ends”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-09-27.
April 8, 2022
The structure of the Chinese government
Scott Alexander reviews The Third Revolution, by Elizabeth Economy, although as he says up front, “It’s a look through recent Chinese history, with The Third Revolution as a very loose inspiration.”:
How Does China’s Government Work?
The traditional answer is a flowchart like this one (source):
But you could give a similarly convoluted flowchart for America, and it would tell people much less than words like “democracy” or “balance of powers”. What’s the Chinese equivalent?
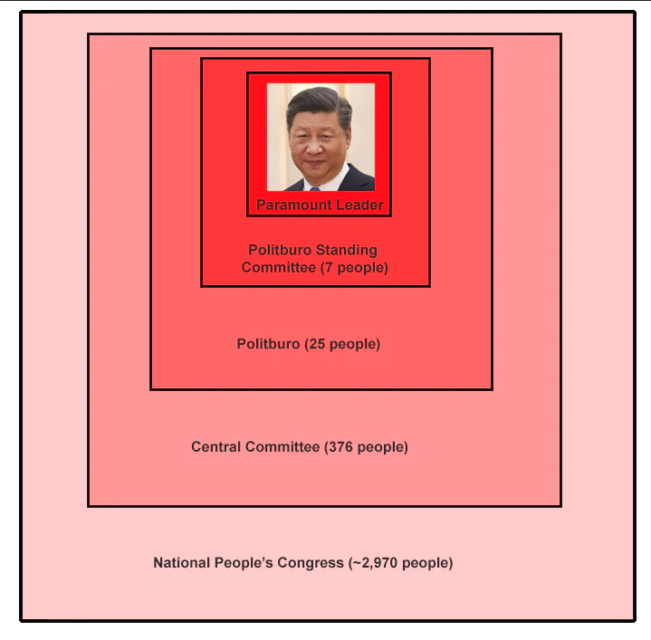
I found it a little more helpful to see it diagrammed it as a series of nested squares:
The inner levels have real power, and the outer layers are theoretically overseers but actually rubber stamps. Things get more and more rubber-stampy as you go out, culminating in the National People’s Congress, which recently voted to re-elect Xi by a vote of 2,970 in favor, 0 against — it’s so irrelevant that it’s literally called “the NPC”.
Who chooses the members of the inner groups? In theory, the outer groups; for example, the Central Committee is supposed to elect the Politburo Standing Committee. In practice, these selections tend to be of the “2,970 in favor, 0 against” variety, so they must be taking marching orders from someone. Who? The Chinese government doesn’t talk about it much, but probably the members of the Politburo Standing Committee hand-pick everyone, including the Paramount Leader and their own successors.
How do they pick? Mostly patron-client relationships. Every leading politician cultivates a network of loyal supporters; if he takes power, he tries to put as many of his people into top posts as he can. The seven Politburo members wheel and deal with each other about whose clients should get which positions, including any unoccupied Politburo seats.
If the two word description of US politics is “democracy, checks-and-balances”, then the two word description of Chinese politics is “oligarchy, patrons-and-clients”. If this seems exotic, it shouldn’t: it’s not much different from how the US fills unelected posts like “ambassador” and “White House staffer”. The Trump presidency put this into especially sharp relief, either because Trump did it more blatantly than usual or just because Trump’s clients were so obviously different from the normal Washington crowd. Consider eg the appointment of Jeff Sessions (among the first Congressmen to endorse Trump) as Attorney General.
In the US, this is a peripheral part of the system, checked by democracy. In China, it’s the whole game.
February 10, 2022
QotD: Classical Greek Polis governance
Before we dive in, I want to give a brief primer on the basics of how nearly all Greek poleis – Athens, Sparta, Corinth, Thebes, Plataea, Tegea, whatever – are structured, because it’ll help in understanding Sparta. (Reminder: the polis, sometimes called a city-state, is the basic unit of Greek governance – these are all independent micro-states).
The standard ingredients of a Greek polis are an assembly of all adult citizen males (often called an ekklesia, meaning “assembly”), a smaller advisory committee (frequently called a boule), and then a set number of elected officials who carried out the laws of the other two (magistrates). I’ve given the common names for these components, but they often have different names in different poleis.
