Another anonymous book review at Scott Alexander’s Astral Codex Ten considers The Weirdest People in the World: How the West Became Psychologically Peculiar and Particularly Prosperous by Joseph Henrich:
Coming as he does from the scientific side of the aisle, Henrich isn’t just going to tell a story. He has a hypothesis about an empirical puzzle. The puzzle is the most important question, the big one, the one that once you think about it’s hard to think about anything else, the economists’ Holy Grail since Adam Smith: why are some countries rich and others poor?
His hypothesis comes from cross-cultural psychology. The West got rich because Westerners are different. People from Western, Educated, Industrialized, Rich and Democratic societies are WEIRD – the acronym comes from a previous article of his. In particular, compared to everyone else in the world and in history, modern Westerners:
- Are individualist, not collectivist or conformist
- Feel more guilt and less shame
- Explain people’s actions by their innate dispositions, not their social role
- Reason analytically not holistically
- Follow more universal norms and less relationship-specific norms
- Are more patient
- Trust strangers more and are more honest.
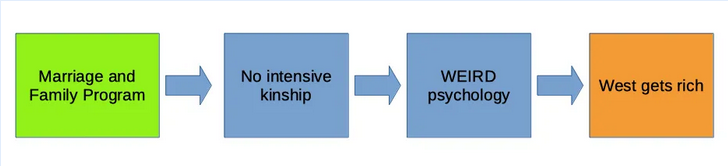
This psychology might make societies richer, for fairly well-known and plausible reasons. The Weirdest People in the World (henceforth just WEIRD) sets out a causal chain from cultural change to psychological change to modern economic growth. The start of that chain is surprising: an obscure set of rules pushed by the medieval Catholic church, which banned marriage between cousins. The most important argument of the book is that these rules created WEIRD psychology.
How it worked: these marriage regulations served to dismantle intensive kin networks, which are the social cement of society almost everywhere else in the world. For most people in history, family hasn’t just been the place where children grow up and couples spend time together. Family has been the basic human group, and there have been extensive and precise rules dictating who counts as family (or clan) and how each person should act with respect to different relatives. The Church’s regulations, the Marriage and Family Programme (MFP), aimed to replace intensive kinship, and over many centuries it was more or less successful in doing that. We’ll come back shortly to why it wanted to.
So, the causal chain looks like this:1
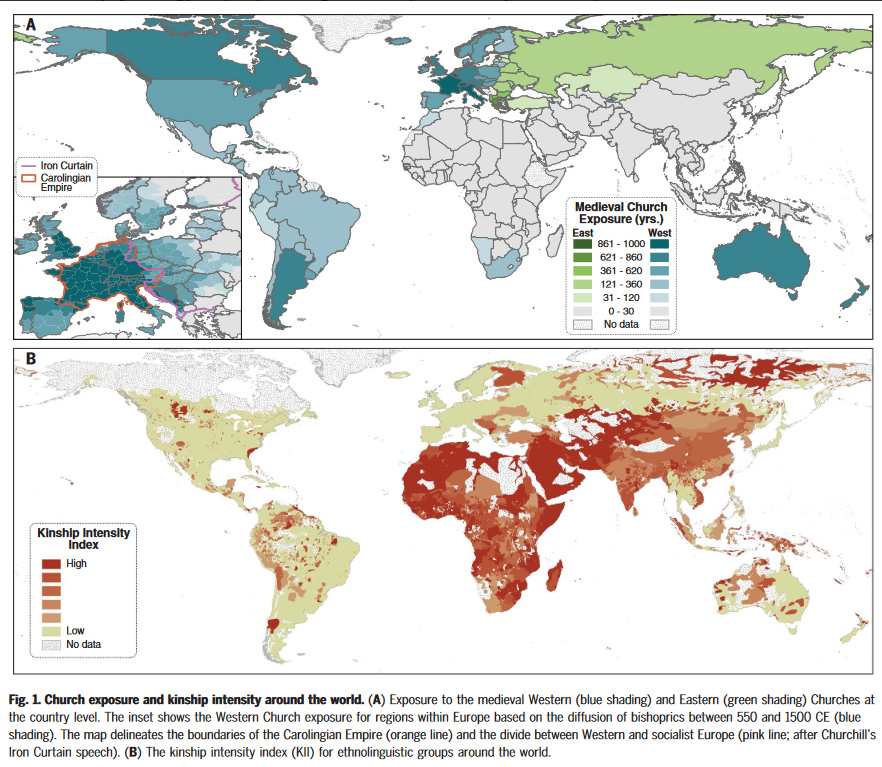
WEIRD‘s key evidence is the link between the places where the Church promulgated the MFP and a set of psychological and social outcomes: the level of cousin marriage, the psychology of people living in those places today, social capital and economic growth. This is the scientific story of European history, and Henrich’s answer to the most important question in the world.
These maps from one of the scientific articles behind WEIRD show the basic causal claim: the medieval church reduced the intensity of kinship institutions.
He tells it with an extraordinary mastery of a very wide range of sources from anthropology, psychology, behavioural economics, economic history, and historical narrative. This book is for everyone, but the connoisseur will enjoy the bibliography: if you think it’s important and relevant, it’s probably in there, and there was also plenty of work which I did not know, and now feel I should. It takes a very smart person to keep this many balls in the air. Being at Harvard probably doesn’t hurt either – that’s the “collective brain” of the human network, which makes an appearance later on in the book.
So this book really sets down a marker: the anthropologists are returning from the Amazon, the Sudan and Polynesia, and coming for Western history and economics. It will be interesting to see how those target disciplines react.
Is it true?
Economists and historians think about Western history very differently.
Historians love irony and contingency. They enjoy byways. Triumphalist, linear narratives of progress are distrusted as “Whig history”. Growth economists, by contrast, are all about the linear bigness. They have a relentless focus on the one question of how the West got rich, and if you call that triumphalist, they will take out a chart of South Sudanese child mortality and laugh at you.
Both historians and historical economists — a more appropriate name than “economic historians” nowadays — are interested in causality. But economists have a crunchier, more “scientific” standard for what counts as proof of causality. You’ve got to have a treatment and a control group, and by default if you claim there are no confounds, they won’t believe you. You need you some plausible exogeneity. A random river where Napoleon’s armies stopped. The distance from Wittemberg where Luther nailed up his theses. And then, how does that affect something that matters today (if it doesn’t, then who cares?) Of course, the longer ago the exogenous treatment, the more impressive the result.
You can see the incentives that these disciplinary demands might set up, and that might worry you. At worst, you might get a kind of “underground river” concept of history, where
- X happened long ago
- [underpants gnomes whispering]
- Y is correlated with X today
Indeed this does seem to skip all the interesting, contingent bits:
On the other hand, if you want to explain an all-important outcome like the take-off into modern economic growth, then you can’t just mumble “one damn thing after another” or “irony and contingency”. That a hundred things randomly conspired to make the West Educated, Industrialized, Rich and Democratic is not a satisfying story. Why would the die rolls keep favouring this one place? (And you can’t invoke the law of large numbers. There are only five continents in the world, and modern economic growth did not have to happen anywhere at all.)
1. It’s a bit more complex than that. In particular, the end of intensive kinship directly helps economic growth because it clears the way for voluntary associations to thrive. But the psychology angle is what’s really unique to WEIRD – in particular, Francis Fukuyama has previously argued that kin institutions might be a problem for higher-level cooperation.