Discussing anything to do with the Russo-Ukraine war is difficult enough due to the signal-to-noise ratio in the information we get from both sides and (theoretically) disinterested observers. Trying to read the tea leaves in the events over the weekend was just an utter waste of time, despite the potentially earth-shaking possibilities being thrown up. The weekend dispatch from The Line doesn’t pretend to have any deep analysis to offer, which I think is by far the wisest approach:

“Sir Humphrey Appleby” tweeted this, saying it was “the intelligence update slide every DI analyst secretly dreams of producing …
As we write this, roughly a day has passed since the sudden end of what briefly looked like a massive event with the potential to reshape global politics for a generation … before it fizzled. The rebellion of Russia’s Wagner mercenary group and its bolt toward Moscow was a stunning story, until it wasn’t. And that itself is a stunning story. Yevgeny Prigozhin, former chef and now Wagner leader, suddenly called off his mutiny, and it just … ended.
Really?
When the mutiny began on Friday, and especially when Wagner seized the southern city of Rostov, home to a major Russian military headquarters overseeing the invasion of Ukraine as well as a million other people, we were surprised, but the more we thought about it, we weren’t particularly shocked. There had been obvious signs of an imminent rupture of some kind in recent months; Line editor Gurney had wondered on Twitter how long it could last before something snapped. That was about three hours before the entire country seemed to snap and Prigozhin marched into Rostov and began moving north.
Events proceeded at a fairly frantic pace after that, with Wagner troops advancing almost all the way to Moscow while Russian security forces fortified the city and tore up roads along the route. It wasn’t clear to us that Wagner had enough men to actually take the city and potentially capture key members of the government. But it wasn’t clear that he didn’t: there are two sides of that equation — the troops Prigozhin had and the troops Putin could count on to oppose Wagner. It was the latter group that captured our interest.
Wagner encountered some resistance along the way, but not much. Most of Russia’s army is deployed in Ukraine, of course, and much of what’s left is now of famously poor quality and morale. But even those military and security forces that were able to block Wagner’s advance didn’t seem that interested in the job. There are reports that some units went over to Prigozhin’s side, but it seems that most of them just did … nothing in particular. And waited to see what happened. For a few hours, we wondered if Prigozhin’s small force would be just large enough in the face of a Russian military that seemed to have no appetite for battle on its own soil.
We can’t pretend to explain the bizarre conclusion to this chaotic day and a half, with an apparent deal brokered by Belarus seeing Wagner’s advance on Moscow called off, a broad amnesty granted to all participants and Prigozhin apparently set to continue to oversee Wagner’s global operations from Belarus in some kind of exile. This is all just wildly unrealistic. Prigozhin cannot be the last person around to realize that he’s put a target on his back and that he’ll soon experience some kind of fatal medical emergency or tragic tumble out of an open window. The moment his mercenaries took Rostov, he had only one path forward: all the way to the Kremlin. What the hell he’s thinking is frankly beyond our ability to guess, and we have fairly vivid imaginations. It’s baffling.
Nor will we try to guess what this will mean for Russia. In a situation like this, your Line editors would normally simply confess that we don’t have the deep knowledge of Russian domestic politics to turn ourselves into credible instant-experts on this. We’d seek out someone with that knowledge. We could interview them, solicit a column from them, or even — as we’ve done in the past — allow someone with deep expertise but who isn’t permitted to speak on the record in public to provide a blurb for one of these dispatches, to run under our shared byline. But in this case, we had to reject all those options, because at least for right now, all the experts seem as baffled as we are. No one seems to understand what the hell just happened in Russia.
We can say with at least reasonable confidence that if you happen to be named Vladimir Putin, it isn’t good. When Prigozhin announced that he was ending his mutiny and began withdrawing his forces from Rostov, the locals cheered them like some kind of conquering heroes. That’s gotta be on Putin’s mind. Also on his mind: the apparent, ahem, reluctance of much of his military and domestic security force to rally to his side during the crisis. This has wounded Putin. Time will tell how badly. Time will also tell how many other people in Russia today have carefully watched recent events, have adjusted their understanding of the facts on the ground there, and are now pondering a variety of intriguing options accordingly.
And the last thing time will tell is what Putin feels he must now do to assert his authority, such as it is. We must recall that whatever Putin’s domestic troubles, he has problems on the battlefield, too. While we haven’t yet seen major breakthroughs by Ukrainian forces, they are not yet fully committed, and their counteroffensive does seem to be making gradual progress in multiple sectors. Events of recent days can only hurt Russia’s combat performance and morale.
We wish we could offer you all a more firm and decisive statement to wrap all this up. But the best we can honestly promise you is that we’ll keep pondering this, trying to figure out what the hell happened, and we’ll certainly be watching this. It’s been a strange war. And we suspect it might get stranger still before it finally ends.
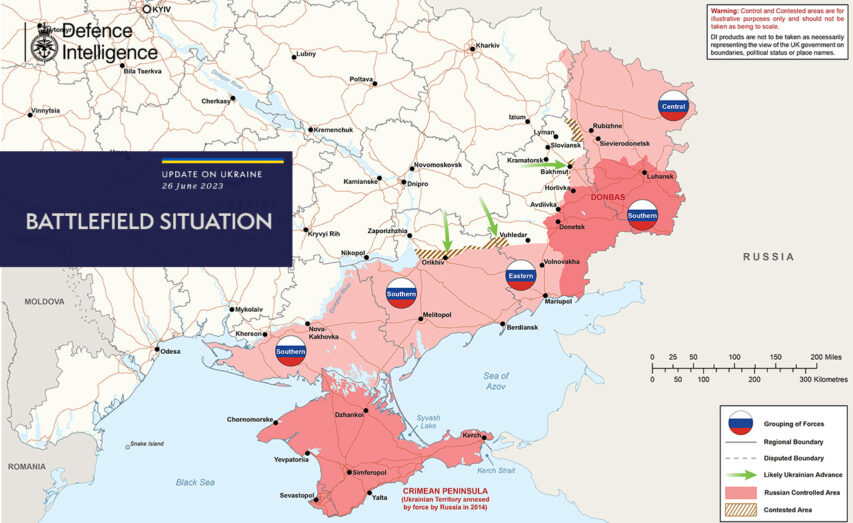
The most recent Defence Intelligence update map from the British Ministry of Defence shows what is thought to be a reasonably accurate representation of the battlefront in eastern Ukraine: