What lessons can we draw from this book [The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire by Edward Luttwak] for today? There are many, but I will leave you with one. Reading about the Roman client state system gave me an uncomfortably familiar feeling. Can we think of another empire that outsources governance to vestigial polities that pretend to be sovereign, and even get called “allies”, but are actually clients? An easy example is the Warsaw Pact. A more controversial one is present-day America and her dependencies. Consider Canada: a normie friend of mine once remarked that Canada pretended to be an independent country, but that if the present world were translated into a computer strategy game its territory would be shaded in the same color as America’s. Indeed, Canada’s sovereignty is exceedingly virtual — it exists only so long as it isn’t tested, just like the sovereignty of a Roman client. Canada is self-governing and self-administering, it passes its own laws and collects its own taxes. But if its foreign policy objectives ever diverged one micrometer from America’s, then Canada would cease to exist. Seriously, imagine Canada offering to host a Chinese or Russian military base and what would immediately occur. There is a real sense in which America rules the land that we know as “Canada”, but has outsourced governance to local elites in a highly federalized structure.
Luttwak has a charmingly racist bit about how some client states have the IQ and sophistication to understand the true nature of the arrangement, while others are too dumb or barbaric to remember who’s boss without having their faces regularly rubbed in it. In the Roman case, the former camp contained the various Hellenistic kingdoms in Asia Minor and the Levant, who didn’t need legionaries standing around and supervising them, because they could imagine the existence of those legionaries and what they would do to them if provoked. The latter camp included many of the Germanic tribes, who tended to forget their place if the legions weren’t garrisoned within eyeshot, and even then would rise up in fruitless rebellion every couple of generations. We can make this marginally less racist by positing something more like a spectrum of how tolerable the client arrangement was, and consequently a spectrum of how coercive it had to be. The Greeks were relatively compatible culturally with the Romans, and the warrior spirit of their ancestors had been sufficiently sanded down that they didn’t mind being told what to do. The Germans were more foreign, and also retained the barbarian’s yearning for freedom, so a careful eye had to be kept on them.
A true cynic might think that there was something similar going on with America’s imperial dependencies … sorry, with America’s “allies”. There are no American garrisons in Canada, because the Canadians are culturally-compatible, and also because they’ve been thoroughly cowed and do not dream of an independent national destiny. But look overseas, for instance at some of our Middle Eastern “allies”, and you will see a situation more analogous to the Germanic tribes. What a coincidence that these same “allies” host a much heavier American military presence! Even here, however, the situation isn’t strictly coercive, and insofar as it is, the coercion is mostly outsourced to local elites. Those elites, in turn, can mostly be handled with carrots: the imperial power subsidizes their trade and security arrangements, not to mention keeps them in charge of their respective countries! The Romans commonly rewarded loyal clients with citizenship and a cushy sinecure for a job well done. It would be rude of us to do otherwise.
Maybe this was already obvious to everyone else, but reading the “rules-based international order”1 as a concealed hegemon/client system feels a bit like having the skeleton key to understanding current events. Like why do European countries so often act in ways contrary to their own economic or geopolitical self-interest, but consonant with America’s interest? How do the political and business elites of these countries maintain such an impressive unified front in the face of popular discontent? Why do the rulers of all these very different countries have seemingly identical tastes, worldviews, and mannerisms? What is the meaning of “populism,” and why do people treat it like it’s a single, consistent thing, despite the fact that “populist” parties in different countries often seek diametrically opposite policies?
Just pretend, imagine with me, that these European “allies” are client kingdoms. They are permitted a certain amount of latitude, but when the chips are down they do not have an independent foreign policy. Their ruling classes are client rulers that administer certain territories, and there is tacit agreement with the imperial overlord on what they may and may not do. Over time, the client rulers identify less and less with their countrymen, more and more with their counterparts in other client states, and most of all with the distant metropole, whose social approval they desperately desire. The “populists” are simply the anti-imperial party, in whatever country. The thing the “populists” have in common is a desire to be free of the suffocating imperial embrace,2 but they all have a thousand different stupid ideas about what to do with that freedom. This includes the “populists” in the United States itself, by the way. The American Empire is called that because it started here, but it has long-since burst free of the host in which it incubated, and the rot of our own political institutions can be understood as our transformation into the biggest client kingdom of them all.
None of what I’ve said above is meant to be a value judgment. I think many people resist the notion that America is an empire because empires are “bad” and we’re obviously the good guys. But others, including myself not too long ago, resist it because we have an overly-simplistic notion of what an empire looks like, especially what it looks like from the inside. Empires exist on a spectrum — America’s subjects certainly have more ability to act independently than Rome’s did. But many empires also go to some lengths to conceal their true nature. Around the time of the birth of Christ, the official story in many of the lands ruled by Rome was that Rome was merely their largest trading partner and a staunch military ally. Some of them might even have believed it.
John Psmith, “REVIEW: The Grand Strategy of the Roman Empire by Edward Luttwak”, Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf, 2023-11-13.
1. The rules-based international order which has no rules, isn’t based, and opposes order.
2. They may also have in common the payments made to their bank accounts by the empire’s enemies.
February 17, 2024
QotD: Lessons for today from the decline of the Western Roman Empire
February 16, 2024
February 12, 2024
Find Me The Votes
Elizabeth Nickson has a giggle while reading through Find Me The Votes by Michael Isikoff and Daniel Klaidman, which presents the other side of the narrative about Bad Orange Man trying to steal the election in Georgia in 2020:
I admit I giggled all the way through the research of this, breaking out in helpless laughter by the end, hoping that I wasn’t going completely mad. First it was the book, Find Me The Votes, written by Michael Isikoff and Daniel Klaidman, about the Crazed Crackers who think the Georgia election was stolen and the Noble Black Woman who was putting things to right.
I persisted in calling the book in my head, The Ballad of Fani Willis, and kept waiting for the melody and lyrics, but I am not a musician and only the title came. Annoyingly, on repeat.
Isikoff, most remembered for writing for Newsweek when it was respectable, and others when they were respectable, is now head of Yahoo News, and has gone completely bonkers with Trump Derangement Syndrome. His associate in This Noble Task wrote, I believe, the first third which was all about the Noble Black Woman and her Noble Career and her Noble Father who was an entirely nice and not-murderous-at-all Black Panther, and how she felt that the massive uptick in violent crime in Atlanta should not take precedence over fighting the Crazed Crackers whose Awful Leader was Donald Trump. Fani gets the full-on-dripping-sentimentality treatment invented by Bill Clinton, her nobility and hard work, and wonderfulness and Godliness percolates all the way through it. I love how complete atheists like Isikoff like to work the God angle thinking that evangelicals will fall under his dark spell. Yeah, it just makes you look sleazy, buddy.