Those basic units don’t change from a democracy (like Athens) to an oligarchy (like Corinth) or even a tyranny (like Syracuse) – the type of government just reflects the division of power between them, and the method of selection. In a democracy, like Athens, the ekklesia will have most of the power, being able to overrule the boule or the magistrates. Often the members of the boule can come from a wide range of wealth classes or even be randomly selected.
In an oligarchy, power is generally focused in the magistrates – drawn from the upper-crust of society – and a smaller boule, with the ekklesia having much less power to restrain them. Alternately, the ekklesia may be restricted in size to only a wealthy subset of the citizenry. In a tyranny, a single person (the tyrant) is able to gain control of the system, through a mix of demagoguery, charisma and well-placed cronies. Even under a tyranny, the basic three-part system still exists, it is simply subverted and controlled by one person (much like how some modern dictatorships have all of the institutions of a democracy – courts, elections, etc – but all of the power is still in one set of hands and the elections are shams).
I want to note this up front because it is important to recognize that the existence of a popular assembly does not make a Greek polis a democracy, nor does the existence of a powerful magistrate make it a tyranny. As we’ll see, Sparta has an assembly, it is just laughably weak; it also has two very powerful magistrates, but their power is strongly checked. What matters is the division of power between these parts. I also wanted to start here because Sparta follows this basic model, but with some interesting variations. Knowing what the normal model looks like will make it easier to spot the variations that are unique to Sparta.
Bret Devereaux, “Collections: This. Isn’t. Sparta. Part V: Spartan Government”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2019-08-29.
November 25, 2021
History of Venice: Rise to Glory
Epic History TV
Published 14 Dec 2018Listen to or download the music HERE: smarturl.it/epichistoryvenice
Music by https://www.musicdesigngroup.comThanks to Elias Tsiantas for the 3D Venetian galley footage
Thanks to Miłek Jakubiec for the Battle of Marignano imageSupport the channel & get exclusive previews at Patreon:
https://www.patreon.com/epichistorytvWant to learn more? We recommend A History of Venice by the late John Julius Norwich, a great popular historian on all things Mediterranean (as an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases): http://geni.us/7q71zx
#EpicHistoryTV #HistoryofVenice
October 26, 2021
The Constitution of Athens
Historia Civilis
Published 15 Dec 2017Patreon | http://historiacivilis.com/patreon
Donate | http://historiacivilis.com/donate
Merch | http://historiacivilis.com/merch
Mailing List | http://historiacivilis.com/mailinglist
Twitter | http://historiacivilis.com/twitter
Website | http://historiacivilis.comSources:
The Athenian Constitution by Aristotle: http://amzn.to/2C1mHLv
Politics by Aristotle: http://amzn.to/2AB6KPV
Parallel Lives: The Life of Solon by Plutarch: http://amzn.to/2AT5Viv
The Constitution of the Athenians by Pseudo-Xenophon: http://amzn.to/2z9rE6l
The Rise of Athens by Anthony Everitt: http://amzn.to/2C2ryMu
The Athenian Democracy in the Age of Demosthenes by Mogens Herman Hansen: http://amzn.to/2AEAtYj
Persian Fire by Tom Holland: http://amzn.to/2AjLB8WMusic:
“Direct to Video,” by Chris Zabriskie
“It’s Always Too Late to Start Over,” by Chris Zabriskie
“Mario Bava Sleeps In a Little Later Than He Expected To,” by Chris Zabriskie
“Hallon,” by Christian BjoerklundWe are a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for us to earn fees by linking to Amazon.com and affiliated sites.
December 8, 2019
History Summarized: Florence
Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published 6 Dec 2019Get 3 months of Audible for just $6.95 a month. That’s more than half off the regular price. Visit http://www.audible.com/overlysarcastic or text
overlysarcasticto 500 500.Can’t start a Renaissance without building a few *Domes* — You’ve seen the memes, now learn the history behind the magnificent city of Florence!
It may sound like sacrilege, but many years ago, Florence was the first Italian city that little Blue had a cartoonishly-overblown obsession for — move over, Venice. In fact, Florentine history is basically THE reason I ever started caring about History in the first place. So I hope that you find this exquisite chapter in world history as enjoyable as I do.
SOURCES & Further Reading:
Death in Florence — Paul Strathern https://www.audible.com/pd/Death-in-F…
Florence: The Biography of A City — Christopher Hibbert
Be Like The Fox: Machiavelli In His World — Erica BennerOur content is intended for teenage audiences and up.
