Well, if by indigenous we mean “the minimally admixed descendants of the first humans to live in a place”, we can be pretty confident about the Polynesians, the Icelanders, and the British in Bermuda. Beyond that, probably also those Amazonian populations with substantial Population Y ancestry and some of the speakers of non-Pama–Nyungan languages in northern Australia? The African pygmies and Khoisan speakers of click languages who escaped the Bantu expansion have a decent claim, but given the wealth of hominin fossils in Africa it seems pretty likely that most of their ancestors displaced someone. Certainly many North American groups did; the “skraelings” whom the Norse encountered in Newfoundland were probably the Dorset, who within a few hundred years were completely replaced by the Thule culture, ancestors of the modern Inuit. (Ironically, the people who drove the Norse out of Vinland might have been better off if they’d stayed; they could hardly have done worse.)
But of course this is pedantic nitpicking (my speciality), because legally “indigenous” means “descended from the people who were there before European colonialism”: the Inuit are “indigenous” because they were in Newfoundland and Greenland when Martin Frobisher showed up, regardless of the fact that they had only arrived from western Alaska about five hundred years earlier. Indigineity in practice is not a factual claim, it’s a political one, based on the idea that the movements, mixtures, and wholesale destructions of populations since 1500 are qualitatively different from earlier ones. But the only real difference I see, aside from them being more recent, is that they were often less thorough — in large part because they were more recent. In many parts of the world, the Europeans were encountering dense populations of agriculturalists who had already moved into the area, killed or displaced the hunter-gatherers who lived there, and settled down. For instance, there’s a lot of French and English spoken in sub-Saharan Africa, but it hasn’t displaced the Bantu languages like they displaced the click languages. Spanish has made greater inroads in Central and South America, but there’s still a lot more pre-colonial ancestry among people there than there is pre-Bantu ancestry in Africa. I think these analogies work, because as far as I can tell the colonization of North America and Australia look a lot like the Early European Farmer and Bantu expansions (technologically advanced agriculturalists show up and replace pretty much everyone, genetically and culturally), while the colonization of Central and South America looks more like the Yamnaya expansion into Europe (a bunch of men show up, introduce exciting new disease that destabilizes an agricultural civilization,1 replace the language and heavily influence the culture, but mix with rather than replacing the population).
Some people argue that it makes sense to talk about European colonialism differently than other population expansions because it’s had a unique role in shaping the modern world, but I think that’s historically myopic: the spread of agriculture did far more to change people’s lives, the Yamnaya expansion also had a tremendous impact on the world, and I could go on. And of course the way it’s deployed is pretty disingenuous, because the trendier land acknowledgements become, the more the people being acknowledged start saying, “Well, are you going to give it back?” (Of course they’re not going to give it back.) It comes off as a sort of woke white man’s burden: of course they showed up and killed the people who were already here and took their stuff, but we’re civilized and ought to know better, so only we are blameworthy.
More reasonable, I think, is the idea that (some of) the direct descendants of the winners and losers in this episode of the Way Of The World are still around and still in positions of advantage or disadvantage based on its outcome, so it’s more salient than previous episodes. Even if, a thousand years ago, your ancestors rolled in and destroyed someone else’s culture, it still sucks when some third group shows up and destroys yours. It’s just, you know, a little embarrassing when you’ve spent a few decades couching your post-colonial objections in terms of how mean and unfair it is to do that, and then the aDNA reveals your own population’s past …
Reich gets into this a bit in his chapter on India, where it’s pretty clear that the archaeological and genetic evidence all point to a bunch of Indo-Iranian bros with steppe ancestry and chariots rolling down into the Indus Valley and replacing basically all the Y chromosomes, but his Indian coauthors (who had provided the DNA samples) didn’t want to imply that substantial Indian ancestry came from outside India. (In the end, the paper got written without speculating on the origins of the Ancestral North Indians and merely describing their similarity to other groups with steppe ancestry.) Being autochthonous is clearly very important to many peoples’ identities, in a way that’s hard to wrap your head around as an American or northern European: Americans because blah blah nation of immigrants blah, obviously, but a lot of northern European stories about ethnogenesis (particularly from the French, Germans, and English) draw heavily on historical Germanic tribal migrations and the notion of descent (at least in part) from invading conquerors.
One underlying theme in the book — a theme Reich doesn’t explicitly draw out but which really intrigued me — is the tension between theory and data in our attempts to understand the world. You wrote above about those two paradigms to explain the spread of prehistoric cultures, which the lingo terms “migrationism” (people moved into their neighbors’ territory and took their pots with them) and “diffusionism”2 (people had cool pots and their neighbors copied them), and which archaeologists tended to adopt for reasons that had as much to do with politics and ideology as with the actual facts on (in!) the ground. And you’re right that in most cases where we now have aDNA evidence, the migrationists were correct — in the case of the Yamnaya, most modern migrationists didn’t go nearly far enough — but it’s worth pointing out that all those 19th century Germans who got so excited about looking for the Proto-Indo-European Urheimat were just as driven by ideology as the 21st century Germans who resigned as Reich’s coauthors on a 2015 article where they thought the conclusions were too close to the work of Gustaf Kossinna (d. 1931), whose ideas had been popular under the Nazis. (They didn’t think the conclusions were incorrect, mind you, they just didn’t want to be associated with them.) But on the other hand, you need a theory to tell you where and how to look; you can’t just be a phenomenological petri dish waiting for some datum to hit you. This is sort of the Popperian story of How Science Works, but it’s more complex because there are all kinds of extra-scientific implications to the theories we construct around our data.