Willis thought her RICO case was her ticket to the Big Show. The White House. The First Noble Black Woman President of the United States of America. Apparently the Georgia Senate gathered the same and charged her with 23 Articles of Impeachment, mostly having to do with using said RICO case for her political career, not to mention paying the inexperienced, still-married, lover-lover $625,000 over 18 months. Charged with “the misuse of her office for political gains rather than the pursuit of justice”, this really needs a western ballad, with a zydeco vibe.
The second part introduced me to Trump Derangement Syndrome, which I mostly have managed to avoid. God in heaven this is awful stuff, purely hate-fueled madness. This part was written by Isikoff and I’d bet a million bucks he was drunk or on edibles all through it. In my opinion. Anyway, he trots out the usual villains and their wild accusations NONE OF WHICH HAVE ANY MERIT WHATSOEVER. THE ELECTION WAS NOT STOLEN. THIS IS ALL RIGHT WING GARBAGE. Even Rudy Guiliani who shut down the Mafia plaguing New York and managed New York through 9/11 is treated with zero respect and a lot of hateful mockery that anyone on the right is not allowed to use because hate, but lefties can express virulent hate all day with impunity.
February 7, 2024
“China is a food-obsessed society”
If your initial reaction to the headline is to assume this is because of the amazingly unsettled history of mainland China over the last several hundred years and the totally understandable fear of famines, I’m with you, but we’d both be wrong, as John Psmith explains:
One sunny December morning years ago, Jane and I were on holiday in the South of China. Far from the city, a little temple had been hewn out of a seaside grotto so that it partially flooded when the tide came in. We stood inside and gazed up at a statue of 觀音, “Guan Yin”, the lady to whom the temple was dedicated. Her legend originated in India, where she was known as the bodhisattva Avalokitasvara, but she’d been absorbed and appropriated by Chinese folk religion many centuries ago, and in this statue there was no trace to be found of her South Asian origins. A minute or two into our reverie, a local came over to us and, seeing that we looked out of place, helpfully explained in unaccented English, “This is one of the most important Christian goddesses.”
The Chinese are almost as bad as the Romans were about pilfering the deities of their neighbors, so you really can’t blame them when they occasionally get confused about who they stole them from. As with goddesses, so with food: earlier that day a different helpful local had steered us towards a restaurant specializing in “Western cuisine”. The menu listed steaks “French style”, “German style”, and “Barbecue style”. Soup options included minestrone and borscht, both of them with the surprise addition of prawns. Their pride and joy, however, was their breakfast menu which included roughly seventy different varieties of toast. The chef told me that there were restaurants in Europe and America that did not have so many kinds of toast, and beamed with pride when I nodded gravely. One of the diners, delighted to see real living and breathing Westerners in her local Western restaurant, told me: “The thing I love about this place is that it’s so authentic.”
This “Western” restaurant may sound ridiculous to you, but it’s only as ridiculous as most of the “Chinese” restaurants you’ve encountered in the West. First of all, there’s no such thing as “Chinese” food. China is a country, but it’s the size of a continent, and it boasts a culinary diversity which exceeds that of many actual continents. Second, the dishes you encounter in the average Chinese restaurant over here bear about as much resemblance to real Chinese food as the seventy varieties of toast and the barbecue steaks do to French cuisine. “American Chinese food” is an interesting topic in its own right, and there are some good books about it, but now that I’m through the mandatory throat-clearing you have to do when writing about Chinese cuisine for a Western audience, I’m never going to mention it again.
China is a food-obsessed society. People are always talking about their next meal. People talk about it incessantly. The Chinese equivalent of talking about the weather, a way of making polite chitchat with strangers, is to mention a restaurant that you like, or a meal that you’re looking forward to. A standard way of saying “hello” in Mandarin is “你吃饭了吗?” In Cantonese it’s “你食咗飯未呀?” Both of them literally translate as something like “have you eaten yet?” and produce a natural conversational opening to begin immediately discussing food. Perhaps most uncanny to foreigners, Chinese people will sometimes discuss their next meal while they are in the middle of eating a fancy dinner. Dozens of gorgeous little dishes spread around them, chomping or slurping away at exquisite cuisine, and happily chattering about what they plan to eat tomorrow.
None of this is remotely new. If anything, between the Revolution and the famines, Chinese food culture is actually tamer than it used to be.1 We know this from literary and historical accounts, from archeological evidence (China had fancy restaurants about a thousand years before France did), and from the structure of the language itself. They say the Eskimos have an improbable number of words for snow,2 but the Chinese actually do have a zillion words for obscure cooking techniques. What’s more, many of the words are completely different from region to region, which is hardly surprising since the food itself is bewilderingly different from one side of the country to the other.
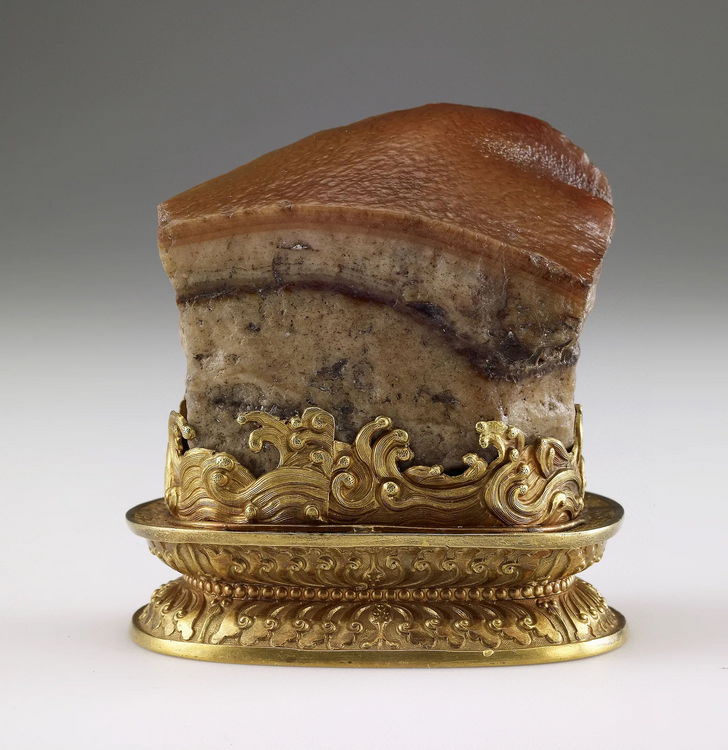
How food-obsessed are the Chinese? One of the most priceless artifacts belonging to the imperial family, the one thing the fleeing Nationalists made sure to grab as communist artillery leveled Beijing, now the most highly-valued object in the National Palace Museum in Taipei is … The Meat-Shaped Stone.3 A single piece of jasper carved into a lifelike hunk of luscious pork belly, complete with crispy skin and layers of subcutaneous fat and meat. Feast your eyes upon it.