DISCORD: https://discord.gg/sS5K4R3
PATREON: https://www.Patreon.com/OSP
MERCH LINKS: https://www.redbubble.com/people/OSPY…
OUR WEBSITE: https://www.OverlySarcasticProductions.com
Find us on Twitter https://www.Twitter.com/OSPYouTube
Find us on Reddit https://www.Reddit.com/r/OSP/
October 8, 2019
Sarah Hoyt on the “rough music”
Sarah Hoyt borrows a notion from Terry Pratchett’s Discworld series to explain a real phenomenon in our world:
Pratchett’s “Witches” world was so similar to my own, from jumping over fires to get married (not legal in my day, but there was memory of it) to various local folk superstitions, that it was always a surprise when he pulled something I’d never heard of.
One of these is the “rough music.”
When someone has done just about enough that a small village can no longer put up with him, the men in the village get together and play a barbarous and terrible music as they nerve themselves up for the barbarous and terrible things they have to do.
In Europe — hell, all over the rest of the world — the rough music is playing. Just because no one is reporting on this, it doesn’t mean it’s not going on, and growing, and nerving itself up to … something.
“Gilets jaunes #12” by Christophe Becker is licensed under CC BY-NC-SA 2.0
The level at which the Gilets Jaunes have been under reported is extraordinary, except that it hasn’t stopped the uprising either.
(And now I think about it, how much do we see in main stream news about Hong Kong? And it hasn’t stopped the uprising either.)
[…]
So, let’s talk about the rough music. Sure, you can hear it. I can hear it too. The stomp and the drumming can be heard all over the world.
That which can’t go on, won’t.
But I implore you to stop and think: if the rough music plays, what comes after?
There might be no hope for Europe, but Europe’s … ah … how do we put this? Europe’s tenets, their stand before the world, an improvement as they were on everything before them, are not ours.
Even in Europe I suspect when this bursts — and there it will burst. The elites flaying and screaming is only making it worse — you’re going to see things that will make you wonder why on Earth good American boys died in WWII. Because we’re about to get National Socialism, the sequel. National because they’re getting tired of the international elites (and who isn’t) and socialism because the poor bastards have not experienced anything else their entire adult lives.
It will happen. It is necessary. The EU was probably one of the most bizarre ideas in the history of bad ideas. The way it’s run which essentially steals the franchise from ordinary people was just the old style “good families” coming back into power through a back door.
But what comes after will probably be horrific. If we’re all lucky it will also be briefish and like France after the revolution they’ll find their way to something slightly less insane. With or without Napoleon and Europe wide war? Ah … that’s where we need to talk.
First however, let me say that hearing the rough music from the rest of the world is starting to echo here. We see what’s going on there. And we hear strange and stupid stuff, like the “whistleblower of the day” and an impeachment without voting and of course, pancake-gate.
Faced with that kind of behavior you obviously think “It’s insane.” And “We have to stop it.”
April 30, 2019
QotD: Successful “democracies” in history have usually been disguised oligarchies
Thus we get the “Revolutions” in America and France, where educated and newly politicised chattering classes try to find a simplistic solution to all the world’s problems. Their solution being to adopt a system which fits their preferred world order, and seems to give them an advantage that will allow them to force people into their way of thinking.
Humans being what they are, it didn’t work of course.
The American Revolution, supposedly about ‘equality for all’ – if you want to fall for idealistic propaganda – was actually a tax rebellion by Northern states (who also wanted to get rid of the English government’s treaties that kept them out of Indian land), and the Southern states (who wanted to block the English anti-slavery legislation from spreading to their nice comfy system). It was never really about equality, and all the exclusions of people from voting on the basis of colour, race, sex, religion, immigration status, etc., should have made it clear to anyone that what was being considered was really an Oligarchy. Similar in fact to the Ancient Greek and Roman slave-based societies, where some special and limited classes shared rights no one else had.
Actually all “successful” democracies in history have always been Oligarchies. The 1,000 year old “Sublime Republic of Venice” – on which large parts of the US constitution were based – for instance, being limited to a certain number of families that had the vote. Similarly the “Republics” of Ancient Greece or Rome, and modern Switzerland or Israel, being based on vote by military service – another way of ensuring the voters might put national interests above selfish ones.
The first few French republics (those squeezed in around the inevitable dictatorships and emperors that are the result of such systems) were also based on a limited franchise. In their case not a race or religion or sex one like the US, but a straight property qualification that saw a small percentage of both sexes as voters.