The migrationist/diffusionist debate is mostly settled, but it turns out there’s another issue looming where data and theory collide: the more we know about the structure and history of various populations, the more we realize that we should expect to find what Reich calls “substantial average biological differences” between them. A lot of these differences aren’t going to be along axes we think have moral implications — “people with Northern European ancestry are more likely to be tall” or “people with Tibetan ancestry tend to be better at functioning at high altitudes” isn’t a fraught claim. (Plus, it’s not clear that all the differences we’ve observed so far are because one population is uniformly better: many could be explained by greater variation within one population. Are people with West African ancestry overrepresented among sprinters because they’re 0.8 SD better at sprinting, or because the 33% higher genetic diversity among West Africans compared to people without recent African ancestry means you get more really good sprinters and more really bad ones?) But there are a lot of behavioral and cognitive traits where genes obviously play some role, but which we also feel are morally weighty — intelligence is the most obvious example, but impulsivity and the ability to delay gratification are also heritable, and there are probably lots of others. Reich is adorably optimistic about all this, especially for a book written in 2018, and suggests that it shouldn’t be a problem to simultaneously (1) recognize that members of Population A are statistically likely to be better at some thing than members of Population B, and (2) treat members of all populations as individuals and give them opportunities to succeed in all walks of life to the best of their personal abilities, whether the result of genetic predisposition or hard work. And I agree that this is a laudable goal! But for inspiration on how our society can both recognize average differences and enable individual achievement, Reich suggests we turn to our successes in doing this for … sex differences! Womp womp.
Jane Psmith and John Psmith, “JOINT REVIEW: Who We Are and How We Got Here, by David Reich”, Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf, 2023-05-29.
1. aDNA works for microbes too, and it looks like Y. pestis, the plague, came from the steppe with the Yamnaya. It didn’t yet have the mutation that causes buboes, but the pneumonic version of the disease is plenty deadly, especially to the Early European Farmers who didn’t have any protection against it. In fact, as far as we can tell, in all of human history there have only been four unique introductions of plague from its natural reservoirs in the Central Asian steppe: the one that came with or slightly preceded the Yamnaya expansion around 5kya, the Plague of Justinian, the Black Death, and an outbreak that began in Yunnan in 1855. The waves of plague that wracked Europe throughout the medieval and early modern periods were just new pulses of the strain that had caused Black Death. Johannes Krause gets into this a bit in his A Short History of Humanity, which I didn’t actually care for because his treatment of historic pandemics and migrations is so heavily inflected with Current Year concerns, but I haven’t found a better treatment in a book so it’s worth checking it out from the library if you’re interested.
2. I cheated with that “pots not people” line in my earlier email; it usually gets (got?) trotted out not as a bit of epistemological modesty about what the archaeological record is capable of showing, but as a claim that the only movements involved were those of pots, not of people.
April 4, 2024
QotD: What we mean by the term “indigenous”
February 1, 2024
Newfoundland – “We used to be a country”
In The Line, James McLeod outlines a difficult period for the Dominion of Newfoundland which ended up narrowly voting to join Canada rather than resume self-rule that they’d had up to 1934 when the Newfoundland House of Assembly abolished itself:

Great Riot of 1932 in front of the legislature, the Colonial Building, in Newfoundland.
Provincial Archives of Newfoundland and Labrador (Reference PANL A2-160), via Wikimedia Commons.
Before 1933, Newfoundland was proudly a dominion within the British empire. Under the Statute of Westminster, Newfoundland had the same legal status as Canada, New Zealand, South Africa and the Irish Free State.
Newfoundland was its own country. But it was a country in rough shape.
A year before the Amulree Report was published, a mob of about 10,000 people had gathered outside the Colonial Building in St. John’s. Families were living in destitution on six-cents-a-day government dole, and the government’s finance minister had just resigned and accused Prime Minister Richard Squires of personally lining his pockets with government funds.
The mob turned into a riot, which ultimately barged into the government building. Notably, the rioters briefly paused to observe a respectful silence when a brass band began playing “God Save The King”, but then they went back to rioting.
Squires fled on foot and went into hiding, and then emerged to call an election, which he lost in a landslide. During the campaign, one of his longtime allies, the prominent leader of the Fishermen’s Protective Union, openly wished for fascism.
“What is required for Newfoundland and what is most essential for the present conditions is a Mussolini,” said William Coaker.
Months later, with a new government, Newfoundland was on the verge of defaulting on its debt, and the British stepped in.
The vastly oversimplified version is that the British government was concerned that a member of the British Commonwealth defaulting on its debt could have major implications for the whole empire. So the British government bailed out Newfoundland, on the condition that a commission would be struck to investigate the island’s political and economic affairs. Lord Amulree, a British politician, was appointed as chair.
A year later, with the Dominion still teetering on the verge of bankruptcy, the Amulree Report was delivered. It contained this passage, with my emphasis added: “That it was essential that the country should be given a rest from politics for a period of years was indeed recognised by the great majority of the witnesses who appeared before us, many of whom had themselves played a prominent part in the political and public life of the Island.”