1. Ferran Adrià, the legendary chef of El Bulli, once said that Mao was the most consequential figure in the history of cooking because: “[Spain, France, Italy and California] are only competing for the top spot because Mao destroyed the pre-eminence of Chinese cooking by sending China’s chefs to work in the fields and factories. If he hadn’t done this, all the other countries and all the other chefs, myself included, would still be chasing the Chinese dragon.”
2. I once tried searching Google to find out whether Eskimos really have a lot of words for snow. The top results were all places like BuzzFeed and the Atlantic denouncing this as an outmoded racist stereotype … followed by a Wikipedia article patiently explaining that no it’s actually true.
3. The Meat-Shaped Stone is not some weird aberration. The runner-up most valuable items in the museum are a piece of jadeite carved to look like a cabbage and a very fancy cooking vessel.
As the media now tell us, it’s dangerous to do your own research and you should just trust them about everything
David Friedman has some timely tips on how you might go about determining the truth of an assertion offered in the legacy media or online source of undetermined trustworthiness:
Following up the claim you come across an article, perhaps even a book, which does indeed support that claim. Should you believe it?
The short answer for all of those examples, some of them claims I agree with, is that you should not. As I think I have demonstrated in past posts, claimed proofs of contentious issues are quite often wrong, biased, even fraudulent.
More examples from previous posts, here or on my old blog:
An estimate of the cost of a ton of carbon dioxide calculated with about half the total depending on the implicit assumption of no progress in medicine for the next three centuries.
A factbook on state and local finance that deliberately omitted the most important relevant fact that readers were unlikely to know.
A textbook, in its third edition, with multiple provably false claims.
The important question is how to tell. There are three answers:
1. Read the book or article carefully, check at least some of its claims — easier now that the Internet provides you with a vast searchable library accessible from your desktop — and evaluate its argument for yourself. Doing this is costly in time and effort and requires skills you may not have; depending on the particular issue that might include near-professional expertise in statistics, history, physics, economics, or any of a variety of other fields. I have taught elementary statistics at various points in my career, both in an economics department and a law school, but gave up on a controversy of considerable interest to me (concealed carry) when the statistical arguments got above the level I could readily follow.
2. Find one or more competent critiques of the argument and see if you find them convincing. This is the previous answer on easy mode. You still have to think things through but you don’t have to search out mistakes in the argument for yourself because the critic will point you at them, with luck offer evidence.
There are three possible conclusions that that exercise may support: that the argument is wrong. that it might be wrong, that it is probably right. The way you reach the last conclusion is from the incompetence or dishonesty of the critique; I am thinking of a real case.
John Boswell, a gay historian at Yale, argued that both the scriptures and early Christianity, unlike modern Christian critics of homosexual sex, treated it as no worse than other forms of non-marital intercourse. What convinced me that Boswell had a reasonable case was reading an attack on him by a prominent opponent which badly misrepresented the contents of the book I had just read. People who have good arguments do not need bad ones.
Of course, there might be other critics with better arguments.
An entertaining version of this approach is to find an online conversation with intelligent people covering a wide range of views and follow discussions of whatever issues you are interested in. With luck all of the good arguments for both sides will get made and you can decide for yourself whether one side, the other, or neither is convincing. Forty years ago I could do it in the sf groups on Usenet, which contained lots of smart people who liked to argue. Five years ago I could do it in the comment threads of Slate Star Codex. Currently Data Secrets Lox works for a few controversies but the range of views represented on it is too limited to provide a fair view of most.
The comment threads of this blog are at present too thin for the purpose, with between one and two orders of magnitude fewer comments than the SSC average used to be, but perhaps in another few years …
3. Recognize that you don’t know whether the claim is true and have no practical way of finding out, at least no way that costs less in time and effort than it is worth. This is the least popular answer but probably the most often correct.
February 2, 2024
Perhaps something for Wodehouse fans who want a bit more sex and violence in their fiction
At The Conservative Woman, Alan Ashworth recommends a book by one of P.G. Wodehouse’s disciples, but only for those who are ready for Plum-like wit with “lashings of sex, violence, murder and drunkenness”:
If, like me, you have read every line of PG Wodehouse’s 90-odd books – at least half a dozen times each in the case of the Jeeves novels – your attention might be piqued, if piqued is the word I seek, by one of the Master’s disciples. His name is Kyril Bonfiglioli.
In a trilogy about an art dealer named Charlie Mortdecai based loosely on himself, Bonfiglioli, or Bon as his friends and enemies called him, combines a Woosterish turn of phrase with lashings of sex, violence, murder and drunkenness. Mortdecai is snobbish, greedy, lustful, unscrupulous, untrustworthy, gloriously politically incorrect and hilarious to boot.
The first book, Don’t Point That Thing At Me, was published in 1973, two years before Wodehouse died. In a short foreword, Bon writes: “This is not an autobiographical novel: it is about some other portly, dissolute, immoral and middle-aged art dealer.”
The action begins with Mortdecai in his Mayfair mansion burning a gilt picture frame in the fireplace. He, of course, has a sidekick whose name begins with J but Jock has little in common with Bertie Wooster’s loyal manservant. As Bon puts it, “Jock is a sort of anti-Jeeves; silent, resourceful, respectful even, when the mood takes him, but sort of drunk all the time, really, and fond of smashing people’s faces in. You can’t run a fine-arts business these days without a thug and Jock is one of the best in the trade … his idea of a civil smile is rolling back part of his upper lip from a long, yellow dogtooth. It frightens me.
“Having introduced Jock – his surname escapes me, I should think it would be his mother’s – I suppose I had better give a few facts about myself. I am in the prime of life, if that tells you anything, of barely average height, of sadly over-average weight and am possessed of the intriguing remains of rather flashy good looks. (Sometimes, in a subdued light and with my tummy tucked in, I could almost fancy me myself.) I like art and money and dirty jokes and drink. I am very successful. I discovered at my goodish second-rate public school that almost anyone can win a fight if he is prepared to put his thumb into the other fellow’s eye.”
Charlie is receiving a visit from a fat policeman named Martland who suspects him, correctly, of involvement in the theft of a Goya from Madrid five days earlier.
“Somewhere in the trash he reads, Martland has read that heavy men walk with surprising lightness and grace; as a result he trips about like a portly elf hoping to be picked up by a leprechaun. In he pranced, all silent and catlike and absurd, buttocks swaying noiselessly. ‘Don’t get up,’ he sneered, when he saw that I had no intention of doing so. ‘I’ll help myself, shall I?’
“Ignoring the more inviting bottles on the drinks tray, he unerringly snared the great Rodney decanter from underneath and poured himself a gross amount of what he thought would be my Taylor ’31. A score to me already, for I had filled it with Invalid Port of an unbelievable nastiness. He didn’t notice: score two to me. Of course he is only a policeman.”
Martland features heavily in the ensuing romp, which involves several murders, a journey across America in a Rolls-Royce, a nymphomaniac millionairess and a remote cave near Silverdale, Lancashire.