Unsurprisingly the Oligarchical Republics of the 18th and 19th centuries were some of the most internally violent (US Slavery, Civil War, Indian Wars, the Terror, multiple revolts and “communes”, Lynchings, Jim Crow laws, etc), and externally aggressive (Napoleonic Wars, Spanish–American Wars, “Interventions” in Central America, Occupations of Hawaii, Philippines, etc.) governments in history. Rivaling the Greek and Roman republics for their aggressive expansionism by land and sea, and certainly being no less effective than more traditional military (Russia and Germany) or trade (Britain and Netherlands) expansionist states.
(And here I would note that the one of the mitigating factors in the idea that German Nationalism was a problem in WWI, was that the populist Navy Leagues and Colonial Leagues of the newly enfranchised voting classes did in fact push Nationalism to dangerous extremes. The Kaiser was a dangerous loon, but he was a dangerous loon responding to the fervor of the dregs of the petit bourgeois who had been enfranchised in his nation, not a man with Napoleonic capabilities in his own right.)
Nigel Davies, “The Solution is… European Union/Multiculturalism/Communism… Name your poison!”, rethinking history, 2015-12-26.
February 20, 2019
History Summarized: Ancient Greece
Overly Sarcastic Productions
Published on 26 Jun 2017What’s that? Blue already did a video on the Athenian empire? Uh… well… um… LOOK, OVER THERE, A DISTRACTION!
For more Greek goodness, check out the following:
History Summarized: Alcibiades: https://youtu.be/kRLkjBUgB2o
History Summarized: Thebes: https://youtu.be/L1x9np5fys8
History Summarized: Athenian Empire: https://youtu.be/cNWDkFkcuP4This video was produced with assistance from the Boston University Undergraduate Research Opportunities Program.
PATREON: http://www.patreon.com/user?u=4664797
Find us on Twitter @OSPYouTube!
August 19, 2018
Poor whites in the pre-Civil War South
Colby Cosh retweeted this fascinating thread by Keri Leigh Merritt (embed through the ThreadReaderApp):
April 14, 2018
QotD: Plato’s ideal society
This [controlling the poor to protect the wealthy] is a problem addressed by Plato in at least two of his works — The Republic and The Laws. The first is his description of an ideal state, the second of a state less than ideal but still worth working towards. I do not claim to be an expert on Plato, though am dubious of many of the claims made against him. However, his general solution to the problem was to stop the enlightenment and to reconstruct society as a totalitarian oligarchy.
His ideal society would be one in which democracy and any degree of accountability would have been abolished, together with married life and the family and private property. Poetry was to be abolished. All other art and music were to be controlled. There was to be a division of society into orders at the head of which was to be a class of guardians. These would strictly control all thought and action.
His workable society would be one in which some property and some accountability would be allowed to remain. Even so, there was to be the same attempt at controlling thought and action.
The stability of these systems was to be maintained by a new theology. A single divine being would take the place of the quarrelling, scandalous gods of mythology and the Homeric poems. The common people could be left with a purified version of the old cults. But these gods would be increasingly aligned with the secondary spirits through which the One God directed His Creation.
People were to be taught that the Platonic system was not a human construct, but that it reflected the Will of Heaven. Rebellion or disobedience would be punished by the direct intervention of God through His Secondary Spirits. Before then, though, it would be punished by the state as heresy. At the end of the fifth century, Anaxagoras had been exiled from Athens for claiming that the sun was a ball of glowing rock. This had been an occasional persecution — indeed, it is hard to think of other instances. In the Platonic system, there was to be a regular inquisition that would punish nonconformity with imprisonment or death.
Thus there is at the heart of the Platonic system a “noble lie” — though Plato may have believed much of it himself. This is of a religion that looks into the most secret places of the mind, and dispenses rewards and punishments according to what is found there. In the old theology, Poseidon had no power beyond on land. Apollo had none in the dark. Zeus had no idea who was thinking what. The Platonic God was just like ours. No sin against His Wishes could go undetected or unpunished.
And so the people were to be kept in line by fear of hellfire, or by fear of everything short of that.
Sean Gabb, “Epicurus: Father of the Englightenment”, speaking to the 6/20 Club in London, 2007-09-06.
October 25, 2017
QotD: Oligarchies and universal franchise democracy
Fortunately the ideologues had a solution to overcome these minor imperfections of limited franchise democracy… universal franchise.