Amulree considered the possibility of some sort of national unity government, but could not get past the conclusion that, “Even if a National Government could be established on a basis which led to a suspension of political rivalry, the underlying influences which do so much to clog the wheels of administration and to divert attention from the true interests of the country would continue to form an insuperable handicap to the rehabilitation of the Island.”
In 1934, the Newfoundland House of Assembly voted itself out of existence. It was replaced by a “Commission of Government” which was just six unelected men, appointed by the British. Fifteen years later, Newfoundlanders narrowly voted to join Canada, although to this day conspiracy theories still linger about how democratic the referendum really was.
I am not a Newfoundlander, and I’m hesitant to make any sweeping statements about how Newfoundlanders relate to their own history. But for a decade, I worked as a journalist in St. John’s, covering politics and public affairs. The collapse of democratic self-rule in the 1930s still looms large in the collective identity of the province.
September 11, 2023
The tiny town that became a beacon of hope on 9/11
60 Minutes Australia
Published 12 Sept 2021The 20th anniversary of the September 11 attacks is understandably a time of deep sadness as the world remembers an act of evil that’s still hard to believe. But for some it’s also a chance to celebrate the opposite: kindness, compassion and the very best of humanity. In the mayhem of the day that saw terror raining from the skies, American airspace was shut down, and a tiny town in a remote part of north eastern Canada suddenly found itself the destination for commercial passenger aircraft ordered to land immediately. Seven thousand plane people with nowhere else to go were about to discover the delights of the wonderful community of Gander.
(more…)
July 1, 2023
The Newfoundlanders at Beaumont-Hamel
Vlogging Through History
Published 12 Feb 2022Just after the explosion of the Hawthorn Ridge mine, the 29th Division assaulted German positions at Hawthorn Ridge and the Y Ravine outside the village of Beaumont-Hamel, suffering dreadful losses. No unit suffered more in that attack than the Newfoundland Regiment, part of the third wave that morning. Join me as we visit the Beaumont-Hamel Newfoundland Memorial.
(more…)
October 10, 2021
Three Years in Vinland: The Norse Attempt to Colonize America
Atun-Shei Films
Published 9 Oct 2021Happy Leif Erikson Day! Some time after Thorvald Erikson’s disastrous voyage to the mysterious lands west of Greenland, a wealthy Icelander named Thorfinn Karlsefni financed and led an expedition of his own, with the goal of establishing a permanent Norse settlement in Vinland. Karlsefni and his crew would spend three summers in the New World, where they would have to deal with internal division, hostile Native Americans, and (according to some) the wrath of demonic mythological creatures.
Support Atun-Shei Films on Patreon ► https://www.patreon.com/atunsheifilms
Leave a Tip via Paypal ► https://www.paypal.me/atunsheifilms
Buy Merch ► https://teespring.com/stores/atun-she…
#LeifErikson #Vinland #History
Original Music by Dillon DeRosa ► http://dillonderosa.com/
Reddit ► https://www.reddit.com/r/atunsheifilms
Twitter ► https://twitter.com/atun_shei~REFERENCES~
[1] Magnus Magnusson & Hermann Pálsson. The Vinland Sagas: The Norse Discovery of America (1965). Penguin Books, Page 7-43
[2] Birgitta Wallace. “Karlsefni” (2006). The Canadian Encyclopedia [https://www.thecanadianencyclopedia.c..].
[3] Lorraine Boissonault. “L’Anse Aux Meadows and the Viking Discovery of North America” (2005). JSTOR Daily https://daily.jstor.org/anse-aux-mead…
July 31, 2021
English sea-borne trade in the early 17th century
In the latest Age of Invention newsletter, Anton Howes reviews a book on English trade … a very old book:
I’ve become engrossed this week by a book written in 1638 by the merchant Lewes Roberts — The Marchant’s Mappe of Commerce. It is, in effect, a guide to how to be a merchant, and an extremely comprehensive one too. For every trading centre he could gather information about, Roberts noted the coins that were current, their exchange rates, and the precise weights and measures in use. He set down the various customs duties, down even to the precise bribes you’d be expected to pay to various officials. In Smyrna, for example, Roberts recommended you offer the local qadi some cloth and coney-skins for a vest, the qadi‘s servant some English-made cloth, and their janissary guard a few gold coins.
Unusually for so many books of the period, Roberts was also careful to be accurate. He often noted whether his information came from personal experience, giving the dates of his time in a place, or whether it came second-hand. When he was unsure of details, he recommended consulting with better experts. And myths — like the rumour he heard that the Prophet Muhammad’s remains at Mecca were in an iron casket suspended from the ceiling by a gigantic diamond-like magnet called an adamant — were thoroughly busted. Given his accuracy and care, it’s no wonder that the book, in various revised editions, was in print for almost sixty years after his death. (He died just three years after publication.)
What’s most interesting about it to me, however, is Roberts’s single-minded view of English commerce. The entire world is viewed through the lens of opportunities for trade, taking note of the commodities and manufactures of every region, as well as their principal ports and emporia. A place’s antiquarian or religious tourist sites, which generally make up the bulk of so many other geographical works, are given (mercifully) short shrift. Indeed, because the book was not written with an international audience in mind, it also passes over many trades with which the English were not involved, or from which they were even excluded. It thus provides a remarkably detailed snapshot of what exactly English merchants were interested in and up to on the eve of civil war; and right at the tail end of a century of unprecedented growth in London’s population, itself seemingly led by its expansion of English commerce.