February 1, 2024
QotD: English hypocrisy, spoken
Sir Guthrie is a hybrid, a scientist-turned-apparatchik. “I’m sorry to be a nuisance,” he says, in that suave, hypocritical English way, which is at once admirable and disagreeable. This manner of speaking, of never saying quite what you mean, was illustrated in a French book of the time, La Vie anglaise, which tried to explain English manners to the French. When an Englishman says, “We must meet again,” the author explains, he means: “I hope never to see you again”; and when he says, “I know a little about”, he means: “I am an expert in”, or possibly even “the world-expert in”.
Alas, this indirect way of speaking, always tinged with irony and humour, has almost disappeared in favour of a cruder and less amusing manner of communicating. Literal-mindedness has replaced subtle codification, and with it, a people who were once subtle, if sometimes perfidious, have become crass and often aggressive. Irony, which the whole population once both understood and employed, and was so strong an aspect of the national character, has now disappeared, replaced by a disposition to querulousness and indignation.
Theodore Dalrymple, “What Seventy Years Have Wrought”, New English Review, 2019-10-26.
January 29, 2024
The residential school system in the historical record and in current politics
Barbara Kay discusses the residential school system debate that’s likely to become one of the issues in the next federal election:
“Canadians deserve to know the truth“, Pierre Poilievre told reporters earlier this week, regarding 2021 claims made — but never investigated — of unmarked graves at the Kamloops, B.C. Indian residential school. Poilievre said he was open to “a full investigation into the potential remains at Residential Schools”, wherever that may lead.
This is a bold move, taken in the full knowledge that the Liberals will put a demonizing spin on his comments, even though the Conservative leader also said that “the residential schools were an appalling abuse of power by the state and by the Church at the time”. If Poilievre feels confident to, as he put it, “stand in favour of historical accuracy” on this file, then he believes a critical mass of Canadians will support the proposal.
Trudeau’s government, by contrast, is wedded to the unquestioning, emotive approach to IRS history. From the day that First Nations announced the “discovery” of 215 unmarked graves in Kamloops, arising solely from a finding of “soil disturbances” by ground penetrating radar the Liberals sprang into supportive action. They were emboldened by an overzealous media, starting with the New York Times, which falsely claimed a “mass grave” had been found. Flags were lowered, and Trudeau issued a plangent apology for the children “whose lives were taken” at Kamloops.
Only there was no evidence of lives illicitly “taken”. To date, in spite of the government’s allocation of $7.9 million for the task, no excavation has been done at Kamloops. Excavations in other suspected sites have not turned up human remains. But the media long avoided contrarian copy. (Post columnist Terry Glavin’s May 2022 feature article on the graves in these pages broke the mainstream silence.)
Not that there wasn’t any published pushback. There was plenty, from a cadre of highly accredited scholars, investigative journalists, judges, lawyers and independent researchers, who have amongst themselves amassed probably a million hours of research into all facets of government-Indigenous relations, including the IRS. Only they appeared in non-mainstream media, such as C2C Journal, the Dorchester Review, True North, the Western Standard, the Frontier Centre for Public Policy, Quillette and in some cases their own substacks. For their pains, most of them were labelled “deniers” by media and politicians.
Excellent articles on the IRS by these indefatigable researchers have now been compiled into a single volume, Grave Error: How the media misled us (and the truth about residential schools), edited by historian Chris Champion, publisher of the Dorchester Review, and Tom Flanagan, professor emeritus of political science at the University of Calgary and chair of the Indian Residential Schools Research Group (I am an IRSRG board member).
January 25, 2024
QotD: How Meritocracy morphed into “Meritocracy”
The current meritocratic system began as an effort to open up a hereditary WASP elite to outsiders — and for a while, as immigrants, minorities, and women earned their way into America’s legacy campuses, writes Markovits, it looked like it was working more or less as intended. In the last few decades, however, the system has morphed into a do-or-die tournament for the prize of an Ivy League degree and a bonus-rich job at a swanky address. Instead of being democracies of talent, Harvard and Yale and their elite cronies are now quasi-exclusive clubs for the children of wealth. Money gives rich parents the means to groom their kids for these clubs as early as infancy with classes, books, and trips to museums meant to enhance kids’ development. They move to wealthy neighborhoods, where schools offer a vast array of (ahem) “enrichment” activities, including test prep and college-essay tutoring. Alternatively, they put their kids through 12 years of $40,000-a-year-plus private schools, whose administrators just happen to be chummy with Princeton admission officers.
Their efforts pay off for their progeny, but in the harsh competition that is the contemporary economy, they leave everyone else in the dust. Nourished in the hothouse of elite homes and communities, rich children have pulled away from their middle-class counterparts when it comes to academic performance, outscoring them on the SAT by twice as much as middle-class kids outscore poor students. The most elite colleges enroll more students from households in the top 1 percent than from the entire bottom half of the income scale. Those students are first in the pipeline to elite jobs. Top banks go only to the Ivy League, MIT, and Stanford for their recruiting. Top Five law schools are the training grounds for partners at the poshest firms. Meantime, middle-class kids are not only a rare sight on elite campuses; they’re also far less likely to get any college degree. Poor kids do worse still.
The result, says Markovits, is precisely the sort of dynastic elite that the putatively unbiased SAT was supposed to put out of business. To the dismay of his critics on the left, Markovits is not entirely unsympathetic to the winners of the tournament. The rich used to be indolent, he reminds us. The whole point of wealth was to be freed from toil, while peasants sweated in fields and manor kitchens to serve their betters and eke out a living for their undernourished families. These days, by contrast, the rich work 16-hour days and weekends under immense competitive pressure to close the deal, make partner, and take a conference call with Japanese businessmen. “No prior elite has ever been as capable or as industrious as the meritocratic elite that such training produces. None comes close,” Markovits asserts. Yes, a few actresses and real estate barons try to bribe and cheat their children into the palaces of learning, but most Ivy Leaguers have used their privileged upbringing to make their way into these bastions according to the rules of achievement. Given the expensive grooming required to make it to the top campuses, he implies, a squeaky-clean meritocracy would still favor the rich.
Kay S. Hymowitz, “Meritocrats versus Meritocracy”, City Journal, 2019-10-11.
January 24, 2024
The father of the “Green Revolution”
In the latest review at Mr. and Mrs. Psmith’s Bookshelf, Jane Psmith reviews The Wizard and the Prophet by Charles C. Mann:
Norman Borlaug is generally estimated to have saved the lives of about a billion people who would otherwise have starved to death.
Yet despite all this — and Borlaug’s is a great story, which Charles Mann tells better and in far more detail than I do above — his book isn’t really a biography of Borlaug or of its other framing figure, early environmentalist William Vogt.1 Rather, it’s a compellingly-written and frankly fascinating overview of various environmental issues facing humanity, and of two different sorts of approaches one can take to addressing them. Mann opens by introducing the two men, but as soon as he’s done that they function mostly as symbols, examples and stand-ins, for these two schools of thought about the world and its problems.