The more recent concept of Universal Franchise Democracy, is founded on the ridiculous, and incorrect, early 1900’s assumption that all Europe’s problems can be traced back to a limited voting Oligarchy.
Clearly if the ‘ruling classes’ in a state are the rich and powerful – i.e., the naturally conservative propertied elements who make the economy work and provide the productive jobs – then the chattering classes who want change will need to enfranchise the not-rich and not-powerful, so they can ride the wave of demand for change into their ideal world. In fact so they can direct it to provide taxpayer funding for non productive jobs… For people like them.
It is certainly no accident that the modern ‘ruling class’ is the nouveau-rich chattering classes – and the power base they have established in the completely unproductive taxpayer-supported lawyers and civil servants and union officials – who lead inevitably to ‘leaders’ who have the right and duty to lecture their stupid populace for not being politically correct enough… People like Merkel, Obama, and the European Union President. (Go on, name him? He has more practical power to interfere in his ‘citizens’ lives than either of the other two. Who is he?)
It is not just the Australian Union Movement of which we can say ‘they used to consist of the cream of the working class, now they consist of the dregs of the middle class’. All the petty tyrants who gorge in the taxpayers trough, and who try and force the ignorant peasants under their care down the correct path – whether medieval monks selling indulgences, or modern human rights lawyers banning free speech on issues they disapprove of – tend to be the dregs.
The dregs, of the intellectual fervor, of the previous generation, of wrong thinkers.
The dregs of any intellectual movement eventually have to accept that their ideal is hogwash. Even Marxists have started to admit that after a century of promoting Communism, they can no longer hide the hideous nature of Communism. Still, they are not going to give up their world-view just because the evidence against it is so overwhelming that continued attempts to argue in favour of it become ridiculous. Instead they move smoothly to supporting another, equally ridiculous ideology that they think will support their worldview. Say Environmentalism, or Multiculturalism.
Nigel Davies, “The Solution is… European Union/Multiculturalism/Communism… Name your poison!”, rethinking history, 2015-12-26.
October 12, 2017
Britain’s Old Boy Network – from “the Establishment” to “the Embarrassment”
In the media rounds supporting his new book, The Square and the Tower: Networks, Hierarchies and the Struggle for Global Power, Niall Ferguson discusses the decline and fall of the oldest power network in Britain:
It used to be that the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Northern Ireland was the United Cronydom of Great Poshhouse and Northern Grousemoor. The only network that mattered was the Old Boy Network. The OBN was formed by men who were the old boys of a tiny elite of boarding schools known as “public schools” because they were closed to the public. Most boys at those schools were scions of the aristocracy or the landed gentry: future barons and baronets.
Even if thick to the point of educational sub-normality, these young gentlemen would attend either Oxford or Cambridge. They would then be given one of the following jobs:
1. Estate manager and courtier (eldest son).
2. Foreign Office or Treasury mandarin (brightest son).
3. Cabinet minister (most extrovert son).
4. Governor of [insert Caribbean island] (youngest son).
5. BBC director-general (Left-wing son).
This is of course a caricature. In reality, there were all kinds of sub-networks — clusters — within the elite network that ran Britain. Sometimes, a brilliant group of talented young men would come together to achieve great things. There was the “Kindergarten” formed by Alfred Milner, which tried (and failed) to transform South Africa into a second Canada or Australia. There were the Apostles — the Cambridge Conversazione, the most exclusive intellectual club of all time — to which the economist John Maynard Keynes belonged.
However, with increasing frequency after 1945, the OBN’s achievements were less than brilliant. Suez. Wilson. Heath. Double-digit inflation. The three-day week. From being the winners of glittering prizes, the OBN degenerated in the eyes of a previously deferential public into the upper-class twits of the year.
In the Sixties the journalists Henry Fairlie and Anthony Sampson popularised the disdainful name that the historian A.J.P. Taylor had given the British elite: “The Establishment”. By the Seventies the Establishment were more like The Embarrassment — objects of sitcom ridicule. By the Eighties they had been almost entirely driven from the corridors of power. Nothing better illustrated this than the Thatcher governments: not only was the prime minister a woman from provincial Lincolnshire (albeit one with an Oxford degree); there were enough ministers in her Cabinet with Jewish backgrounds to inspire off-colour jokes about “Old Estonians”.