So, what did English merchants consider important? It’s especially illuminating about England’s trade in the Atlantic — or rather, the lack thereof.
Roberts spends remarkably little time on the Americas, which he refers to as the continents of Mexicana (North America) and Peruana (South America). Most of his mentions of English involvement are about which privateers had once raided which Spanish-owned colonies, and he gives especial attention to the seasonal fishing for cod off the coast of Newfoundland — a major export trade to the Mediterranean, and a source of employment to many English West Country farmers, who he refers to as being like otters for spending half their lives on land and the other half on sea.
But as for the recently-established English colonies on the mainland, which Roberts refers to collectively as Virginia, he writes barely a few sentences. Although he reproduces some of the propaganda about what is to be found there — no mention yet of tobacco by the way, with the list consisting largely of foodstuffs, forest products, tar, pitch, and a few ores — the entirety of New England is summarised only as a place “said to be” resorted to by religious dissenters. The island colonies on Barbados and Bermuda were also either too small or too recently established to merit much attention. To the worldly London merchant then, the New World was still peripheral — barely an afterthought, with the two continents meriting a mere 11 pages, versus Africa’s 45, Asia’s 108, and Europe’s 262.
The reason for this was that the English were excluded from trading directly with the New World by the Spanish. It was, as Roberts jealously put it, “shut up from the eyes of all strangers”. The Spanish were not only profiting from the continent’s mines of gold and silver, but he also complained of their monopoly over the export of European manufactures to its colonies there. It’s a striking foreshadowing of what was, in the eighteenth century, to become one of the most important features of the Atlantic economy — the market that the growing colonies would one day provide for British goods. Indeed, Roberts’s most common condemnation of the Spanish was for having killed so many natives, thereby extinguishing the major market that had already been there: “had not the sword of these bloodsuckers ended so many millions of lives in so short a time, trade might have seen a larger harvest”. The genocide had, in Roberts’s view, not only been horrific, but impoverished Europe too (he was similarly upset that the Spanish had slaughtered so many of the natives of the Bahamas, known for the “matchless beauty of their women”).
April 2, 2021
The science must bow to the political narrative yet again
In Quillette, Bruce Bourque outlines some fascinating archaeological discoveries on Canada’s east coast and how the scientific findings are being actively blocked to avoid offending First Nations people for undermining or even contradicting their beliefs:
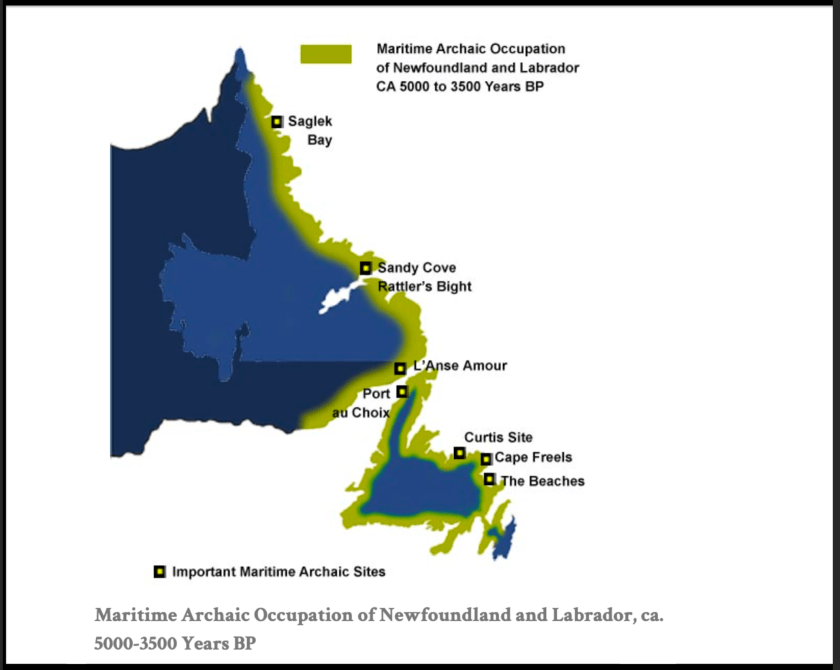
One of the major North American archaeological discoveries of the 20th century was made in 1967 by a bulldozer crew preparing a site for a movie theater in the small fishing village of Port au Choix (PAC), on Newfoundland’s Northern Peninsula. It was a vast, 4,000-year-old cemetery created by a complex maritime culture known among researchers as the Maritime Archaic. The graves contained beautifully preserved skeletons covered in a brilliant red powder called red ocher (powdered specular hematite). Buried with the skeletons were many finely crafted artifacts. A few similar ones had previously turned up in earlier field surveys on the island, but no archaeologist had suspected that such a large and magnificent ceremonial site existed in the North American subarctic.
Had the discovery been made only a few years earlier, it is likely that no trained archaeologist would have taken over from the bulldozer crew. But fortunately, Memorial University in St. Johns had just added archaeologist James (“Jim”) Tuck (1940–2019) to its faculty. The American-born scholar set out to explore the cemetery, eventually excavating more than 150 graves spread over three clusters (which he referred to as loci).