Borlaug is the Wizard of the title, the avatar of techno-optimism: with hard work and clever application of scientific knowledge, we can innovate our way out of our problems. Vogt is the Prophet, the advocate of caution: he points to our limitations, all the things we don’t know and the complex systems we shouldn’t disturb, warning that our constraints are inescapable — but also, quietly, that they are in some sense good.
It’s not hard to identify the Wizards all around us. Inventors and innovators, transhumanists and e/acc, self-driving cars and self-healing concrete … every new device or technique for solving some human problem — insulin pumps! heck, synthetic insulin at all! — is a Wizardly project.
It’s a little more difficult to pin down what exactly the Prophets believe, in part because they spend so much time criticizing Wizardly schemes as dangerous or impractical that it’s easy to take them for small-souled enemies of human achievement.2 That isn’t fair, though — there’s a there there, a holistic vision of the world as an integral organic unity that we disturb at our peril, because the constraints are inextricably linked to the good stuff.
If that seems too abstract, here’s an example. Imagine for a moment (or maybe you don’t have to imagine) that you have a friend who subsists entirely on Soylent. It’s faster and easier than cooking, he says, and cheaper than eating out. He’s getting all his caloric needs met. And he’s freed up so much time for everything else! Now, anyone might express concern for his physical health: does Soylent actually have the right balance of macronutrients to nourish him? Is he missing some important vitamins or other micronutrients that a normal diet might provide? Is the lack of chewing going to make his jaw muscles atrophy? And those are all reasonable concerns about your friend’s plan, but they all have possible Wizardly solutions. (A multivitamin and some gum would be a start.)
If you’re a Prophet sort, on the other hand, you’re probably going to start talking about everything else your friend is missing out on. There’s the taste of food, for one, but also the pleasures of color and texture and scent, the connection to the natural world, the role of community and tradition in shared meals, the way cooking focuses thought and attention on incarnate reality. You might throw around words like “lame” and “artificial” and “sterile” and “inhuman”. Your friend’s Soylent-only plan assumes that the whole point of food is to consume an appropriate number of calories as quickly and easily as possible, hopefully in a way that doesn’t meaningfully degrade his health, but a Prophet rejects his premise entirely. Instead, a Prophet argues that your friend’s food “problem” is actually part of the richly textured beauty of Creation. Yes, feeding yourself and your loved ones delicious, healthful, and economical meals takes time and effort, but that’s simply part of being human.5 You should consider that a challenge to be met rather than a threat to be avoided.
Unfortunately, Mann does the Prophets a disservice by choosing William Vogt as their exemplar. Yes, he was an important figure in the history of the modern environmental movement. Yes, he wrote a very influential book.4 And yes, his careful attention to the integrity of the ecosystems he studied was quintessentially Prophet. But he saw human beings mostly as disruptions to the integrity of those ecosystems, and pretty much every one of his specific predictions — not to mention the predictions of his many followers, most famously Paul Erlich in The Population Bomb5 — have simply failed to come true. Compared to Borlaug’s obvious successes, Vogt’s dire warnings that humanity will soon exhaust the Earth’s capacity and doom ourselves to extinction (unless we abort and contracept our way there first; his second act was as director of Planned Parenthood) seem laughable. Reading about his life can leave you with the impression that Prophets are just people who are more worried about a spotted owl than a starving child, and frankly who cares what those people think?
1. They were roughly contemporaries, but this is emphatically not the story of a pair of rivals; they encountered each other in person only once, in passing, after which Vogt wrote an angry letter to the Rockefeller Foundation demanding they cease Borlaug’s Mexican project at once.
2. And, to be fair, a lot of the language and arguments pioneered by Prophets does get employed by a sclerotic managerial class opposed to anything they can’t fit neatly into their systems and processes and domain-agnostic expertise. But more on that later.
3. Incidentally, this is more or less the argument between the Wizards and the Prophets when it comes to soil. Wizards are delighted with the Haber-Bosch process and artificial fertilizers; Prophets decry the “NPK mentality” that sees the soil as a passive reservoir of chemicals and instead laud composting, manure, and other techniques that encourage the complex interactions between soil organisms, plant roots, and the physical characteristics of humus. This is the origin of the fad for “organic”, a label that doesn’t mean much when applied to industrial-scale food production and is often more trouble than it’s worth for small-time farmers and ranchers. Still, Mann’s story of the movement’s birth is interesting.
4. You’ve probably never heard of it, but it was influential!
5. Apparently out of print! Good.
January 23, 2024
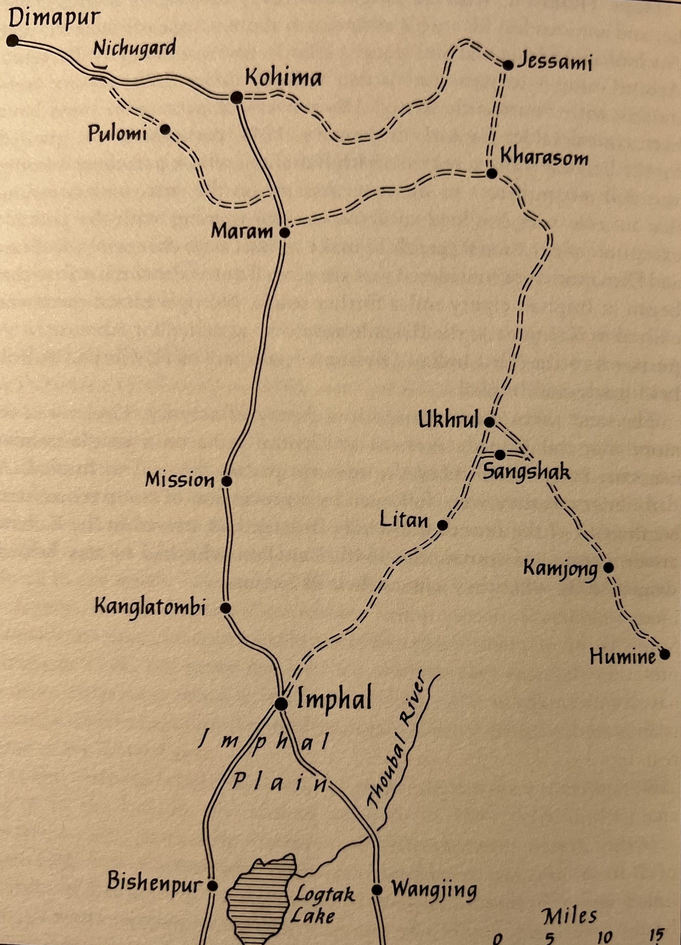
The battle of Sangshak, 1944
Dr. Robert Lyman discusses a new book by David Allison that covers one of the many small battles that made up the large Imphal-Kohima campaign:
When Wavell, by then Viceroy of India, visited Imphal after the battle in October, to bestow knighthoods on the four victors — Lieutenant Generals Bill Slim (14 Army), Montagu Stopford (33 Corps), Geoffrey Scoones (4 Corps) and Philip Christison (15 Corps) — he admitted to Slim that he found the battle hard to follow, as it seemed to have been fought in “penny-packets”. In professing his ignorance of Slim’s great triumph, Wavell nevertheless hit the nail on the head. Sangshak was one of those penny-packet fights which cumulatively determined the outcome of Japan’s audacious invasion of India.
Like many battles in insufficiently examined wars, Sangshak has suffered over the years from a paucity of rigorous examination. Louis Allen’s magisterial The Longest War gave it short treatment in 1984, and very little else. Until now. I’m delighted to say that a Hong Kong-based Australian lawyer with a military background — David Allison — has produced a new account of this crucial battle, and it is absolutely outstanding. It can be purchased here. I recommend it very strongly. It’s not long: at 159-pages of text you can make your way through this in a couple of days, but it is diligently researched, well written and judiciously argued. For those who know something of the battle, the big arguments in the past about the state training of the 50 Indian Parachute Brigade, the temporary breakdown of its commander, Hope-Thomson and the supposed loss of the captured Japanese map and orders by HQ 23 Indian Division, are calmly and satisfyingly explained.
The story can be briefly told. The territory to the north-east of Imphal (centring on the Naga village of Ukhrul) had only the lightest of garrisons and no real defences. Until 16 March it was home to 49 Brigade, which was then despatched to the Tiddim Road to deal with the advance in the south of Lieutenant General Yanagida’s 33 Division. The brigade had considered itself to be in a rear area, and, extraordinarily, no dug-in and wired defensive positions had been prepared. It was one of the most serious British planning failures of the campaign. The entire north-eastern portion of Imphal lay effectively undefended. The gap left by the brigade’s departure had been filled in part by the arrival of the first of the two battalions of the newly raised 50 Indian Parachute Brigade (comprising the Gurkha 152 Battalion and the Indian 153 Battalion), whose young and professional commander, 31-year-old Brigadier M.R.J. (“Tim”) Hope-Thomson, had persuaded New Delhi to allow him to complete the training of his brigade in territory close to the enemy. The area north-east of Imphal was regarded as suitable merely for support troops and training. At the start of March, the brigade HQ and one battalion had arrived in Imphal and began the leisurely process of shaking itself out in the safety of the hills north-east of the town. To the brigade was added 4/5 Mahrattas under Lieutenant Colonel Trim, left behind when 49 Brigade was sent down to the Tiddim Road. To Scoones and his HQ, the area to which Hope-Thomson and his men were sent represented the lowest of all combat priorities. Sent into the jungle almost to fend for themselves, it was not expected that they would have to fight, let alone be on the receiving end of an entire Japanese divisional attack. They had little equipment, no barbed wire, and little or no experience or knowledge of the territory. No one considered it worthwhile to keep them briefed on the developing situation. To all intents and purposes, 50 Indian Parachute Brigade was an irrelevant appendage, attached to Major General Ouvry Roberts’ 23 Indian Division for administrative purposes but otherwise left to its own devices.
Before long, information began to reach Imphal that Japanese troops were advancing in force on Ukhrul and Sangshak. Inexplicably, however, this information appeared not to ring any warning bells in HQ IV Corps in Imphal, which was preoccupied with the developing threat in the Tamu area where the main Japanese thrust was confidently predicted. On the night of 16 March, the single battalion of 50 Parachute Brigade took over responsibility for the Ukhrul area from 49 Brigade, which was hastily departing for the Tiddim Road. They had no idea that an entire Japanese division of 20,000 men was crossing the Chindwin in strength opposite Homalin. On 19 March, large columns of Japanese infantry were reported advancing through the hills.
No one had expected them to be where they were. But the first shock came to the Japanese 3/58 battalion (Major Shimanoe), part of Lieutenant General Sato’s 31 Division – troops whose objective was Kohima, and not Imphal – who were bloodily rebuffed by the determined opposition of the young Gurkha soldiers at an unprepared position forward of Sheldon’s Corner. The 170 Gurkha recruits refused to allow the 900 men of 3/58 to roll over them and inflicted 160 casualties on the advancing Japanese. In the swirling confusion of the next 36 hours, Hope Thomson and his staff kept their heads, attempting to concentrate what remained of the dispersed companies of 152 Battalion and 4/5 Mahrattas back to a common position at the village of Sangshak, which dominated the tracks southwest to Imphal.
It was at this now-deserted Naga village that Hope-Thomson, on 21 March, decided to group his brigade for its last stand, his staff desperately attempting to alert HQ 4 Corps in Imphal to the enormity of what was happening to the north-east. The Japanese columns infiltrated quickly around and through the British positions, heading in the direction of Litan. The Japanese now began days of repeated assaults on the position in a battle of intense bravery and sacrifice for both sides. Hope Thomson’s men could only dig shallow trenches, which provided no protection from Japanese artillery.
Sometimes the deciding factor in success really is just “dumb luck”
Virginia Postrel doesn’t disparage the role of quality, but as one of her own experiences clearly illustrates, you can’t discount the sometimes disproportionate role of luck:
No amount of planning beats dumb luck. That saying, which I will always associate with the gubernatorial campaign of South Carolina’s James Edwards1, occurred to me while reading Damon Linker’s latest Substack post. His praise of Martin Gurri’s book The Revolt of the Public reminded me of a corollary: When it comes to books, no amount of intellectual quality is enough without dumb luck. It’s an absolute miracle Martin Gurri’s book, which is excellent, has become well known.
I know because I gave The Revolt of the Public a crucial boost — and I only discovered it because my own book, The Power of Glamour, was languishing in obscurity (where it remains). Frustrated with the lack of attention, I spent an evening Googling “visual persuasion” in hopes of finding smart people who might find my analysis interesting enough to mention to others. My search led me to a 2010 article for the Army War College, co-authored by Gurri, titled “Our Visual Persuasion Gap“. I sent him a note: “I read your article on the visual persuasion gap and would like to send you a copy of my book. Could you send me your mailing address? Are you related to Adam?” He responded that he preferred to think that Adam was related to him — his son — and that we should trade books.
To review: 1) I wrote a book related to visual persuasion. 2) Martin Gurri has a long-standing interest in visual persuasion. 3) Gurri wrote a book relevant to visual persuasion. 4) I knew Gurri’s son. And neither of us knew the other existed.
I was impressed by his book. So when Cato Unbound invited me to write an essay on “visual persuasion and politics” and to suggest people to write responses, I recommended him. That was in July 2014. The symposium came and went. Still The Revolt of the Public didn’t break into public consciousness, even among the kind of people who read Cato Institute publications.