[…]
In regard to the Red Paint People, Reich’s lab at Harvard Medical School analyzed material from the Nevin site in Blue Hill, Maine — the only known Red Paint cemetery that is likely ever to produce well-preserved human remains. Reich’s analysis was not confined to mDNA (which, unlike nuclear DNA, is transmitted through the maternal line, and so cannot address paternal ancestry), and focused instead on autosomal DNA (aDNA) found in cell nuclei, thereby adding information on the paternal line. (This addition can be critically important because, as Reich’s lab had demonstrated, a population can be founded by males and females with very different origins.) The Reich team has yet to publish comprehensive results of its Nevin site analysis. But from what I have heard, their work will confirm the existence of genetic discontinuities between the Red Paint People and later populations in the region, much as with Duggan’s work in regard to the Maritime Archaic.
But this is where events took a strange turn: It was when Duggan’s group announced that they’d gained the capacity to analyze aDNA, and made known their plans to apply this technology to the male genome of their Labrador/Newfoundland skeletal sample, that a sense of apprehension seemed to spread through some quarters of the paleogenetic community.
During the summer of 2020, amid the COVID-19 pandemic and Black Lives Matter protests, Duggan’s project went noticeably quiet. I inquired among team members with whom I regularly communicated, but received oblique and evasive responses about the pace of research and publication. Suspecting that this might be related to sensitivities surrounding Indigenous populations (a topic that has consumed Canadian academia in recent years), I contacted Duggan directly, expressing concern that her valuable work might not be published.
[…]
When the Maritime Archaic tradition vanished, it was replaced, as noted earlier, by unrelated Paleoeskimos, an Arctic people who had then recently derived from Siberia. Following their own disappearance, more recently arrived inhabitants migrated from Labrador, these probably being ancestors of the historic Beothuk, who still lived in the region when Europeans arrived. The last surviving Beothuk, a woman named Shanawdithit, died of tuberculosis in 1829. And since that time, there has been no descendant Beothuk community with whom Duggan, or anyone else, could engage in the “discussions and agreements” she’d described to me.
And even if there were, moreover, Duggan’s own research has demonstrated that the Beothuk were not descended from the Maritime Archaic people of Port au Choix. The only community Duggan might be referring to is the (genealogically unrelated) Newfoundland Mi’kmaq community, whose ancestors arrived on Newfoundland from Nova Scotia in the 18th century, several hundred years after the arrival of Europeans.
February 18, 2021
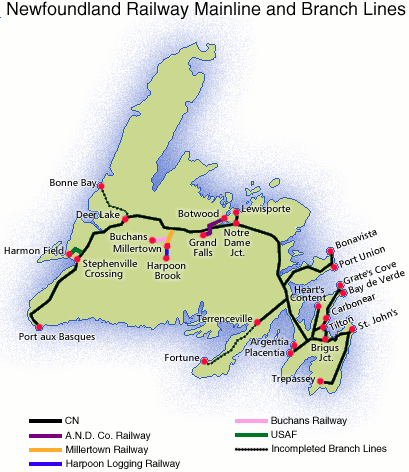
Fallen Flag — The Newfoundland Railway

Newfoundland played a pivotal role in World War II during the Battle of the Atlantic and as a staging point for ship convoys and aircraft movements. Construction of Allied bases and the associated movement of personnel resulted in a railway traffic surge. A British and Canadian airfield grew near the main line at Gander, and the United States also exploited Newfoundland’s relative proximity to Europe. The two largest American installations were a naval base at Argentia — site of the 1941 shipboard meeting between President Roosevelt and Prime Minister Churchill — and Harmon Field, an Air Force base on the west coast at Stephenville. Rail traffic was a barometer of wartime pressures; between 1941 and 1943, NR’s passenger count rose from 223,000 to 500,000; freight tonnage also doubled. So important was the line to American military interests that the U.S. government allocated $2 million of “lend-lease” funds for locomotive and car construction.
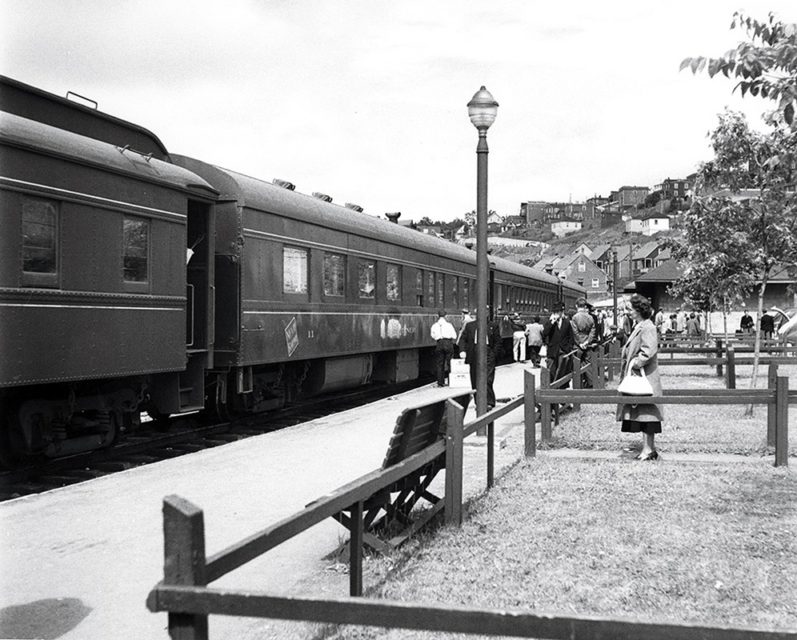
Newfoundland Railway’s Overland Limited (a.k.a. the “Newfie Bullet”) calls at Corner Brook in 1948, the year before CN took over.