Then, in December 2015, I wrote a Bloomberg Opinion column on The Revolt of the Public. I’m sure many people read the column, but only one of them mattered to the book’s public profile: Arnold Kling, who wrote about it on his blog in January 2016. The timing was perfect and Arnold proved an effective, well-connected evangelist. In 2018 Stripe Press issued an updated version in print, audio, and electronic formats. Since then, the book has become a touchstone for understanding the rise of populist movements. Agree or disagree, people trying to figure out our political moment have to consider Gurri’s analysis — which they know about because of dumb luck.
1. Edwards, an oral surgeon by profession, was a Republican party activist who ran in the 1974 primary against the much better known General William Westmoreland. Then, as now, South Carolina did not have party registration. Any voter could vote in either primary, but if you voted in one party’s primary you couldn’t vote in the other party’s runoff election. The Democratic primary was where the action was that year, with multiple candidates. Only the most stalwart Republicans voted in that primary and they preferred the guy they knew to the celebrity general. The Democratic primary went to a runoff between young post-Watergate reformer Charles “Pug” Ravenel and old guard Congressman William Jennings Bryan Dorn. Ravenel, a South Carolina native who’d only recently moved from New York, won the runoff, only to have his candidacy disqualified for not meeting residency requirements. The Democrats put Dorn in his place, but he was a weakened candidate and voters went with Edwards, making him the first Republican governor since Reconstruction. Edwards used to have a sign with this motto, or some version of it, on his desk.
January 22, 2024
“He lied. That was what he had to say at the time.”
At First Things, Robert Carle reviews Tania Brannigan’s Red Memory: The Afterlives of China’s Cultural Revolution:
At a 1979 White House dinner, actress Shirley MacLaine told Deng Xiaoping, China’s new leader and the guest of honor that evening, about a Chinese scientist she had met. He said that he’d been happier and more productive when he worked on a Chinese farm. Deng cut her short: “He lied. That was what he had to say at the time.” Deng spent three years working in a tractor factory during the Cultural Revolution, and he refused to romanticize it. The memoirs of Cultural Revolution survivors written in the 1980s echo Deng’s view that it was a brutal and pointless experiment.
Today, there is widespread nostalgia in China for the Cultural Revolution. President Xi Jinping has reflected positively on the time he spent exiled in the remote town of Liangjiahe in Shaanxi province, living in a cave, hauling coal carts, carrying manure, building dikes, enduring bitter winters, flea bites, and hunger. This experience, Xi claims, bonded him with China’s common people and prepared him to be an empathetic ruler. Liangjiahe is now a “red tourist” attraction where students can visit Xi’s old home and admire the well he built.
Xi’s glamorization of the Cultural Revolution is reflected in Beijing’s chic dining scene. In Red Classics Restaurant, for example, waitresses in Red Guard uniforms serve meat and vegetables in plain style to invoke an era of stark living. You can have a fully themed wedding in this restaurant, posing for photos in matching Mao suits on a tractor parked in one corner.
In her new book, Red Memory, Tania Branigan describes the clashing memories of the Cultural Revolution. Those who suffered under the brutality of the Red Guard describe an infernal decade when Mao turned his murderous paranoia on his own people, leading them to tear each other to pieces. Children denounced their parents, and students murdered their teachers. In Mao’s campaign against the four “olds” (Old Ideas, Old Culture, Old Customs, and Old Habits), traditional Chinese culture and morality became targets for destruction.
But Branigan also tells stories of people who are nostalgic for a time when life was more austere and when people lived for a cause other than individualism and materialism. Some former Red Guards have set up a bookstore and website called Utopia. Others organize trips to North Korea to admire society as it should be, or set up rural communes for students. One Utopia co-founder, a professor, made headlines for slapping an eighty-year-old “traitor” who had dared to criticize Mao.
Red Memory is full of chilling stories of brutality and betrayal. Fang Zhongmou witnessed the torture and beating of her husband by adolescent Red Guards. She endured years of interrogations at her workplace because her father had been a landowner. One night in 1970, while doing laundry at home, she launched into a tirade against Mao. Her son told her, “If you go against my dear Chairman Mao, I will smash your dog head in”. He reported her to officials. After two months of violent “struggle sessions”, Fang was executed. The son grew up to be a guilt-ridden adult who agonizes over his mother’s gravesite.
Song Binbin was eighteen when she viciously denounced her school’s deputy principal, Bian Zhongyun. Bian had told the students that they should run out of the building in the event of an earthquake. Because she did not instruct the students to take Mao portraits with them, Red Guards hunted her down and beat her to death with nailed clubs. As the Cultural Revolution swept China, beatings and executions became increasingly baroque. Students poured boiling water over teachers’ heads and made them swallow excrement, crawl over embers, drink ink and glue, and beat one another.
January 21, 2024
A Book and a Rifle: The Vercors Resistance in WWII
Forgotten Weapons
Published 20 May 2018One of the single largest actions of the French Resistance during World War Two was Operation Montagnards — the plan to drop about 4,000 Allied paratroops onto the Vercors Massif when the resistance was activated in support of the Allied landings in Normandy and Provence. If you are scratching your head trying to figure out why you don’t remember that operation, it is because it never actually happened. The two Allied landings were originally intended to take place simultaneously, but logistical limitations forced the southern landings to be delayed about two months. In an deliberate decision to prevent the Germans from immediately understanding the nature of the Allied attack, the whole of the French Resistance was activated to support the Normandy landings in June 1944. The internal attacks in the south would force the Germans to keep significant forces in that area in expectation of a second landing, which would increase the chances of the Normandy landings succeeding. Unfortunately, the other result of this decision was that Resistance cells would come into the open in anticipation of imminent military support, which would not be coming. The southern elements of the Resistance were basically sacrificed in this gambit.
The Vercors Massif is a large geographical feature near Lyon and Grenoble which comprises basically a triangular sheer-walled plateau rising well above the surrounding plains. It offers a fantastically defensible redoubt, and that is what it was planned to be. Paratroops dropped onto the top of the massif would reinforce a substantial force of Maquis fighters, and create a serious strong point behind the German lines to aid in the fight inland from the landing beaches. The plan was organized in Algiers by Resistance representatives from the Vercors and Free French officers earlier in the war. Some have argued that the lack of support was simply due to the compromises of the single-landing plan, while others fault de Gaulle for deliberately abandoning the men and women on Vercors as part of a strategy to consolidate post-war political support — but that debate is beyond the scope of today’s discussion.
The fighters and civilians on the massif ultimately held out for about 6 weeks — only just too little to still be there when the Allied armored columns reached Grenoble. The German commander in the area spent several weeks making small probing attacks before the final assault with about 10,000 veteran Wehrmacht soldiers, glider-borne infantry, and tanks. Once that attack came, the fate of the Vercors was sealed. With proper military backing they could have defended their redoubt, but instead they had only a smattering of small arms and no heavy weaponry at all. It was a fight that was gloriously courageous but hopelessly doomed to failure.