Canadian National photo via Classic TrainsAlthough the war brought profits and a revitalized equipment roster, the railway was not immune from the conflict’s brutality. On October 14, 1942, the Port aux Basques–North Sydney (N.S.) ferry Caribou was torpedoed and sunk by a German submarine. Of 237 passengers and crew on board, 136 perished.
Canadian National control
Newfoundland’s 1949 entry into Canada saw responsibility for much of the transport infrastructure assumed by the Canadian government, whose Canadian National Railways was charged with the management and operation of the railway, as well as coastal steamship services and the ferry link to Nova Scotia. The federal government agreed to subsidize the operations. Despite wartime profits and some postwar rebounds, though, the railway had been and would continue to be a chronic money-loser.
Newfoundland Railway was exclusively steam-powered for all but the final seven months of its pre-Confederation existence, as GE 47-ton center-cab diesels 5000–5002 arrived in August 1948. The last new NR locomotives were class R-2-d Mikados 324–329, built by Montreal and delivered just weeks before Confederation. They became the youngest steam locomotives, by five years, on the entire CNR. In all, four 4-6-0s, a 2-8-0, 10 4-6-2s, and 30 2-8-2s were conveyed to CN.
[…]
Well into the 1960s, the railway provided the only land link spanning Newfoundland. When the first road across the island opened as part of the Trans-Canada Highway in late 1965, it triggered an irreversible shift of traffic off the railway. In the highway’s first 15 years, the percentage of island freight handled by train dropped by more than half. More than 24 hours — double the road time — was required for the St. John’s–Port aux Basques rail trip, and that was if the trains ran on time, a spotty prospect especially in winter.
Passengers benefitted from CN’s continued investment in rolling stock, although the non-air-conditioned fleet couldn’t provide mainland comfort levels. The principal pre-Confederation passenger train was the overnight Overland Limited. CN renamed it Caribou in 1950, a fitting tribute to the ferry lost in 1942. To most folks, though, the train was known from the war onward as the “Newfie Bullet,” a wry reference to its leisurely schedule (daily in summer, triweekly the rest of the year). Although CN buses replaced the “Bullet” in July 1969, mixed trains kept serving isolated mainline points and the Carbonear, Bonavista, and Argentia branches.
From the Wikipedia entry on the post-abandonment fate of the line:
The former Newfoundland Railway station in St. John’s now hosts the Railway Coastal Museum. Numerous towns across the island have preserved railway equipment on display.
With few exceptions, the roadbed now forms the T’Railway Provincial Park rail trail. Until 2005, the Trinity Loop Amusement Park operated a miniature train, one of the few remaining places on Newfoundland with tracks still in place. The park closed down and was abandoned in 2005 due to lack of interest. Since then, all of the buildings have been heavily vandalized and Hurricane Igor washed away part of the park, including a large section of the rail bed. Local railway fans have been pushing government to retain the park as an historic site but officials have expressed little interest.
Some rolling stock was converted to a narrower gauge of 914 mm (3 ft) and sold to the White Pass & Yukon Route (WP&YR) railway, which reopened for service in 1988. Gravel cars used by WP&YR are still painted in CN orange; unconfirmed information indicates that some Newfoundland passenger cars were converted into passenger cars of vintage appearance for WP&YR.
December 16, 2020
Storm in the Labrador Sea
Draken Harald Hårfagre
Published 20 Aug 20168 minutes with the amazing Draken Viking Ship. This is the film we showed in our exhibition tent on the festivals around the Great Lakes, filmed between Greenland and Newfoundland on the crossing of the North Atlantic Ocean.
November 12, 2020
The history of Canada explained in 10 minutes
Epimetheus
Published 19 Jan 2019The history of Canada explained in 10 minutes
Support new videos on this channel on Patreon! 🙂
https://www.patreon.com/Epimetheus1776Canadian history from the discovery of the Vikings to the French and English colonization until modern times.
Tags:
Canadian history documentary, Canadian history crash course, Canada history, history of Canada documentary, history Canada summarized, Canada, history, Canadian history, Canadian American history, animated history of Canada, canadian history in a nutshell, canadian history for kids, educational, Canada Indians, Canada great Britain, English Canada, Quebec, French Canada, French English Canada,
October 10, 2020
When Vikings Met Native Americans: The Voyage of Thorvald Erikson
Atun-Shei Films
Published 9 Oct 2020Happy Leif Erikson Day! After Leif’s discovery of unknown lands to the west of Greenland, his brother Thorvald set off on an expedition of his own. Thorvald’s voyage, as related in the medieval Icelandic text The Saga of the Greenlanders, marks the first time in recorded history that Europeans came face-to-face with Native Americans. In this video, I regale you with this tale of adventure, exploration, and cultural collision. And for some reason, I spend about a third of the video talking about a bowl, a coin, and some yarn made of goat hair.
Support Atun-Shei Films on Patreon ► https://www.patreon.com/atunsheifilms
Leave a Tip via Paypal ► https://www.paypal.me/atunsheifilms (All donations made here will go toward the production of The Sudbury Devil, our historical feature film)
Buy Merch ► teespring.com/stores/atun-shei-films
#LeifErikson #Vinland #History
Original Music by Dillon DeRosa ► http://dillonderosa.com/
Reddit ► https://www.reddit.com/r/atunsheifilms
Twitter ► https://twitter.com/atun_shei~REFERENCES~
[1] Magnus Magnusson & Hermann Pálsson. The Vinland Sagas: The Norse Discovery of America (1965). Penguin Books, Page 59-61
[2] Sîan Grønlie. The Book of the Icelanders / The Story of the Conversion (2006). Viking Society for Northern Research, Page 4
[3] Ingeborg Marshall. “Beothuk Transportation” (1998). Heritage Newfoundland and Labrador https://www.heritage.nf.ca/articles/a…
[4] Patricia Sutherland. Dorset-Norse Interactions in the Canadian Arctic (2000). Canadian Museum of Civilization, Page 2-9
September 7, 2020
Who Was Leif Erikson?
Atun-Shei Films
Published 9 Oct 2019Happy Leif Erikson Day! Allow me to regale you with the saga of the daring Viking who sailed to North America five hundred years before Columbus (that hack) and called it Vinland. We all know his name and his famous deeds – but what sort of man was Leif Erikson?
Support Atun-Shei Films on Patreon ► https://www.patreon.com/atunsheifilms
#LeifErikson #Viking #History
Watch our film ALIEN, BABY! free with Prime ► http://a.co/d/3QjqOWv
Reddit ► https://www.reddit.com/r/atunsheifilms
Twitter ► https://twitter.com/alienbabymovie
Instagram ► https://www.instagram.com/atunsheifilms
Merch ► https://atun-sheifilms.bandcamp.com
August 16, 2020
February 20, 2020
So that’s why John Cabot got hired!
Anton Howes explains something that I’d wondered about in the latest edition of his Age of Invention newsletter:
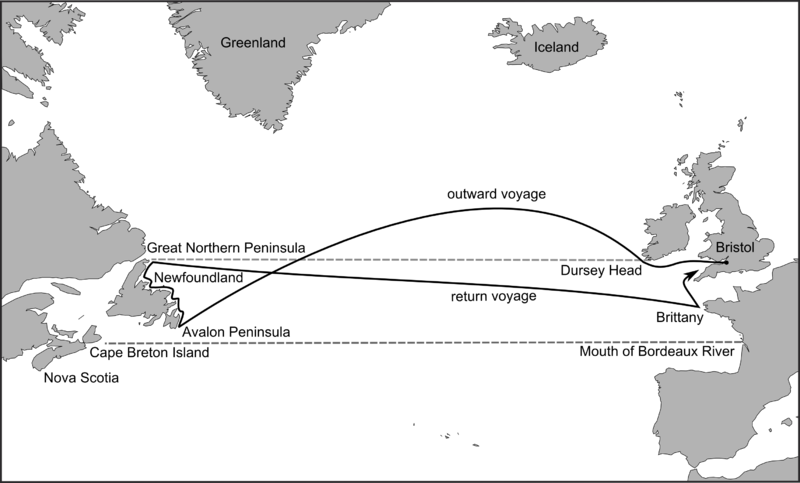
Route of John Cabot’s 1497 voyage on the Matthew of Bristol posited by Jones and Condon: Evan T. Jones and Margaret M. Condon, Cabot and Bristol’s Age of Discovery: The Bristol Discovery Voyages 1480-1508 (University of Bristol, Nov. 2016), fig. 8, p. 43.
Wikimedia Commons.
… in 1550 the English were still struggling with latitude. Their inability to find it, unlike their Spanish and Portuguese rivals, was one of the main things holding them back from voyages of exploration.
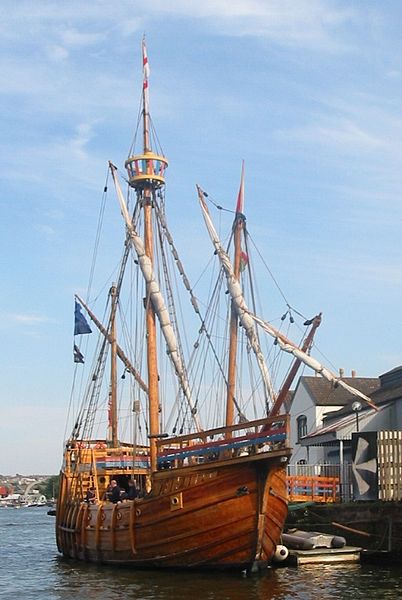
The replica of John Cabot’s ship Matthew in Bristol harbour, adjacent to the SS Great Britain.
Photo by Chris McKenna via Wikimedia Commons.The traditional method of navigation for English pilots was to simply learn the age-old routes. They were trained through repetition and accrued experience, learning to recognise particular landmarks and using a lead and line – just a thin rope weighted with some lead – to determine their location from the depth of the water. Cover the lead with something sticky, and you might bring up some sediment from the sea floor to double-check: a pilot would learn the kinds of sand and pebbles from to expect from different areas. And when they travelled out to sea, away from the coastline, they used a basic system of dead reckoning, taking their compass bearings from a known location, estimating their speed, and keeping in a particular direction for long enough. Or at least hoping to. They might keep track of their progress on a wooden traverse table, inserting pegs to indicate how far they had sailed, but it was ultimately a matter of rough estimation. Should they make any mistake — in terms of their speed, heading, or point of departure — they might easily get lost. But it was still a matter of trying to follow an already-known route. And English mariners of the 1550s did not even know that many routes.