I am privileged to have in my own collection a Berthier carbine tied to the Vercors Resistance, as evidenced by the brass embellishments on its stock. While I cannot conclusively prove it came from the Resistance, it was sold to me without any premium attached to them, and I have no reason to believe it is fake. And, of course, since I have no plans to sell it, I am not really concerned about conclusively proving its veracity to others. For me, it is a poignant icon of a tremendously heroic group. I hope I would live up to the bar they set should I ever be in a comparable situation!
(more…)
January 17, 2024
QotD: Did Hari Seldon live in vain?
Both cliodynamics and psychohistory assume these differences and problems “come out in the wash” over a long enough period and a big enough sample. It doesn’t take much of a counterfactual thought experiment about how small changes by individuals could lead to enormous historical differences to see that they don’t. The defense that cliodynamics only deals in probabilities is little comfort here: in fact the apparent randomness (which one may argue is merely complexity on a scale that is beyond simulation) swallows the patterns. One could easily argue, for instance, that the extremely unlikely career of our fellow Temujin is a necessary cause (albeit merely one of many, several of which might be considered deeply improbable) for the fact that all commercial pilots and air traffic controllers worldwide have to learn a form of English (which one may well assume has its own structural knock-on effects in terms of the language used for business and from there the outsized cultural impact of English-speaking countries).1 No one in 1158 was likely to have supposed that English – a language at that time not even spoken by the English nobility (they spoke French)! – would become the first truly global lingua franca (and arguably the only one, though here caveats may overwhelm the claim) and thus the language of aviation. But that is precisely the kind of big structural change that is going to be really impactful on all sorts of other questions, like patterns of commerce, wealth, culture and influence.
Such complex causation defies general laws (even before we get into the fact that humans also observe history, which creates even more complexity) with such tremendous import from such unlikely events in an experiment which can only be run once without a control.
The other problem is evidence. Attempting to actually diagnose and model societies like this demands a lot of the data and not merely that you need a lot of it. You need consistent data which projects very far back in history which is accurate and fairly complete, so that it can be effectively compared. Trying, for instance, to compare ancient population estimates, which often have error bars of 100% or more, with modern, far more precise population estimates is bound to cause some real problems in teasing out clear correlations in data. The assumptions you make in tuning those ancient population figures can and will swallow any conclusions you might draw from the comparison with modern figures beyond the fairly obvious (there are more people now). But even the strongest administrative states now have tremendous difficulty getting good data on their own lower classes! Much of the “data” we think we have are themselves statistical estimates. The situation even in the very recent past is much worse and only degrades from there as one goes further back!
By way of example, I was stunned that Turchin figures he can identify “elite overproduction” and quantify wealth concentration into the deep past, including into the ancient world (Romans, late Bronze Age, etc). I study the Romans; their empire is only 2,000 years ago and moreover probably the single best-attested ancient society apart from perhaps Egypt or China (and even then I think Rome comes out quite solidly ahead). And even in that context, our estimates for the population of Roman Italy range from c. 5m to three to four times that much. Estimates for the size of the Roman budget under Augustus or Tiberius (again, by far the best attested period we have) range wildly (though within an order of magnitude, perhaps around 800 million sestertii). Even establishing a baseline for this society with the kind of precision that might let you measure important but modest increases in the size of the elite is functionally impossible with such limited data.
When it comes to elites, we have at best only one historical datapoint for the size of the top Roman census class (the ordo equester) and it’s in 225 BC, but as reported by Polybius in the 140s and also he may have done the math wrong and it also isn’t clear if he’s actually captured the size of the census class! We know in the imperial period what the minimum wealth requirement to be in the Senate was, but we don’t know what the average wealth of a senator was (we tend to hopefully assume that Pliny the Younger is broadly typically, but he might not have been!), nor do we know the size of the senatorial class itself (formed as a distinct class only in the empire), nor do we know how many households there were of senatorial wealth but which didn’t serve in the Senate because their members opted not to run for public office. One can, of course, make educated guesses for these things (it is often useful and important to do so), but they are estimates founded on guesses supported by suppositions; a castle of sand balanced atop other castles of sand. We can say with some confidence that the Late Roman Republic and the Early Roman Empire saw tremendous concentrations of wealth; can we quantity that with much accuracy? No, not really; we can make very rough estimates, but these are at the mercy of their simplifying assumptions.
And this is, to be clear, the very best attested ancient society and only about 2,000 years old at that. The data situation for other ancient societies can only be worse – unless, unless one begins by assuming elite overproduction is a general feature of complex, wealthy societies and then reads that conclusion backwards into what little data exists. But that isn’t historical research; it is merely elevating confirmation bias to a research methodology.
As noted, I have other nitpicks – particularly the tendency to present very old ideas as new discoveries, like secular cycles (Polybius, late 2nd century BC) or war as the foundation of complex societies (Heraclitus, d. c. 475 BC) without always seeming to appreciate just how old and how frequently recurring the idea is (such that it might, for instance, be the sort of intuitive idea many people might independently come up with, even if it was untrue or that it might be the kind of idea that historians had considered long ago and largely rejected for well established reasons) – but this will, I hope, suffice for a basic explanation of why I find the idea of this approach unsatisfying. This is, to be clear, not a rejection of the role of data or statistics in history, both of which can be tremendously important. Nor is it a rejection of the possible contributions of non-historians (who have important contributions to make), though I would ask that someone wading into the field familiarize themselves with it (perhaps by doing some traditional historical research), before declaring they had revolutionized the field. Rather it is an argument both that these things cannot replace more traditional historical methods and also that their employment, like the employment of any historical method, must come with a very strong dose of epistemic humility.
Psychohistory only works in science fiction where the author, as the god of his universe, can make it work. Today’s psychohistorians have no such power.
Bret Devereaux, “Fireside Friday: October 15, 2021”, A Collection of Unmitigated Pedantry, 2021-10-15.
1. For those confused by the causation, the Mongols are considered the most likely vector for the transmission of gunpowder from China, where it was invented, to Europe. Needless to say, having a single polity spanning the entire Eurasian Steppe at the precise historical moment for this to occur sure seems like a low probability event! In any event, European mastery of gunpowder led directly into European naval dominance in the world’s oceans (its impact on land warfare dominance is much more complex) which in turn led to European dominance at sea. At the same time, the English emphasis on gunnery over boarding actions early in this period (gunpowder again) provided a key advantage which contributed to subsequent British naval dominance among European powers (and also the British navy’s “cult of gunnery” in evidence to the World Wars at least), which in turn allowed for the wide diffusion of English as a business and trade language. In turn, American and British prominence in the post-WWII global order made English the natural language for NATO and thus the ICAO convention that English be used universally for all aircraft communication.