For a voyage of exploration, by contrast, landmarks and sediment from the sea floor would be seen for the first time rather than recalled. By definition, there was no route to follow. So to launch their own voyages of discovery, the English needed to learn a new skill. They needed to look to the heavens.
Celestial navigation — measuring the altitude of heavenly bodies and then using geometry to determine one’s latitude on the earth’s surface — was by the 1550s already hundreds of years old. It had primarily been used to cross the deserts of North Africa and the Middle East — seas of sand, in which there might also be no landmarks from which to take bearings — and to navigate the Indian Ocean. Thus, while pilots in the Atlantic and the Mediterranean stuck to dead reckoning and soundings, Islamic navigators had for centuries used quadrants and astrolabes to take their bearings at sea. By the mid-fifteenth century, these instruments and techniques had found their way to Europe, where they were put to use especially by Portuguese, Spanish, and Italian explorers, along with additional instruments such as the cross-staff.
[…]
So for decades, English explorations relied on foreigners who either knew the routes that the English pilots didn’t, or who at least possessed the skill of mathematical, celestial navigation. The Italian explorer John Cabot (Zuan Chabotto), when he sailed to Newfoundland from Bristol in the late 1490s, was able to take latitude readings (he may even have been familiar with the older Islamic navigational practices, as he claimed to have visited Mecca). When Cabot died, the English expeditions that set out from Bristol in 1501-3 relied on Portuguese pilots from the mid-Atlantic islands of the Azores. And John Cabot’s son, Sebastian Cabot, who was involved in a few English expeditions, was so expert in mathematical navigation that he was eventually appointed pilot major for the entire Spanish Empire, making him responsible for the training and licensing of all its pilots — a position he held for three decades. When he led a voyage of exploration on behalf of Spain in 1526-30, a few English merchants became investors so that they could justify sending with him an English mariner, Roger Barlow, to secretly learn the Spanish routes across the Atlantic and have immediate knowledge if an onward route to Asia was discovered (as it turned out, South America got in the way).
November 29, 2019
England’s early search for new markets
In the latest installment of Anton Howes’ Age of Invention, he looks at the multiple crises that afflicted England in the mid-sixteenth century and some of the reactions to those setbacks:
Ships from the period of John Cabot (Giovanni Caboto) and Jacques Cartier.
Illustration by Thomas Wesley McLean (1881-1951) via Wikimedia Commons.
From the 1540s through to the 1560s, [England] was beset by religious uproar, high inflation, hunger, rural and then urban unemployment, a fall-off in its major export trades, and widespread unrest. It was diplomatically isolated too. And I did not even mention the epidemics: the terrifying “sweating sickness” returned in 1551, deadly influenza swept the country in 1557, and in 1563 some 17,000 people in London were reportedly killed by the plague.
Yet, in the face of such problems, innovation in England began to pick up pace. The country, having once been a scientific and technological backwater, began to show signs of catching up. Why?
[…] The fall-off in trade with Europe, for example, seems to have had something to do with spurring the voyages of exploration in search of a north-west and north-east passage to the East Asia. Having lost Antwerp as a place to sell cloth in 1551, the English went in search of an arctic route to northern China and Japan. The expert geographers believed that those regions had a similar climate to that of Antwerp and the surrounding Netherlands, and so reasoned that the Japanese would therefore demand the same kinds of cloth. Although the English expeditions from 1553 onwards did not find a passage to Japan, they did establish trade routes with Russia via the White Sea, and they began to more actively consider the exploration and colonisation of North America. More importantly, with those voyages of exploration came greater experience of navigation, and it was not long before English ships were circumnavigating the globe (Francis Drake in 1577-80). Improvements to navigational techniques and instruments, as well as the ships themselves followed.
So it is tempting to think that necessity was initially the mother of invention, and that the many navigational and shipbuilding improvements of late-sixteenth-century England were its result. But I don’t think that this narrative quite works. I do not believe that necessity was the mother of invention.
For a start, voyages of navigation had already been attempted a number of times, long before the more successful ones in the early 1550s. The first explorers had reputedly gone west from Bristol in 1465, and certainly from 1480. And soon after the announcement of Columbus’s discoveries in the 1490s, the Venetian Zuan Chabotto (aka John Cabot), had sailed from Bristol with Henry VII’s blessing and claimed Newfoundland for both crown and Catholicism. Cabot had even hoped to found a penal colony on his second voyage in 1497, though for some reason the king did not provide the criminals. Throughout the early sixteenth century, the voyages continued. John Rastell, brother-in-law to Thomas More, the famous statesman and author of Utopia, in 1517 went in search of a north-west passage (though he never got beyond Ireland, because his crew decided it would be better to leave him there and sell the ship’s cargo in Bordeaux). Yet another voyage went west with Henry VIII’s support in 1527, but it mostly just found other Europeans — fishing fleets from Spain, Portugal, and France off the coast of Newfoundland (the English had made some catches there in the early 1500s, but apparently could not compete), and the Spanish everywhere else. The expedition made its way down to the Caribbean and then went home, with little to report. So people had already gone off exploring, long before the mid-sixteenth-century English commercial crisis. It suggests that there had already been both a latent supply and demand for such explorations.